Interactive PowerPoint on Computer Networks
advertisement

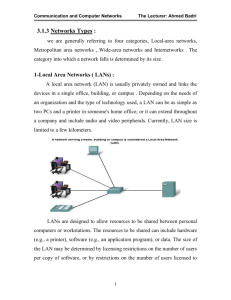
Task: Interactive PowerPoint presentation. The presentation is to be arranged as follows: A card containing a list of terms (shown below). Clicking on a term (or its button) will take the user to a card containing information on the topic. The following terms are to be used Local Area Network A computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings and owned by an organisation. However, one LAN can be connected to other LANs over any distance via telephone lines and radio waves. A system of LANs connected in this way is called a wide-area network (WAN). Wide Area Networks A wide-area network (WAN) is formed when LANs are connected via communications lines and radio waves. Node Networks connect devices such as printers and personal computers together. Any device such as this that is connected directly to the network is called a node. Network Benefits Generally a user is able to access data and devices anywhere on the LAN. This means that many users can share expensive devices, such as laser printers, as well as data. Users can also use the LAN to communicate with each other, by sending e-mail or engaging in chat sessions. Network Topologies The organisation of a local-area network (LAN) or other communications system. There are three principal topologies used in LANs. bus topology: All devices are connected to a central cable, called the bus or backbone. Bus networks are relatively inexpensive and easy to install for small networks. Ethernet systems use a bus topology. ring topology : All devices are connected to one another in the shape of a closed loop, so that each device is connected directly to two other devices, one on either side of it. Ring topologies are relatively expensive and difficult to install, but they offer high bandwidth and can span large distances. star topology: All devices are connected to a central hub. Star networks are relatively easy to install and manage, but bottlenecks can occur because all data must pass through the hub. These topologies can also be mixed. For example, a bus-star network consists of a high-bandwidth bus, called the backbone, which connects a collections of slower-bandwidth star segments. Protocols : An agreed-upon format for transmitting data between two devices. The protocol determines the following: the type of error checking to be used data compression method, if any how the sending device will indicate that it has finished sending a message how the receiving device will indicate that it has received a message There are a variety of standard protocols in use. Each has particular advantages and disadvantages; for example, some are simpler than others, some are more reliable, and some are faster. Common From a user's point of view, the only interesting aspect about protocols is that your computer or device must support the right ones if you want to communicate with other computers. TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, the suite of communications protocols used to connect computers on the Internet. As it is used by the Internet, it is becoming the de facto standard for transmitting data over networks. The rules and encoding specifications for sending data. media : Devices can be connected by twisted-pair wire, coaxial cables, or fiber optic cables. Some networks do without connecting media altogether, communicating instead via radio waves. LANs are capable of transmitting data at very fast rates, much faster than data can be transmitted over a telephone line; but the distances are limited, and there is also a limit on the number of computers that can be attached to a single LAN. Packet Switching Refers to protocols in which messages are divided into packets before they are sent. Each packet is then transmitted individually and can even follow different network or communication routes to its destination. Once all the packets forming a message arrive at the destination, they are recompiled into the original message. Most modern Wide Area Network (WAN) protocols, including TCP/IP, are based on packet-switching technologies. In contrast, normal telephone service is based on a circuit-switching technology, in which a dedicated line is allocated for transmission between two parties. Circuit-switching is ideal when data must be transmitted quickly and must arrive in the same order in which it's sent. This is the case with most real-time data, such as live audio and video. Packet switching is more efficient and robust for data that can withstand some delays in transmission, such as e-mail messages and Web pages. Internet The Internet was used originally to refer to the global network connecting millions of computers - the physical or hardware side. The Internet offered a range of services including email, Usenet and the World Wide Web. Due to the growth of the WWW the terms Internet and WWW are now used interchangeably. As of 2000, the Internet has more than 400 million users worldwide, and that number is growing rapidly. More than 100 countries are linked into exchanges of data, news and opinions. There are a variety of ways to access the Internet. The most common is through a commercial Internet Service Provider (ISP). World Wide Web A system of Internet servers that support specially formatted documents. The documents are formatted in a language called HTML (HyperText Markup Language) that supports links to other documents, as well as graphics, audio, and video files. This means you can jump from one document to another simply by clicking on hot spots(links). Not all Internet servers are part of the World Wide Web. There are several applications called Web browsers that make it easy to access the World Wide Web; Two of the most popular are Netscape Navigator and Microsoft's Internet Explorer. Encryption The translation of data into a secret code. Encryption is the most effective way to achieve data security. To read an encrypted file, you must have access to a secret key or password that enables you to decrypt it. Unencrypted data is called plain text ; encrypted data is referred to as cipher text. There are two main types of encryption: asymmetric encryption (also called public-key encryption) and symmetric encryption.