4C.NVM.4.5.12.7.11
advertisement

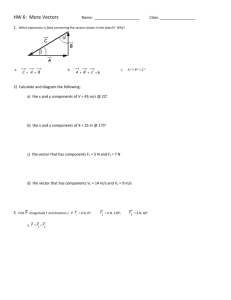
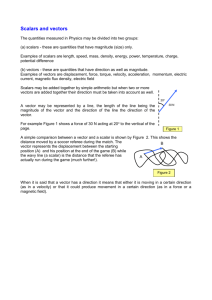
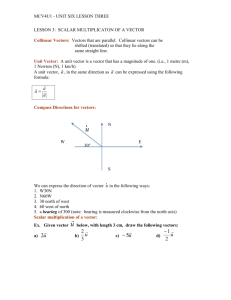
4C.NVM.4.5.12.7.11 2011 Domain: Number and Quantity Cluster: Perform Operations on Matrices Standard: 4. (+) Add and subtract vectors. Add vectors end-to-end, component-wise, and by the parallelogram rule. Understand that the magnitude of a sum of two vectors is typically not the sum of the magnitudes. Given two vectors in magnitude and direction form, determine the magnitude and direction of their sum. Understand vector subtraction v – w as v + (–w), where –w is the additive inverse of w, with the same magnitude as w and pointing in the opposite direction. Represent vector subtraction graphically by connecting the tips in the appropriate order, and perform vector subtraction component-wise. 5. (+) Multiply a vector by a scalar. Represent scalar multiplication graphically by scaling vectors and possibly reversing their direction; perform scalar multiplication component-wise, e.g., as c(vx, vy) = (cvx, cvy). Compute the magnitude of a scalar multiple cv using ||cv|| = |c|v. Compute the direction of cv knowing that when |c|v ≠ 0, the direction of cv is either along v (for c > 0) or against v (for c < 0). Essential Questions Enduring Understandings How can we use contextual situations from a variety of disciplines to model vector addition and subtraction? How can scalar multiplication be connected to dilations and similarity? What real life examples can be used to justify vector addition and scalar multiplication? The parallelogram rule is used to find the sum of two vectors. Vectors are added using components. The magnitude of a sum of two vectors is typically not the sum of the magnitudes. The resultant is the sum of the horizontal and vertical components of the vectors. Activities, Investigation, and Student Experiences 1. Vector addition activities. http://www.teacherlink.org/content/science/instruct ional/activities/vectoraddition/Vectors-print.PDF 4C.NVM.4.5.12.7.11 Content Statements Students will add vectors end-to-end, component wise, and by the parallelogram rule. Students will subtract vectors and represent subtraction graphically. Students will multiply a vector by a scalar and compute the magnitude and direction of a vector. Assessments 1. Describe each resultant as an ordered pair (example problems) 2. Open-ended question, such as: Under what conditions is the scalar product of the sum of two vectors the same as the sum of the scalar products of the two vectors? 2. Classwork problems: 3. Finding the resultant vector: 2011 4C.NVM.4.5.12.7.11 2011 3. Under what conditions is the sum of the magnitudes of two vectors be equal to the magnitude of the sum? Equipment Needed: Smart board Teacher Resources: Calculators Computer/Internet access White boards Overhead http://www.teacherlink.org/content/scien ce/instructional/activities/vectoradditi on/Vectors-print.PDF http://mathworld.wolfram.com/VectorMultiplication.ht ml http://www.onlinemathlearning.com/vectormultiplication.html http://mathworld.wolfram.com/DotProduct.html http://www.netcomuk.co.uk/~jenolive/vect6.html http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/vect.html http://schools.utah.gov/CURR/mathsec/Com mon-Core/Secondary-I/IHNVM.aspx http://www.nhn.ou.edu/~walkup/demonstrations/WebTu torials/HeadToTailMethod.htm