10. Chapter 10 outline notes
advertisement

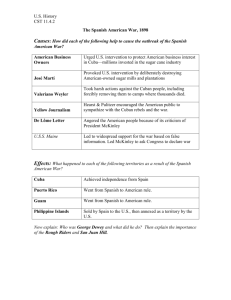
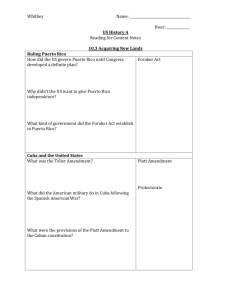
Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire Section 1 Imperialism and America Imperialism: the policy which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Three reasons for Imperialism: 1. Desire for military strength, 2. New markets, 3. Belief in cultural superiority Alfred T. Mahan: Publishes The Influence of Sea Power upon history which states that control the seas with the military would control the world. America believed in this idea. William Seward acquires Alaska for 7.2 million dollars Sanford b. Dole overthrows Queen Liliuokalani and sets up government and Congress makes Hawaii a territory in 1898. Section 2 The Spanish American War America initially wants Cuba and offers money to Spain to buy it and they refuse. Jose Marti: A Cuban poet and journalist in New York leads revolutionist ideas and start of revolt against the Spanish which control Cuba. Valeriano Weyler: General sent from Spain to restore order through strong military presents in Cuba. Yellow Journalists: They exaggerate news accounts and pictures or drawings supported it. They called Weyler the butcher for his actions. De Lome letter: letters between the Spanish calling the Americans weak. The cause/ start of the Spanish American War is caused by the accusation of the sinking of the USS Maine blamed on the Spanish. The battle fought in the Phillippines led by Commodore George Dewey which was very successful and freed them from the spanish. The battles in the Carribean led by the Rough Riders and Teddy Roosevelt which led to major victory at San Juan Hill. The US also blockaded the island. The Treaty of Paris 1898: It gave Guam, Puerto Rico, and the Phillippines to the US. It freed Cuba from Spain Section 3 Acquiring new lands Puerto Rico: Under military control at first and then given civil government set up under the Foraker Act. Cuba: Teller Amendment which said America had no intention of taking over Cuba Platt Amendment set up how Cuba would be governed: Stated it could make no treaties to limit independence, gave right of US to intervene in Cuban affairs, Cuba could not go into debt, and US could buy or lease land for a military base. Phillippines: Emilio Aguinaldo once helped the US against Spain, now felt that the US was the same as the Spanish rule and led a revolt against the US which became the Phillippine American War US: It would win the war and eventually give to it a civil government to it like Puerto Rico Foreign Influence in China: Spheres of Influence: Each nation claimed special interest in China John Hay and the Open Door Notes: All nations would have equal access to China and its markets Boxer Rebellion: Chinese try to get rid of all foreign influence in china by violently expelling all foreigners. Americans belief: US depended on exports, US could intervene to keep markets open, and closing foreign ports would threaten US survival. Section 4 America as a World Power Roosevelt makes peace between the Russians and Japanese after the Russo-Japanese War Hay-Pauncefote treaty of 1901: gave land in panama to the US to create a Canal to connect the oceans (Panama Canal). Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine: US would intervene military if necessary in the Western Hemisphere if needed when protecting US interests. Dollar Diplomacy: investing millions of dollars into the western hemisphere and then gaining a vested interest in that country through investment. Woodrow Wilson’s Missionary Diplomacy: US had responsibility to deny and Latin government recognition if it viewed it hostile to American interests Wilson and Mexico Wilson formally recognized Carranza after government went to corruption. Francisco Pancho Villa and Emiliano Zapata opposed American involvement in Mexico and attacked border towns in the US. Wilson sends General John J Pershing to capture and stabilize the situation along the south west border. America was not able to intervene more due to possible WWI in Europe.