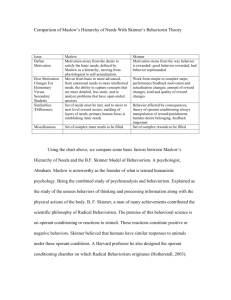
Radical Behaviorism is misunderstood when:
advertisement

EXAM #1 Session #1 Terms and concepts: 1. Describe the basic procedures used by Thorndike and Pavlov. 2. What are the 3 causes of behavior, according to the philosophy of behaviorism? 3. What is the difference between radical and methodological behaviorism? Give an example in which a private event is the dependent variable in a treatment program or research study (you can just make up a program that addresses a private event if you want). 4. James Lind and scurvy 5. Joseph Lister 6. Significance of diphtheria in history of medicine Discussion Questions 1. What are the 3 levels of selection? (include what is selected and the mechanism). Give examples of each. 2. Explain why people may implement treatments for autism that are not supported by scientific research, or why people in the past tried to cure diseases with treatments that had no basis in science. 3. Be able to discuss how incorrect assumptions about the cause of disease gave rise to wildly inappropriate treatment procedures (include the system with the 4 humours – and the use of the gods). 4. Discuss the characteristics of science using the 6 elements. 5. Be able to discuss the history of behavior analysis using Thorndike, Watson, Pavlov, and Skinner Session #2 Terms and concepts 1. Placebo effect 2. Post hoc, ergo propter hoc – what is wrong with this logic 3. Behavioral view of values 4. Teleology 5. Why scientists have left the lab 6. Spontaneous recovery - what is it 7. Spontaneous recover – why it occurs 8. Primary dv in science of behavior 9. Inductive reasoning 10. Deductive reasoning 11. Skinner’s objection to theories 12. Standard chart: 1 behavior in the entire observation-where plotted 13. Standard chart: 0 behavior in the entire observation-where plotted Discussion Questions 1. Be able to discuss a few alternative explanations of behavior that differ from that afforded by the 3 levels of selection. 2. Give an example of the intermingling of contingencies of reinforcement and contingencies of survival (e.g., betta splendens) 3. Explain the experiment that demonstrated what imprinting was all about. What is the ultimate conclusion of that study? (i.e. what is actually inherited?) 4. What was the main point of Methods and theories? a. Why people leave the lab b. Where do they go? 7. Explain the DOE and then critique the explanation provided by the researchers who studied this. 8. Be able to give 3 common objections to behaviorism, and then provide a rejoinder to each. Session #3 Terms and concepts 1. Metaphor 2. Meaning of a word 3. Give a behavioral interpretation of “awareness.” 4. Give an example in which we construct SDs to affect future behavior. 5. Rules 6. Rule-governed behavior 7. Contingency 8. Contingency-shaped behavior 9. How do rules function (according to Skinner) 10. Problem 11. Solution 12. Problem solving repertoire 13. Impure tact Discussion questions 1. Describe the typical tact training procedure. 2. Describe the 4 ways that we come to tact private events. 3. Describe the Thorndike experiment. How would Skinner have dealt with the problem in the puzzle box? 4. Give an advantage and disadvantage of contingency-shaped behavior and rulegoverned behavior. 5. Explain how rules might be function-altering – give an example Exam #2 Session #5 Terms and concepts 1. Phylogeny 2. Ontogeny 3. SSDR 4. Auto shaping 5. What is tabula rasa? Who, in modern times, came up with this? What is the current view? 6. In what way is reinforcement a function-altering operation? 7. Describe the experiment involving superstitious behavior. 8. What is point about explaining behavior by appealing to “instinct?” 9. What is a genotype’s fitness? 10. What is a fixed action pattern? Give an example. 11. What do natural selection and operant conditioning replace as explanations of behavior? 12. What is equipotentiality? Provide evidence that it does not obtain. 13. Bait shyness or taste aversion (if you want to research this, look up studies by Garcia – or ask me about this in class) Discussion Questions 1. What is RTE? What are some factors that influence it. 2. Give examples in which phylogeny interferes with ontogeny. 3. Contrast gradualism and punctuated equilibrium. Explain the appearance of giraffes with long necks using each theory. 4. Give an example of the intermingling of contingencies of reinforcement and survival. 5. Breland and Breland studies (Misbehavior of organisms) – give some examples and what was the conclusion? 6. Be able to recreate the table that compares natural selection and operant conditioning. Session #6 Terms and concepts 1. What are some traditional views of emotion? 2. According to Skinner, how does a lie detector work? 3. What are some of problems in identifying emotion with a. internal responses of the smooth muscles and glands and b. common expressions of facial and postural muscles 4. Given an emotion, provide an explanation using the bipartite explanation of emotion provided by Skinner. 5. What is “frustration” caused by? 6. What are emotional operations? Give some examples. What is the current classification of emotional operations (i.e., where do they fit into the operant paradigm)? 7. Talk about some practical uses of emotional operations. 8. What is the view of punishment according to Holz and Azrin? 9. What are some side effects of positive reinforcement? Include good and unfortunate effects. 10. What are some side effects of punishment? 11. What is the difference between forgetting and extinction? 12. Punishment contrast Discussion Questions 1. Design and graph an experiment that studies the rate of extinction as a function of previous schedule of reinforcement. 2. Give an explanation of phobias using Skinners view of emotion. Be prepared to discuss a behavioral Tx program for a phobia (include both respondent and operant behavior). 3. Given a punished behavior, explain its reduction by appealing to effects #2 and #3 of Skinner’s view. 4. Explain Skinner’s view of punishment, and cite all 3 effects. Include the two factor elements of the explanation. 5. What are some alternatives to punishment? 6. Explain taste aversion and how it addresses the concept of equipotentiality. Session #7 Terms and concepts 1. Give an example of a variable with multiple effects. 2. Why does extinction sometimes involve an oscillation of behavior undergoing extinction? 3. Give an example of a behavior being under the control of multiple variables. 4. Explain the use of projective tests in behavioral terms. (include supplemental stimuli in the explanation) 5. What is the verbal summator? 6. In behavioral terms, explain the following: a. Projection b. Repression 7. Is there really any “self” in self control? 8. What is the role of the surrounding community in self control? 9. Diagram the expanded model of self control choices that involve aversive stimuli. 10. How can a reinforcer have SD/S-Delta effects? Explain using an example. 11. Explain how drugs might used in self control. Discussion Questions 1. Explain the following: a. Formal prompts b. Thematic prompt c. Formal probe d. Thematic probe 2. Discuss Skinner’s example in which the appearance of candy evokes much nagging and whining. 3. What is Skinner’s view of self control? What are the two repertoires? What are some techniques that he describes? 4. What is the EAB model of self control? What are some research findings about how to strengthen (or teach) self control? 5. Conditioned suppression: a. EAB b. ABA