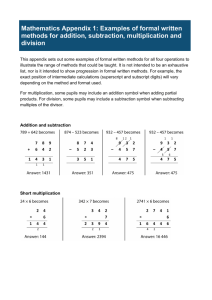
Addition: from 2
advertisement

Addition: from 2.1 and 2.3: Pos + pos = pos (add as usual) Neg + neg = neg (add the absolute values) 1. Signs the same, add absolute values and keep the sign 2. Signs different, subtract absolute values and take the sign of the number with a greater absolute value. Subtraction: from 2.2 and 2.3 Neg – pos = neg (add the absolute values) Pos – neg = pos (add the absolute values) 1. In general, add the opposite: change the operation to addition and the sign of the subtrahend (second number) Fact Families: from 2.4 All fact families follow the same format. For addition and subtraction: Addition Subtraction a+b=c c-a=b b+a=c c-b=a Notice that the ‘c’ is always the sum and always the minuend (first number in subtraction.) To find an unknown in an equation, find the fact family member that gets the ‘n’ at the end. Graphing: from 2.5 Rene DesCartes invented the Cartesian Coordinate System The origin is where the 2 axes intersect (0,0) The x-axis is horizontal. It is always the first coordinate graphed. The y-axis is vertical Ordered pair tells the address of a point on the graph. It is always written (x,y) The intersection of the axes forms 4 Quadrants, labeled I, II, III and IV going counter-clockwise from the top right-hand corner. The characteristics of a point in each quadrant are as follows: Quadrant I (+, +) Quadrant II (-, +) Quadrant III (-,-) Quadrant IV (+, -) Standard test ends here Multiplication: 3.1 and 3.2 +*+=+ -*-=+ -*+=+*-=Multiplication is commutative Division: 3.3 Same as multiplication +÷+=+ -÷-=+÷-=-÷+=Division is not commutative Distributive Property of Multiplication over Addition 4.2 A * (b + c) = ab + ac Factor by finding the common factor, that’s the ‘a’. The other 2 are the b and c. Distributive Property of Multiplication over Subtraction 4.3 Same as above, except with subtraction A(b-c) = ab - ac