APPSYCHBIOLOGYHWtest2
advertisement
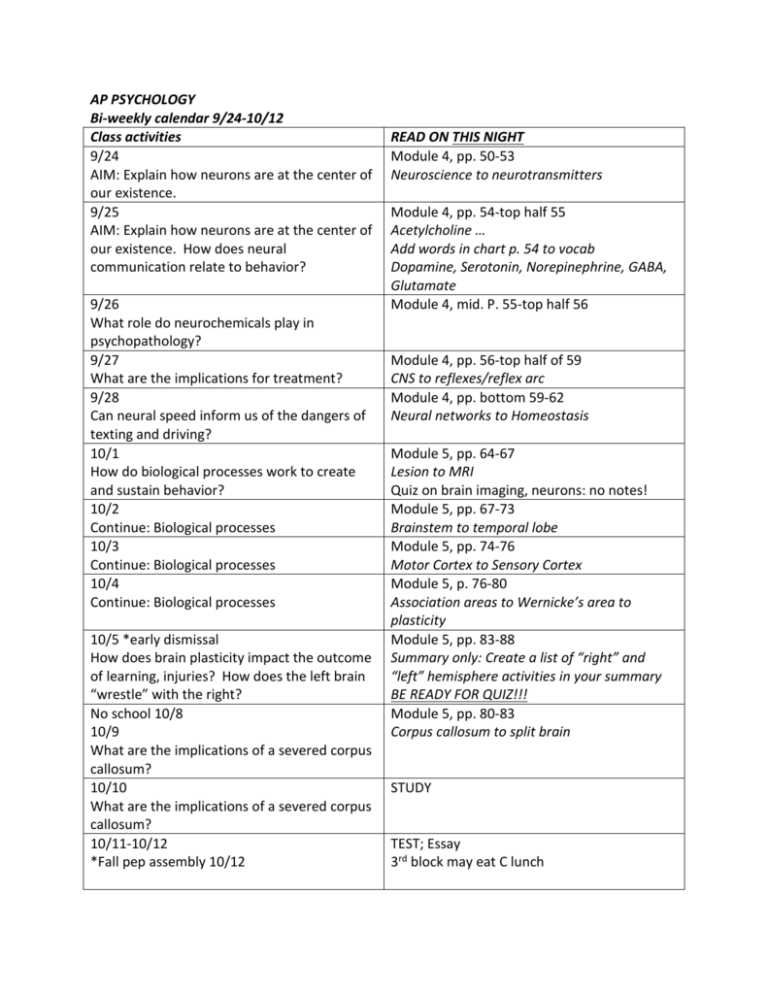
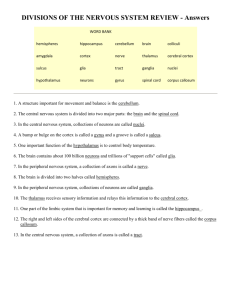
AP PSYCHOLOGY Bi-weekly calendar 9/24-10/12 Class activities 9/24 AIM: Explain how neurons are at the center of our existence. 9/25 AIM: Explain how neurons are at the center of our existence. How does neural communication relate to behavior? 9/26 What role do neurochemicals play in psychopathology? 9/27 What are the implications for treatment? 9/28 Can neural speed inform us of the dangers of texting and driving? 10/1 How do biological processes work to create and sustain behavior? 10/2 Continue: Biological processes 10/3 Continue: Biological processes 10/4 Continue: Biological processes 10/5 *early dismissal How does brain plasticity impact the outcome of learning, injuries? How does the left brain “wrestle” with the right? No school 10/8 10/9 What are the implications of a severed corpus callosum? 10/10 What are the implications of a severed corpus callosum? 10/11-10/12 *Fall pep assembly 10/12 READ ON THIS NIGHT Module 4, pp. 50-53 Neuroscience to neurotransmitters Module 4, pp. 54-top half 55 Acetylcholine … Add words in chart p. 54 to vocab Dopamine, Serotonin, Norepinephrine, GABA, Glutamate Module 4, mid. P. 55-top half 56 Module 4, pp. 56-top half of 59 CNS to reflexes/reflex arc Module 4, pp. bottom 59-62 Neural networks to Homeostasis Module 5, pp. 64-67 Lesion to MRI Quiz on brain imaging, neurons: no notes! Module 5, pp. 67-73 Brainstem to temporal lobe Module 5, pp. 74-76 Motor Cortex to Sensory Cortex Module 5, p. 76-80 Association areas to Wernicke’s area to plasticity Module 5, pp. 83-88 Summary only: Create a list of “right” and “left” hemisphere activities in your summary BE READY FOR QUIZ!!! Module 5, pp. 80-83 Corpus callosum to split brain STUDY TEST; Essay 3rd block may eat C lunch Biological Bases of Behavior 8-10% of AP Exam VOCAB III: BIO (72 terms) *Antagonist Blood-brain barrier (psychotropic drugs) L-dopa MODULE 4 Reticular Formation/ *RAS-reticular activating Thalamus Cerebellum Central Nervous System (CNS) Biopsychology Limbic System Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) *Neuroscience Sensory Neuron (afferent) Amygdala Motor Neuron (efferent) Hypothalamus Neuron *Soma/cell body Interneuron Dendrite *Hippocampus Somatic Nervous System Axon Cerebral Cortex *Receptors Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Myelin/myelin sheath Reflex *Nodes of Ranvier Endocrine System Action potential Hormones Glial cells Frontal Lobe Threshold *Corticoids Synapse *Melatonin Neurotransmitters Parietal Lobe Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe Pituitary Gland Motor Cortex Reuptake MODULE 5 Sensory Cortex *Terminal Buttons Lesion/*Ablation *Resting Potential Association Areas *Phineas Gage case study *All or None Law *Excitatory vs. Inhibitory signals Acetylcholine Aphasia Electroencephalogram (EEG) Broca’s area [Paul Broca] *Norepinephrine Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) *Computed Tomography Scan (CT) Brainstem Endorphins Medulla *Serotonin *Dopamine *GABA *Glutamine *Agonist Wernickes’s area [Carl Wernicke] Plasticity Corpus Callosum Split Brain *Roger Sperry, Michael Gazzaniga *Forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain *Pons