i. early developmental stages
advertisement

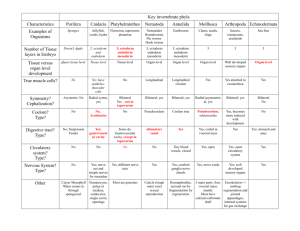
Development I. EARLY DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES A. All chordates have a notochord at some time in their life history 1. In vertebrates this rod is replaced by the vertebral column B. Stages 1. Cleavage a) Division without growth b) Zygote divides forming a solid ball of cells called a morula 2. Blastula a) Morula forms a hollow ball of cells (1) Space within the ball called the blastocoel 3. Gastrulation a) Cells invaginate into the blastocoel, forming three germ layers (1) Ectoderm (a) Outer layer (2) Endoderm (a) Inner layer (3) Mesoderm (a) Middle layer (b) Formed from outpocketing of the endoderm b) Space formed between the mesoderm becomes the coelom c) Invagination creates the primitive gut (archenteron) with the opening termed the blastopore, which becomes the anus in vertebrates (1) Since a second pore becomes the mouth, vertebrates are called deuterostomes C. Germ layers give rise to future organs 1. Ectoderm a) Forms the part of the skin b) Forms the nervous system 2. Mesoderm a) Forms the muscles and other structures 3. Endoderm a) Forms the digestive tract and other structures II. HUMAN EMBRYONIC AND FETAL DEVELOPMENT A. Definitions 1. Zygote a) A fertilized egg 2. Embryonic development a) Conception to 2 months b) Consists of the early formation of major organs 3. Fetal development a) 3-9 months b) Refinement of embryonic structures B. Extraembryonic membranes 1. Chorion a) Becomes fetal half of placenta 2. Amnion a) Surrounds embryo for protection and prevents drying out 3. Allantois a) Becomes umbilical blood vessels 4. Yolk sac C. Is the first site of blood cell formation