answer
advertisement
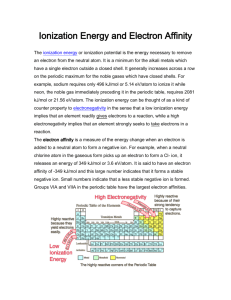
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING TEST 2 (ANSWER) TRIMESTER 2 ACADEMIC YEAR 2010/11 PROGRAM COURSE COURSE CODE DATE DURATION : : : : : FOUNDATION IN ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY I CHEF 114 7th January 2011 1.5 HOUR SECTION A 1. B 2. E 3. A 4. A 5. B 6. D 7. E 8. D 9. C 10. A 1 SECTION B Answer ALL the questions in this section. Show your calculations clearly. All work should be done within the space provided in this question booklet. -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Question 1 a) Calculate the work done in Joules when 1.0 mol of water is frozen at 0oC and 1.0 atm. H2O(l) → H2O(s) The volumes of 1 mol of water and 1 mol of ice at 0 oC are 0.0180 L and 0.0196 L respectively. [2 marks] Answer: V = (0.0196 - 0.0180) L = 1.6 x 10-3 L w = -P V = -1.0 atm x 1.6 x 10-3 L = -1.6 x 10-3 L. atm w in J = -1.6 x 10-3 L. atm x 101.3 J/1 L.atm = -0.163 J b) Calculate the heat given off when 266 g of white phosphorus (P4) burns in air according to the equation: P4(s) + 5O2(g) → P4O10(s) H = -3013 kJ/mol [2 marks] Answer: Amount of heat evolved c) = 266 g P4 x 1 mol P4/124 g P4 x -3013 kJ/mol P4 = -6463.4 kJ The combustion of methane (CH4) is used to heat water. Calculate how much methane in grams is required to increase the temperature of 2.5 L of water by 30 oC? Given: specific heat of water = 4.184 J/g.oC; density of water = 1 g/mL. Hof H2O(l) = -285.83 kJ/mol Hof CH4(g) = -74.85 kJ/mol Hof CO2(g) = -393.31 kJ/mol Hof O2(g) = 0 kJ/mol [4 marks] Answer: Mass of 2.5 L water = 2.5 kg = 2500 g qH2O = msT = 2500g x 4.184 J/g. oC x 30 oC = 313.5 x 103 J = 313.5 kJ Balanced equation for combustion of methane: CH4 + 2O2 → Hreaction = ? CO2 + 2H2O Hreaction = ∑Hof product - ∑Hof reactant = [ -393.31 + 2 x -285.83 ] - [-74.85 + 0] = -393.31 – 571.66 + 74.85 = -890.12 kJ Mass of CH4 required = 16 g CH4/890.12 kJ x 313.5 kJ 2 = 5.635 g d) State whether the following statements below are TRUE or FALS. [2 marks] (i) For the reaction: H2(g) + F2(g) → 2HF(g), the surrounding is doing work on the system. (ii) Hof of ozone, O3(g) = 0 Answer: (i) False (ii) False Question 2 (a) Write the electron configuration and give the four quantum numbers for the electrons in the outermost orbital for the following atom/ion: 3+ (i) [2½ marks] 26Fe Answer: Fe 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6 Fe3+ 1s22s22p63s23p6 4s0 3d5 ℓ =2 n=3 mℓ = -2,-1, 0, 1, 2 ms= +½ OR -½ Alternative answer to the four quantum numbers: (3, 2, -2, +½) (3, 2, -2, -½) (3, 2, -1, +½) (3, 2, -1, -½) (3, 2, 0, +½) (3, 2, 0, -½) (3, 2, 1, +½) (3, 2, 1, -½) (3, 2, 2, +½) (3, 2, 2, -½) (ii) 50Sn [2½ marks] Answer: 50Sn n=5 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d10 4p65s24d10 5p2 ℓ=1 mℓ = -1, 0, 1 ms= +½, OR -½ Alternative answer to the four quantum numbers: (5, 1, -1, +½) (5, 1, -1, -½) (5, 1, 0, +½) (5, 1, 0, -½) (5, 1, 1, +½) (5, 1, 1, -½) (b) Draw the shapes (boundary surfaces) for the orbitals of n = 2, ℓ = 1. Label the orbitals. [1½ marks] 3 (c) Calculate the wavelength in nanometer of a photon emitted by a hydrogen atom when its electron drops from the n=4 state to the n=2 state? [3½ marks] Answer: ) = 2.18 x = -0.408x10-18 J (ignore the –ve sign for wavelength calculation!) = = 48.75 x 10-8 m = 487.5 nm Question 3 a) Consider the data of the ionic radii for the following cations Ion Na+ Mg2+ Radius/nm 0.095 0.066 Al3+ 0.050 Si4+ 0.041 i) With the help of Periodic Table, state the proton number of each cation.[1 mark] Answer: Na = 11, Mg = 12, Al = 13, Si = 14 ii) Write the electron configuration of each cation. What do we call them? [1 mark] Answer: All ions have the same electron configuration; 1s22s22p6. The ions are isoelectronic. iii) Explain the variation of ionic radii shown in the table.[2 marks] Answer: Na, Mg, Al and Si are in the same period. As we move from left to right, the radii of the ions decrease. This is because as the proton number increases or Zeff increases the outermost electrons are pulled closer towards the nucleus thus reducing the radii of the ions. 4 b) Define the term ‘ionization energy’. [1 mark] Answer: Ionization energy is the minimum energy (in kJ/mol) required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom in its ground state. c) The successive ionization energy (in kJ/mol) of an element X is given in the Table below: Ionization First energy 999.6 Second 2 260 Third 3 380 Fourth 4 565 Fifth 6 996 Sixth 8 490 Seventh 28 080 Eight 31 720 Based on the data given, i) Deduce the electron configuration of the valence electron of X. [2 marks] Answer: From the data, there is a large increase in the seventh ionization energy, therefore, the seventh electron in X comes from the inner orbital, X has six electron in the valence orbital, which has the configuration of ns2 np4. ii) Predict the group in the Periodic Table to which X belongs. Answer: X is an element of group 6A [1 mark] iii) Write the complete electron configuration of X, if X is an element of the third period. [1 mark] Answer: Since X is an element of the third period, therefore the highest value of n must be 3. So, X has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 iv) Name the element X. Answer: X is sulfur (S) [1 mark] 5