Chapter 17 Notes American and French Revolution The Beginning
advertisement

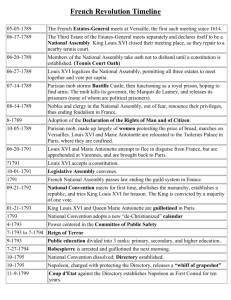
Chapter 17 Notes American and French Revolution The Beginning of the French Revolution commoners are tired of high taxes and the nobility is not taxed at all church is subordinate to the church Clergy: Catholic churchmen Nobility: Members of the French aristocracy. 3rd estate: anyone. Peasants, farmers, those who were neither peasants, farmers, clergery and nobility. The Clergy and Nobility could always out vote the third estate. June 17, 1789 the 3rd estate declared itself a National Assembly: two days later the clergy joined them. June 20 the King closed and locked the doors of the room in the palace at Versailles where the third estate was to meet. Louis Reacts to the Revolution Louis XVI during the Revolution Bastille: prison were Louis XVI kept his victims National Assembly: informed of the fall of the Bastille and the bloodshed involved, was uncertain what steps to take. Peasants repeated the attack on Bastille by invading the closest castles. Killed local noblemen and their families. Within two days of the fall of the Bastille Louis XVI agreed to leave Versailles and go to Paris and meet with the revolutionaries. France doesn't want to be ruled by an Absolute Monarch again. A Declaration of Right The Declaration Rights of Man Serfdom comes to an end. Declaration Rights of Man contained a list of rights and liberties which the Assembly intended to recognize and protect. Own property, equality before the law, right to resist tyranny, freedom of speech and of the press, and religious toleration. French Declaration very similar to the American Declaration of Independence Reign of Terror Jacobins' campaign of Fear. Collapse of the Girondians, the Jacobins gained control. The Age of Napoleon The French Revolution: A Roller Coaster Ride. 1799 a General named Napoleon Bonaparte seized power by force. He established a dictaroship, ending a decade of change reform, war and failure called the French Revolution. Napoleon at War Napoleon War Efforts Napoleons's Domestic Policies demanded state influence created public elementary and secondary schools By 1810 civil and commercial laws were in place By 1882 single power Emperor of France Creating an Empire An Empire in the Making Problems for Napoleon Napoleon and his unpleasant encounters French armies occupied Portugal