File
advertisement

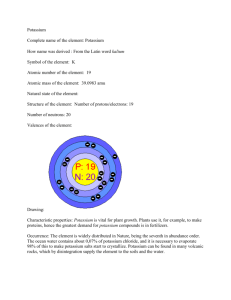
Science 9 Study of an Element The Periodic Table is a method of showing the chemical elements. The Periodic Table was developed by Russian chemist Dimitri Mendeleev in 1869 to illustrate reoccurring trends (“periodic”) in the trends of elements. For example, all elements in Column 1 have one electron in their outer orbit. The layout of the Table has been altered and extended over time as new elements were discovered. Your Task: Select an element from the Periodic Table Using the Internet, your textbook or library resources, research your selected element. Possible web sources include Web Elements – Periodic Table at www.webelements.com Pictorial Periodic Table at chemlab.c.maricopa.edu/PERIODIC/Li.html ChemiCool at www.chemicool.com/elements Prepare a short written summary containing information about your element (see template). Your written summary should include the following components: General chemistry information (e.g., Symbol, Atomic Number, Atomic Mass) History (e.g., date of discovery, who discovered) State of element MOST COMMON in nature Diagram of element’s atomic structure (Planetary Model) Physical properties (e.g., colour, density, hardness, melting point, ductility, malleability, texture, shape (…such as helix, cube), smell, electromagnetivity) Chemical properties (e.g., combustibility, reacts with air) Uses and applications Precautions (if necessary) for humans and the environment Other information you found interesting Prepare a creative presentation that highlights the key points listed above. DUE DATE: ___________________________________________ Example: Element Study of Potassium Introduction The name of the element is Potassium Potassium is an Alkali Metal General Chemistry The chemical symbol for potassium is K. Potassium’s Atomic Number is 19. This means potassium has 19 protons and 19 electrons. The number of protons and electrons of the element must always be the same. The Atomic Mass of potassium is 39. This means potassium has 19 protons and 20 neutrons. The total of 19 protons and 20 neutrons is 39. History Potassium was discovered in 1807. It was discovered by Sir Humphrey Davey. He discovered potassium while processing caustic soda using a process called electrolysis. Electrolysis is using electricity to cause a chemical reaction. Potassium was the first alkali metal to be discovered via this process. Potassium has the symbol K because its name in Latin in kalium. Most Common State in Nature (i.e., How does it occur naturally?) Potassium is a solid. It is a metal. Atomic Structure The picture shows the electron configuration of potassium. Potassium has 19 protons and 20 neutrons found in the nucleus (i.e., centre of the atom) In total, potassium has 19 electrons. Each electron is represented by a black dot. Physical Properties Colour is silvery-white. When burned, a colour of lilac is given off. Melting Point is 63.65OC Boiling Point is 774.0OC – much higher than water (100OC) Density is how close the atoms are packed together. Potassium’s density is 0.862 g/cm3. This is less than water. Hardness is low; potassium is a soft metal Potassium has no distinguishing smell At low concentrations (i.e., small amounts), potassium is sweet, but high concentrations (i.e., large amounts), potassium is bitter and salty. For this reason, large amounts of potassium are not found in drinks. Texture is soft. Potassium can be easily cut with a knife Potassium is very malleable. This means potassium can be pounded into different shapes very easily Potassium is also very ductile. This means potassium can be stretched. Potassium is a good conductor of electricity and heat. Chemical Properties Potassium reacts with water Potassium is a strong reducing agent. That means it oxidizes in air and loses its outer orbit electron very easily Uses Potassium ions are necessary for the function of all living cells. It is the 9 th most common element in our bodies. Potassium ions are a key mechanism in nerve transmission, and potassium depletion in animals, including humans, results in many heart problems. Potassium is used a lot as a fertilizers for plants Potassium is commonly used to make glass, soaps and gunpowder Major potassium chemicals are potassium hydroxide (KOH), potassium carbonate, potassium sulfate, and potassium chloride. KOH is a very strong base. It is used as a cleaner. Precautions Potassium is very reactive with water. The reaction produces a lot of heat and hydrogen gas. It becomes so hot the hydrogen gas explodes. Safe lab practices (e.g., goggles) must be used at all times. Potassium will burn in air. For this reason, potassium must be stored in oil. Potassium can burn your skin. Other Facts Foods rich in potassium include parsley, dried apricots, dried milk, chocolate, various nuts (especially almonds and pistachios), potatoes, bamboo shoots, bananas, avocados, soybeans, and bran. Potassium is also present in smaller quantities in most fruits, vegetables, meat and fish. Potassium makes up about 2.4% of the weight of the crust (i.e., rocks, soil, clay and sand) of the Earth Potassium is the 7th most common element on Earth. Potassium makes up about 0.0003% of the entire Universe. In the Universe, potassium is rare. You are about 0.2% potassium Potassium is very reactive. Due to this property, potassium is not commonly found by itself in nature. Rather, it is usually in a compound (i.e., bonded to another chemical). TEMPLATE for a report TITLE___________________ Your Name: ___________________________ Introduction The name of the element is ___________________ Other stuff (e.g., What Group on the Periodic Table does it belong in?) General Chemistry The chemical symbol is ____________________. Atomic Number is __________. o This means ____________ has ____ protons and ____ electrons. The number of protons and electrons of the element must always be the same. The Atomic Mass is ________. o This means ____________________ has ____ protons and ____ neutrons. The total of ____ protons and ____ neutrons is ____. History It was discovered in __________. It was discovered by ______________________. It was discovered while _________________________________________________ __. It has the symbol __________ because its name in Latin is __________________. Most Common State in Nature (i.e., How does it occur naturally?) ______________ is a _____________ Atomic Structure (**** insert a diagram ****) The picture shows the atomic structure of ________________. It has __________ protons and _________ neutrons found in the nucleus (i.e., centre of the atom) In total, the element has _________ electrons. Each electron is represented by a black dot. Physical Properties Colour is ____________. When burned, a colour of ____________ is given off. Melting Point is _____________OC Boiling Point is _____________OC Density is how close the atoms are packed together. The element’s density is ___________ g/cm3. This is __________ than water. Hardness is _________________ The smell is _____________________ Taste Texture is _______________ Malleable means it can be pounded into different shapes very easily Ductile means it can be stretched. It is a ______________ conductor of electricity and heat. Chemical Properties Does it react with water? Does it explode or catch on fire? Does it react with air? Does it rust? Uses List some common uses Precautions List the major precautions (e.g., “Will it burn you?”, “Does it cause blindness?”, “Does it make your sick?”) List safety gear you should use. Other Facts Anything you found interesting (e.g., “Is it found in the Sun?” “Do you need it to live?” “Is it used to make food last longer?”)