附件1 理论课程教学大纲样本
advertisement
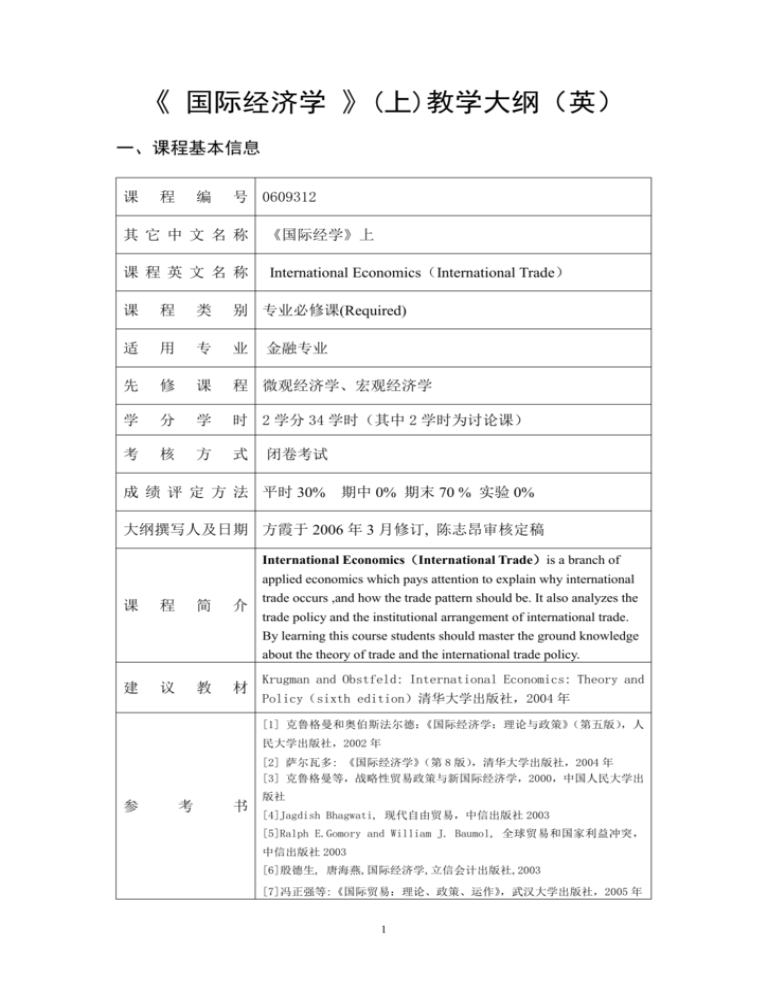
《 国际经济学 》(上)教学大纲(英) 一、课程基本信息 课 程 编 号 0609312 其 它 中 文 名 称 《国际经学》上 课 程 英 文 名 称 International Economics(International Trade) 课 程 类 别 专业必修课(Required) 适 用 专 业 先 修 课 程 微观经济学、宏观经济学 学 分 学 时 2 学分 34 学时(其中 2 学时为讨论课) 考 核 方 式 金融专业 闭卷考试 成 绩 评 定 方 法 平时 30% 期中 0% 期末 70 % 实验 0% 大纲撰写人及日期 方霞于 2006 年 3 月修订, 陈志昂审核定稿 International Economics(International Trade)is a branch of applied economics which pays attention to explain why international 课 程 简 介 trade occurs ,and how the trade pattern should be. It also analyzes the trade policy and the institutional arrangement of international trade. By learning this course students should master the ground knowledge about the theory of trade and the international trade policy. 建 议 教 材 Krugman and Obstfeld: International Economics: Theory and Policy(sixth edition)清华大学出版社,2004 年 [1] 克鲁格曼和奥伯斯法尔德:《国际经济学:理论与政策》(第五版),人 民大学出版社,2002 年 [2] 萨尔瓦多: 《国际经济学》 (第 8 版) ,清华大学出版社,2004 年 [3] 克鲁格曼等,战略性贸易政策与新国际经济学,2000,中国人民大学出 参 考 书 版社 [4]Jagdish Bhagwati, 现代自由贸易,中信出版社 2003 [5]Ralph E.Gomory and William J. Baumol, 全球贸易和国家利益冲突, 中信出版社 2003 [6]殷德生, 唐海燕,国际经济学,立信会计出版社,2003 [7]冯正强等:《国际贸易:理论、政策、运作》 ,武汉大学出版社,2005 年 1 二、课程的对象和性质 课程对象:本课程适用于全日制金融专业本科生,拟于大二第二学期授课。 课程性质:本课程属于专业必修课。 三、课程的教学目的和要求 Grasping the theory and policy of international trade can give us a global perspective to the whole economy. The course’s basic goal is to make students set up the consciousness of international economical activity, grasp the basic concept of worldwide business, generate an understanding of many key events that shape our domestic and international environment. 四、Teaching methods 1. Case study: This course adopts two kinds of cases, firstly, logic case would be used in the course of giving lessons, for stating the theory and practice of international trade; Secondly, comprehensive case would offer students some historical background and the result of empirical research to improve the understand of theory. 2. Multimedia teaching: This course adopts multimedia teaching, is furnished with PPT courseware and audio-video teaching materials. 3. Reading, Write and Discussion: This course would offer students some material to read. Students should write 2 papers according these material and discuss together. 五、理论教学内容与基本要求(含学时分配) Chapter 1 Introduction 课时安排(Class hour):1 教学要求(teaching requirement of this chapter): The intent of this chapter is to provide both an overview of the subject matter of international economics and to provide a guide to the organization of the text. Students need to master the framework of international economics. At this chapter, students should understand the effects of dislocations due to international competition, and their experience through travel abroad. 教学重点和难点(The key content and difficulty of this chapter) :what is the International Economics. about 教学内容(Chapter Content): Introduction What is International Economics about? International Economics: Trade and Money Chapter 2 Labor Productivity and Comparative Advantage: 2 The Ricardian Model 课时安排(Class hour):3 教学要求(teaching requirement of this chapter): Students should master concepts such as comparative advantage, absolute advantage, relative wages specialization,.the Ricardian model, opportunity cost. At this chapter, students should know about the general equilibrium, and the gains from trade, the pattern of trade, trade amount, determining the relative wage with a two-goods model under the Ricardian model. 教学重点和难点(The key content and problem of this chapter) :The key content of this chapter is the Ricardian model.. Students should know why international trade take place, how a nation can gain from trade, what the pattern of trade would be constructed under the model. 教学内容(Chapter Content): The Concept of Comparative Advantage A One-Factor Economy Production Possibilities Relative Prices and Supply Trade in a One-Factor World Box: Comparative Advantage in Practice: The Case of Babe Ruth Determining the Relative Price After Trade The Gains from Trade A Numerical Example Box: The Losses from Non-Trade Relative Wages Misconceptions About Comparative Advantage Productivity and Competitiveness The Pauper Labor Argument Exploitation Box: Do Wages Reflect Productivity? Chapter 3 Specific Factors and Income Distribution 课时安排(Class hour):3 periods 教学要求(teaching requirement of this chapter):Students should master concepts such as mobile factor, specific factors, optimal trade policy, specific-factors model. At this chapter, students should be familiar with the specific-factors model, know how to use graph to analyze income distribution and the gains from international trade, the pattern of trade. A solid understanding of those topics proves useful in other parts of this course when students try to know the distinction between the Ricardian model and the specific-factors model, and why protectionism is so heatedly discussed in the press. 教学重点和难点(The key content and the problem of this chapter) :The key content of this chapter are how to use graph to analyze income distribution and the gains from international trade, the pattern of trade, under the specific-factors model. 教学内容(Chapter Content): 3 The Specific Factors Model Assumptions of the Model Box: What is a Specific Factor? Production Possibilities Prices, Wages, and Labor Allocation Relative Prices and the Distribution of Income International Trade in the Specific Factors Model Resources and Relative Supply Trade and Relative Prices The Pattern of Trade Income Distribution and the Gains From Trade The Political Economy of Trade: A Preliminary View Optimal Trade Policy Box: Specific Factors and the Beginnings of Trade Theory Income Distribution and Trade Politics Chapter 4 Resources and Trade: The Heckscher-Ohlin Model 课时安排(Class hour):4 教学要求(teaching requirement of this chapter):Students need to master concepts such as Factor Intensity, Factor Abundance, Stolper-Samuelson Theorem , Rybczynski Theorem , Heckscher-Ohlin Theorem, Factor-Price Equalization Theorem, the Leontief paradox. At this chapter, students should be familiar with the Heckscher-Ohlin Theorem, and know how to use graph to analyze income distribution and the gains from international trade, the pattern of trade. It is important to understand why empirical results could not support its predictions on the patterns of trade according the resource endowments. A solid understanding of those topics proves useful in other parts of this course when students need to understand the political implications of factor price equalization and the distinction among the Ricardian model, the specific-factors model and the Heckscher-Ohlin Theorem. 教学重点和难点(The key content and problem of this chapter) :The key contentof this chapter are how to use graph to analyze income distribution and the gains from international trade, the pattern of trade, in the Heckscher-Ohlin Theorem. 教学内容(Chapter Content): A Model of a Two-Factor Economy Assumptions of the Model Factor Prices and Goods Prices Resources and Output Effects of International Trade Between Two-Factor Economies Relative Prices and the Pattern of Trade Trade and the Distribution of Income Factor Price Equalization Case Study: North-South Trade and Income Inequality Empirical Evidence on the Heckscher-Ohlin Model 4 Testing the Heckscher-Ohlin Model Implications of the Tests Chapter 5 The Standard Trade Model 课时安排(Class hour):4 教学要求(teaching requirement of this chapter):Students need to master concepts such as the standard trade model , terms of trade , biased growth, export-biased growth, import-biased growth, immiserizing growth , import tariffs and export subsidies. At this chapter, students need to be familiar with the how to use the standard trade model to address a wide range of issues, such as the welfare and distributional effects of economic growth, transfers between nations, and tariffs and subsidies on traded goods. Four relationships on which the standard trade model is based upon should be emphasized. A solid understanding of those topics proves useful in other parts of this course when students need to understand distinctions among the Ricardian model, the specific-factors model , the Heckscher-Ohlin Theorem and the standard trade model. 教学重点和难点(The key content and problem of this chapter) :The key contentof this chapter is how to use the standard trade model to address a wide range of issues, such as the welfare and distributional effects of economic growth, transfers between nations, and tariffs and subsidies on traded goods. Four relationships on which the standard trade model is based upon should be emphasized. 教学内容(Chapter Content): A Standard Model of a Trading Economy Production Possibilities and Relative Supply Relative Prices and Demand The Welfare Effect of Changes in the Terms of Trade Determining Relative Prices Economic Growth: A Shift of the RS Curve Growth and the Production Possibility Frontier Relative Supply and the Terms of Trade International Effects of Growth Case Study: Has the Growth of Newly Industrializing Countries Hurt Advanced Nations? International Transfers of Income: Shifting the RD Curve The Transfer Problem Effects of a Transfer on the Terms of Trade Presumptions about the Terms of Trade Effects of Transfers Case Study: The Transfer Problem and the Asian Crisis Tariffs and Export Subsidies: Simultaneous Shifts in RS and RD Relative Demand and Supply Effects of a Tariff Effects of an Export Subsidy Implications of Terms of Trade Effects: Who Gains and Who Loses? Chapter 6 Economies of Scale, 5 Imperfect Competition, and International Trade 课时安排(Class hour):6 教学要求(teaching requirement of this chapter):Students should master concepts such as internal economies of scale, external economies of scale, marginal revenue , intraindustry trade, interindustry trade, dumping, learning curve, dynamic increasing returns. At this chapter, students should know why trade can occur when there are no technological or endowment differences, but when there are economies of scale or increasing returns in production. Students need to be familiar with distributional effects of trade when motivated by comparative advantage with those when trade is motivated by increasing returns to scale in production, main differences between interindustry and intraindustry trade, main reasons why a cluster of firms may be more efficient than an individual firm in isolation, the patter of trade and welfare with external economies. A solid understanding of those topics proves useful in other parts of this course when students need to understand reciprocal dumping and limitations of the monopolistic competition model. 教学重点和难点(The key content and problem of this chapter) :The key content of this chapter is why economies of scale lead to international trade. Main differences between interindustry and intraindustry trade, main reasons why a cluster of firms may be more efficient than an individual firm in isolation, the patter of trade and welfare with external economies should be emphasized. 教学内容(Chapter Content): Economies of Scale and International Trade: An Overview Economies of Scale and Market Structure The Theory of Imperfect Competition Monopoly: A Brief Review Monopolistic Competition Limitations of the Monopolistic Competition Model Monopolistic Competition and Trade The Effects of Increased Market Size Gains from an Integrated Market: A Numerical Example Economies of Scale and Comparative Advantage The Significance of Intraindustry Trade Why Intraindustry Trade Matters Dumping The Economics of Dumping Reciprocal Dumping The Theory of External Economies Specialized Suppliers Labor Market Pooling Knowledge Spillovers External Economies and Increasing Returns External Economies and International Trade External Economies and the Pattern of Trade 6 Trade and Welfare with External Economies Case: Tinseltown Economics Dynamic Increasing Returns Chapter 7 International Factor Movements 课时安排(Class hour):4 教学要求(teaching requirement of this chapter):It is important to master concepts such as FDI, and the causes and effects of international labor mobility, and to know why multinational.coorerra Students need to understand the analysis of international capital movements. 教学重点和难点(The key content and problem of this chapter) :The key contentof this chapter are causes and effects of international labor mobility, elements explain the existence of a multinational. Enterprise 教学内容(Chapter Content): International Labor Mobility A One-Good Model without Factor Mobility International Labor Movement Extending the Analysis International Borrowing and Lending Intertemporal Production Possibilities and Trade The Real Interest Rate Intertemporal Comparative Advantage Direct Foreign Investment and Multinational Firms The Theory of Multinational Enterprise The Theory of Direct Foreign Investment Multinational Firms in Practice Chapter 8 The Instruments of Trade Policy 课时安排(Class hour):6s 教学要求(teaching requirement of this chapter):Students need to master concepts such as specific tariffs, ad valorem tariffs, export subsidies, import quotas, voluntary export restraints, local content requirements, the effective rate of protection, Consumer surplus, Producer surplus, consumption distortionary efficiency losses, distortionary efficiency losses, gains from terms of trade improvement At this chapter, students need to be familiar with analyzing the economic effects of trade policies by describing the tools of trade policy and analyzing their effects on consumers and producers in domestic and foreign countries, taking a partial equilibrium view. A solid understanding of those topics proves useful in other parts of this course when students need to understand some specific episodes, such as Europe's common agricultural policy, U.S. sugar imports trade restrictions, the oil import quota in the United States in the 1960's. 教学重点和难点(The key content and problem of this chapter) :Analyzing the economic effects of trade policies by describing the tools of trade policy and analyzing their 7 effects on consumers and producers in domestic and foreign countries, taking a partial equilibrium view should be emphasized. 教学内容(Chapter Content): Basic Tariff Analysis Supply, Demand, and Trade in a Single Industry Effects of a Tariff Measuring the Amount of Protection Costs and Benefits of a Tariff Consumer and Producer Surplus Measuring the Costs and Benefits Other Instruments of Trade Policy Export Subsidies: Theory Case Study: Europe's Common Agricultural Policy Import Quotas: Theory Case Study: An Import Quota in Practice: U.S. Sugar Voluntary Export Restraints Case Study: A Voluntary Export Restraint in Practice: Japanese Autos Local Content Requirements Box: American Buses, Made in Hungary Other Trade Policy Instruments The Effects of Trade Policy: A Summary Chapter 9 The Political Economy of Trade Policy 课时安排(Class hour):3 教学要求(teaching requirement of this chapter):Students need to master concepts such as the theory of the second best , free trade area , customs union , common market , trade creation , trade diversion, the infant industry argument, strategic trade policy. At this chapter, students need to be familiar with the cases for and against free trade, income distribution and trade policy, and the history of international trade agreements, trade policy in developing countries and in developed countries. A solid understanding of those topics proves useful in other parts of this course when students need to understand distinctions among free trade area , customs union , common market. 教学重点和难点(The key content and problem of this chapter) :The key content of this chapter is the cases for and against free trade, income distribution and trade policy, and the history of international trade agreements, trade policy in developing countries and in developed countries. 教学内容(Chapter Content): The Case for Free Trade Free Trade and Efficiency Additional Gains from Free Trade Political Arguments for Free Trade National Welfare Arguments against Free Trade Income Distribution and Trade Policy 8 International Negotiations and Trade Policy Trade Policy in Developing Countries Import-Substituting Industrialization The Infant Industry Argument Problems of the Dual Economy Export-Oriented Industrialization: The East Asian Miracle Strategic Trade Policy in Developed Countries Sophisticated Arguments for Activist Trade Policy Globalization and Low-Wage Labor Discussion: 2 hours are distributed in the teaching period 9