AP Gov't Unit 4 – Public Policy Handout
advertisement

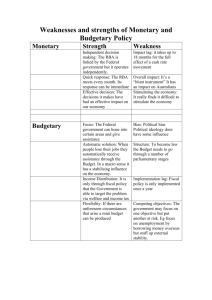
AP US Government UNIT IV: PUBLIC POLICY Readings: CHAPTERS 17, 18 & 19 Testing: Chap. 17, 18, 19 quizzes & Unit IV Multiple Choice Exam Assignments: Term Cards KEY TERMS TO DEFINE AND REMEMBER: UNIT IV Directions: Define 15 terms from each lecture. o Each term must be defined on its own note card. o Each term must appear on 1 side of the card with the corresponding definition on the back. o No points will be given for terms defined on anything other than note cards. o No points will be given for Term Cards not in your own handwriting. o Term Cards will always be due the day of the multiple-choice portion of the unit exam. o Term Cards are worth 1 point a piece. o For your own sanity’s sake, do not wait until the night before the exam to define all your terms! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. Chap. 17 Antitrust Policy Bond Capitalism Clayton Antitrust Act of 1914 Collective bargaining Command economy Consumer price index (CPI) Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) Discount rates Federal Reserve System Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Fiscal policy Food & Drug Administration (FDA) Globalization Indexed Inflation Keynesian economic theory Labor union Laissez-faire Minimum wage Mixed economy Monetarism Monetary policy Multinational corporations National Labor Relations Act North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) Outsourcing Private sector Protectionism 30. Public sector 31. Reserve rates 32. Securities & Exchange Commission (SEC) 33. Supply-side economics 34. Taft-Hartley Act of 1947 35. Unemployment rate 36. World Trade Organization 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Chap. 18 Earned Income Tax Credit Entitlement programs Feminization of poverty Great Society Programs Income Income distribution Means-tested programs Medicaid Medicare (Part A) Medicare (Part B) Medicare (Part D) Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (OBRA) of 1981 Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act Poverty line Progressive tax Proportional tax Regressive tax Social Security Act of 1935 Social Security Trust Fund Social welfare policies 21. Tax incidence 22. Temporary Assistance to Needy Families (TANF) 23. Transfer payments 24. Unemployment Insurance (UI) 25. Wealth 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Chap. 19 Clean Air Act Defensive medicine Endangered Species Act Emissions Trading Environmental impact statement (EIS) Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Health maintenance organizations (HMOs) Infant Mortality Rate Kyoto Agreement of 1997 Life expectancy Malpractice suits Medicaid Medicare National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) National health insurance National Institutes of Health Superfund Toxic waste Water Pollution Control Act AP RELEASE FRQ’s COVERED IN UNIT IV 1. 2002: Using your knowledge of United States politics, A. Describe the trend in distribution of government benefits for children and for the elderly from 1965 to present. B. Identify two politically relevant factors that have affected the changing distribution of government benefits between children and the elderly. C. Explain how each of the two factors identified in B has affected the changing distribution of governmental benefits. 2. 2006: In recent decades, entitlement programs have constituted substantial portion of the United States federal budget. Social Security is the largest entitlement program in the United States. From your knowledge of United States politics, perform the following tasks. A. Define entitlement program B. What is the primary source of revenue for the Social Security program? C. Identify one threat to the future of the Social Security program should the trends we see today continue. D. Describe one demographic trend that threatens the future of the Social Security program AND explain how it is responsible for the threat you identified in C. E. Explain how any one of the trends would change if the age of eligibility for Social Security were raised. 3. 2008: Fiscal policy and monetary policy are two tools used by the federal government to influence the United States economy. The executive and legislative branches share the responsibility of setting fiscal policy. The Federal Reserve Board has the primary role of setting monetary policy. A. Define fiscal policy. B. Describe one significant way the executive branch influences fiscal policy. C. Describe one significant way the legislative branch influences fiscal policy. D. Define monetary policy. E. Explain two reasons why the Federal Reserve Board is given independence in establishing monetary policy.