1.4 section notes
advertisement
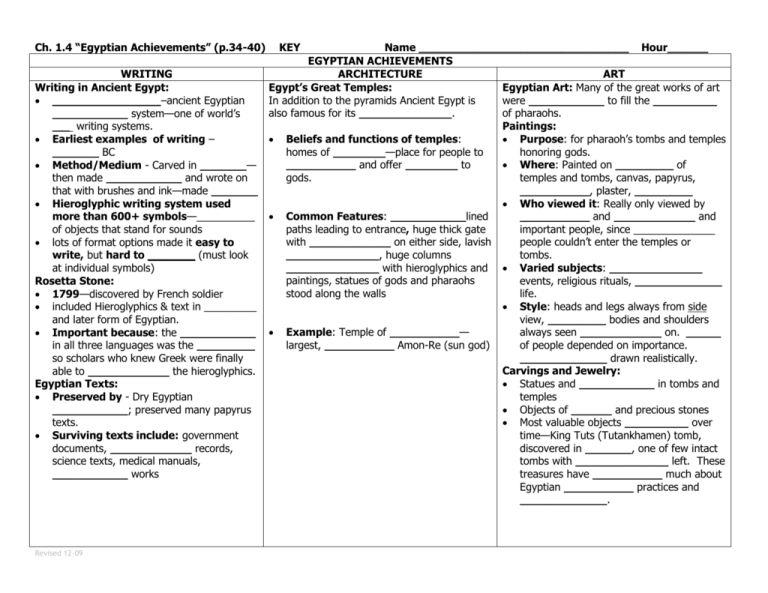
Ch. 1.4 “Egyptian Achievements” (p.34-40) WRITING Writing in Ancient Egypt: ________________–ancient Egyptian _____________ system—one of world’s ___ writing systems. Earliest examples of writing – ________ BC Method/Medium - Carved in ________— then made _____________ and wrote on that with brushes and ink—made ________ Hieroglyphic writing system used more than 600+ symbols—__________ of objects that stand for sounds lots of format options made it easy to write, but hard to _______ (must look at individual symbols) Rosetta Stone: 1799—discovered by French soldier included Hieroglyphics & text in _________ and later form of Egyptian. Important because: the _____________ in all three languages was the __________ so scholars who knew Greek were finally able to ______________ the hieroglyphics. Egyptian Texts: Preserved by - Dry Egyptian _____________; preserved many papyrus texts. Surviving texts include: government documents, ______________ records, science texts, medical manuals, _____________ works Revised 12-09 KEY Name _______________________________ Hour______ EGYPTIAN ACHIEVEMENTS ARCHITECTURE ART Egypt’s Great Temples: Egyptian Art: Many of the great works of art In addition to the pyramids Ancient Egypt is were _____________ to fill the ___________ also famous for its ________________. of pharaohs. Paintings: Beliefs and functions of temples: Purpose: for pharaoh’s tombs and temples homes of _________—place for people to honoring gods. ____________ and offer _________ to Where: Painted on __________ of gods. temples and tombs, canvas, papyrus, ____________, plaster, __________ Who viewed it: Really only viewed by Common Features: _____________lined ____________ and ______________ and paths leading to entrance, huge thick gate important people, since ______________ with ______________ on either side, lavish people couldn’t enter the temples or ________________, huge columns tombs. ________________ with hieroglyphics and Varied subjects: ________________ paintings, statues of gods and pharaohs events, religious rituals, _______________ stood along the walls life. Style: heads and legs always from side view, __________ bodies and shoulders Example: Temple of ____________— always seen ______________ on. ______ largest, ____________ Amon-Re (sun god) of people depended on importance. _______________ drawn realistically. Carvings and Jewelry: Statues and _____________ in tombs and temples Objects of _______ and precious stones Most valuable objects ___________ over time—King Tuts (Tutankhamen) tomb, discovered in ________, one of few intact tombs with ________________ left. These treasures have ____________ much about Egyptian ____________ practices and _______________. Revised 12-09