The Role of the Project Sponsor
advertisement

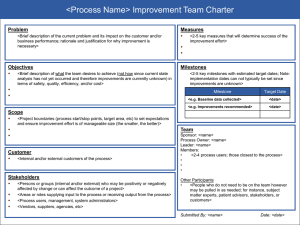
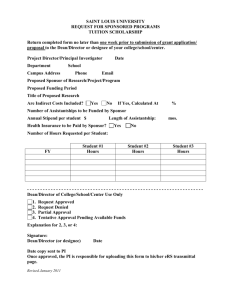
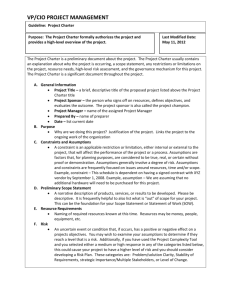
CIS99H IT Project Management Human Resource Management Roles & Responsibilities The Role of the Project Sponsor The PMBOK defines this person as the one who provides the financial resources for the project. WARNING: This may be different than the role of the sponsor in your organization. ANOTHER WARNING: In most instances the customer fulfills the role of the sponsor as well as customer. If the project is being done for an outside customer (you are the seller) the customer may fulfill the role of the sponsor as well as customer, and some of these functions would be taken over by senior management in the performing organization. (Management is anyone senior to the project manager in the organization(s).) During or prior to project initiating o Has requirements that must be met o Is a project stakeholder o Provide funding o Provide statement of work o Provide information for preliminary project scope statement o May dictate milestones, key events or project end date (along with customer) o Issue the project charter o Give the project manager authority as outlined in the project charter o Help organize work into appropriate projects o Set priorities between projects o Determine the priorities between the “triple Constraint” components o Encourage the finalization of requirements and scope by the stakeholders During project planning o Provide the project team with time to plan o May review the WBS o Supply lists of risks o Determine the reports needed by management to oversee the project o Provide expert judgement o Help evaluate tradeoffs during crasing, fast tracking and re-estimating o Approve the final project management plan During project executing and project monitoring and controlling o Approve changes to the project charter o Protect the project from outside influences and changes o Enforce quality policies o Provide expert judgment o Help evaluate tradeoffs during crashing, fast tracking and re-estimating o Resolve conflicts that extend beyond the project manager’s control o Approve or reject changes or authorize someone representing them to do so (change control board) o May direct that a quality assurance review be performed o Clarify scope questions During project closing o Provide formal acceptance of the deliverables (if he is the customer) o Support the collection of historical records from past projects Along with the customer, the sponsor formally accepts the product of the project (formal acceptance) during scope verification and administrative closure. Along with the customer, the sponsor’s threshold for risks should be taken into account. The sponsor does not sign the project charter! That is the role of senior management. CIS99H IT Project Management Human Resource Management Roles & Responsibilities The Role of Senior Management Management is anyone senior to the project manager in the organization(s). In some situations the word “senior management” is a catch-all phrase to include the sponsor, functional managers and anyone higher in the performing organization than the project manager. Management has a unique role on projects that cannot be fulfilled by anyone else. Unfortunately, many managers do not realize that project management is a profession and a science that requires unique efforts from management. Management must have at least an overview understanding of the tools and techniques of project management. It is important for management to know that they are the only ones who can: Help organize work into appropriate projects Provide the project team with time to plan Encourage the finalization of requirements and scope by the stakeholders Determine the priorities between the triple constraint components Set priorities between projects Issue the project charter Identify many risks Protect the project from outside influences Help evaluate tradeoffs during crashing, fast tracking, and re-estimating Determine the reports needed by management to mange the project Approve the final project plan during project plan development Resolve conflicts that extend beyond the project manager’s control CIS99H IT Project Management Human Resource Management Roles & Responsibilities The Role of the Team The team is a group of people who will complete work on the project. The team members can change throughout the project as people are added and removed from the project. Team members have some project management responsibilities in addition to responsibilities for implementing the work. Generally it is the team’s role to help plan what needs to be done (WBS) and create time estimates for their tasks. During project execution, the team members simply complete work packages or tasks and help look for changes from the project plan. More specifically, the team may help: Identify and involve stakeholders Execute the project management plan to accomplish work defined in the project scope statement Attend project team meetings Process improvement Comply with quality and communication plans Enforce ground rules Depending on the size and complexity of the project, the team role might also include helping the project manager do the following: Define the product of the project Identify and analyze constraints and assumptions Define requirements Determine the definition of quality on the project and how it will be met Create the work breakdown structure Decompose work packages they are responsible for into schedule activities Identify dependencies and create the network diagram Provide cost and time estimates Identify risks Perform qualitative and quantitative risk analysis and risk response planning Determine time and cost reserves for the project Produce project performance reports Measure project performance Determine the need for corrective action Close out phases of the project Select appropriate processes Create the change control system Determine and measure corrective action CIS99H IT Project Management Human Resource Management Roles & Responsibilities The Role of the Stakeholders Stakeholders are anyone who can positively or negatively influence the project. Stakeholders should be involved in planning the project and managing it. Stakeholders must first be identified and their communications needs determined. Stakeholders: May be involved in the creation of the project charter and the preliminary and project scope statements Are involved in: o Project management plan development o Approving project changes and being on the change control board o Scope verification o Identifying constraints o Risk management Become risk response owners Are distributed information during the life of the project Have their knowledge and skills assessed Are notified of project plan changes Use expert judgment throughout the project and especially in the creation of the contents of the project charter and the scope statement Information needs are considered and analyzed throughout the project processes as part of stakeholder analysis Are listed in the project team directory Are considered in team development Have presentations made to them Receive performance reports Have their risk tolerances identified and incorporated into the risk management process The Role of the Functional Manager The individual who manages and “owns” the resources in the IT, engineering, public relations, marketing, and other departments and generally directs the technical work of individuals from their functional area that are working on the project. The amount of involvement of the functional manager depends on the form of organizational structure. In a matrix organization, this responsibility to direct the work of individuals is shared with the project manager. In a projectized organization, the project manager does all of the directing. The project manager does little directing in a functional organization. To avoid conflict, the project manager and functional manager must coordinate their respective needs regarding the use of resources to complete project work. It is generally the responsibility of the project manager to manage this relationship. The specific activities performed by the functional manager vary greatly based on the type of organizational structure and the type of project. They MAY include: Assigning specific individuals to the team and negotiating with the project manager regarding resources Letting the project manager know of other projects that may impact the project Participating in the initial planning until work packages or tasks are assigned Involved in go, no-go decisions Approving the final project plan during project plan development Approving the final schedule during schedule development Recommend corrective action Assisting with problems related to team member performance Improving their staff utilization CIS99H IT Project Management Human Resource Management Roles & Responsibilities The Role of the Project Manager The project manager is responsible for managing the project to meet project objectives. The project manager’s level of authority can vary depending on the form of organization. Such authority generally means that the project manager: Is assigned to the project no later than project initiating Is in charge of the project, but not necessarily the resources Does not have to be a technical expert Leads and directs the project planning efforts Must realize that an unrealistic schedule is his fault and know how to handle those situations Understands professional and social responsibility Determines and delivers required levels of quality Assists the team and stakeholders during project execution Creates a change control system Maintains control over the project by measuring performance, determining if corrective action is needed, recommending corrective actions, preventive actions and defect repair Must have the authority and accountability necessary to accomplish the project management work Must say “no” when necessary Is the only one who can integrate the project components into a cohesive whole that meets the customer’s needs Spends more time being proactive than in dealing with problems (reacting) Is held accountable for project failure Must be able to deal with conflicting or unrealistic scope, quality, schedule, risk, and other requirements Must come up with a project management plan that can be agreed to, that people believe is realistic, and most importantly, that they can stake their reputations on