TEMY na PREZENTACIE
advertisement

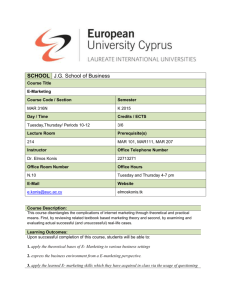
E-business and E-marketing Lecturer: Doc. RNDr. Michal Greguš, PhD Mgr. Andrea Studeničová Date: 2012-2013, summer term Detailed syllabus (6 credits) 1) Introduction to E-marketing a. b. c. d. What is e-marketing? New rules for the digital economy? E-marketing challenges and opportunities Comparing Web to other marketing channels 2) Internet User Characteristics and Behavior a. b. c. d. e. f. Customers in the 21st century Market segmentation E-marketing segments Consumer navigation behavior Country profiles Internet marketing research 3) Marketing Knowledge a. b. c. Marketing databases and data warehouses Data analysis and distribution Online privacy 4) E-Marketing Strategies a. b. c. d. B2C B2B B2B2C G2B 5) Product and Pricing Online a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. Creating customer value online E-marketing solutions based on new technology Enablers, application service providers, VSPs (Vertical service providers) Electronic data interchange, Collaboration platforms, E-learning Multimedia, convergence Branding strategies Taxonomy for Internet products Is the Internet an efficient market? E-business pricing models: segmented pricing, negotiation Online pricing strategies 6) Distribution a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Distribution functions Distribution channels online Disintermediation and Reintermediation Length of distribution channels Power relationships among channel players E-commerce models Content sponsorship Direct selling Intermediary models: the brokerage model, agent models, e-tailing Logistics 7) E-Marketing Communication a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. Integrated marketing communication online IMC e-business models Content publishing Community building Online advertising Online sales promotions Direct e-mail and viral marketing The net as a medium, including measurement metrics 8) Customer Relationship Management a. b. c. d. e. Building Customer Relationships CRM Customization Tools: e-mail, Web site customization, Intranet, Extranet, data mining, Real-time profiling, agents, Web log analysis, cookies, collaborative filtering Building Partnerships through Community Guarding customer privacy 9) The Internet Marketing Plan a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. A Multistep E-Marketing Plan The Venture Capital E-Marketing Plan Conducting a situation analysis Designing e-marketing mix strategies Creating an action plan Budgeting for e-marketing Evaluating the plan Selling the Plan 10) Leveraging Technology a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. Product Technologies Building a Web Site: Multimedia, Database Marketing, Computer Viruses, Denial of Service Attacks Price Technologies: Shopping Agents Distribution Technologies: Bandwidth and Market Opportunities, Content Filtering, Transaction Security IMC Technologies: Site Rating Services, Proxy Servers and Cache, Leveraging Search Engines Work, Privacy, Log Files, and Cookies, Rotating and Targeted Ad, Banners Relationship Marketing Technologies 11) Applications: Success and failure? a. b. c. d. Amazon.com and B2C eBay and classified sales Yahoo E-trading 12) Online Ethics and Law a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. Codes of Conduct Privacy: Background in Law and Ethics Privacy: Digital Concepts Copyright, Patent and Trademark Law Hyperlinks, Metatags, and Framing Cyber-Squatting, Domain Names and Site Development Issues Expression and Defamation Spam Jurisdiction and other pending problems Evaluation of this subject can be obtained fulfilling the following two conditions: 1. The student will prepare a presentation on the assigned topic from e-business, emarketing or e-commerce in general. (This must not be any advertising presentation on software commercial product or company). I recommend that the presentation is to be done in two-or three-student team. Presentation can be on the assigned topic, or you can send me a proposal with a short outline of the proposed presentation for approval. The presentation must be presented in front of the whole class during the semester (and submitted to me in advance in electronic form). The length of presentation in the case of a two-student team should be about 25 minutes, the team consisting of three students for about 35 minutes. The presentation must be prepared and realized during the semester on assigned dates. (at seminars).. or, as an alternative web site for an e-shop or on-line marketing research questionnaire, etc. 2. Student is assigned four questions (take-home exam), each should be answered thoroughly on in average at least two and a quarter of a page (i.e. a total of at least nine pages or 16200 characters). Responses should be forwarded in the format MSWord document - sent to andrea.studenicova@fm.uniba.sk, not later than at the end of April. Assigned questions can be sent to a student on request via e-mail. Questions The questions that follow are the type of the questions assigned to students as a take home exam. (usually four questions are assigned and answers should be at least nine pages of text long). 1. Describe how the Internet and the World Wide Web have impacted e-commerce. 2. Outline what should be done with a Web site to gain audience interest. 3. List what is important in motivating customers to take action (buy online, etc.). 4. Explain distribution in relationship to e-commerce. 5. Explain the -strategies e-businesses are using to create value for customers. 6. Compare and contrast how e-commerce is being used as a strategic tool by eretailers and traditional retailers. 7. Describe how online communities are targeting individuals and what it takes to make a successful online community. 8. Describe how businesses are using data and new technologies to gain competitive advantages. 9. Explain the importance of brand names of e-business. 10. Explain how e-businesses are organizing themselves to compete. 11. List and describe the major legal issues related to e-business. 12. Describe the importance of quality online customer service. 13. Explain the importance of long-term customer relations in e-business. 14. Explain how you would measure the value of the web site. 15. Explain how Google has attained its success. 16. Discuss the various online marketing communications efforts that exist through the use of sponsorship and affiliate deals 17. What are Web transaction logs, and how do they work in combination with registration forms, shopping cart databases, cookies, and Web bugs to help firms understand how customers behave online? 18. What are the values or benefits of search engine marketing? Describe the types of search engine marketing that exist 19. Define the term industry structure and discuss the ways the Internet and ecommerce have changed the five forces that characterize industry structure And some more questions: Question 20: One of your customers complains about the delivery of goods that she claims she did not order. (a) What is needed to establish that a contract actually existed? (b) What other information is it useful to keep about your customers, and what could you use it for? (c) Describe some of the problems of anonymous payment schemes such as digital cash. Where might they be useful? (d) What recourse would the customer have if she had paid using such a system, and how would you detect whether such a complaint was fraudulent? Question 21: A company proposes to introduce a new e-mail service, one with a small postage charge for each message. It is believed that by charging for each message sent the amount of spam will be reduced. The response rate for spam is about 0.005%, that is about five in a hundred thousand messages elicit a positive response. (a) Estimate a price that might economically discourage spam. (b) Describe approaches to handling the micro-payments involved. (c) What is meant by a network externality, and how might it be overcome in this case? (d) The postage charges might be credited to the recipient, less a handling fee. Describe a mechanism for this. Question 22: It is said that the Internet played a significant role in the US presidential election. You are asked by a major UK political party to advise them on their Internet policy and associated website. The party has about 200,000 members, each paying a fee of £25 per annum. Its total annual income, mainly from donations, is about £20M. The UK has about 46 million people registered to vote. There are about 646 parliamentary constituencies. (a) Describe in brief bullet points the key elements of your proposed Internet strategy. (b) Draw an outline block diagram of the architecture that would be needed. (c) Make and justify some estimates of the size and cost for its implementation. (d) Outline relevant regulations. Question 23: Suppose that the annual fixed cost of operating and maintaining a merchant web site is $100,000. The only source of traffic for your site is a pay-for-performance referral site that charges you 25 cents for each click through. If the average value of a sale is $50.00 at this site what is the number of referrals that will be necessary to breakeven? You may assume that the site’s average variable operating expense is 15% of sales, the site’s conversion rate is 20% and the margin on the merchandise sold is 40%. Possible topics for presentations E-marketing planning E-marketing environment Accumulation of online marketing knowledge Online consumer behavior E-marketing strategies Viral marketing And so like... Describe the background, current and future potential of e-marketing, e-business models, e-marketing process, and different types of e-marketing strategies. Analyze the e-marketing environment and opportunity, online consumer behavior, and information collected from Internet sources Explain the impact of Internet and how it changes the traditional marketing in the aspects of segmentation, targeting, differentiation, positioning, product, price, distribution, communication and customer relationship management Design e-marketing plan for a real company. Literature 1. Kenneth Laudon, Carol Guercio Traver: E-Commerce 2009 Business, Technology, Society(5th Edition) , Prentice Hall; 5 edition, 2008, ISBN-10: 0136007112 2. Fellenstein, C., Wood, R.: Exploring E-commerce, Global E-business, and Esocieties, Prentice Hall PTR, 2000 3. Turban E., Leidner D., McLean E., Wetherbe J., Information Technology for Management: Transforming Organizations in the Digital Economy, 5th Edition, Wiley, New York 2006. ISBN: 978-0-471-70522-2 4. Knight P., Vysoce efektivní marketingový plán, Grada, Praha 2007, ISBN 97880-247-1999-3 Contact Information: Doc. RNDr. Michal Greguš, PhD : +421 (2) 50117488, +421 (2) 50117487 Office: 3rd floor office no. 325 Faculty of Management, Comenius University in Bratislava Ul. Odbojárov 10 820 05 Bratislava 25 |Slovak republic Web: http://www.fm.uniba.sk E-Mail: michal.gregus@fm.uniba.sk Mgr. Andrea Studeničová :+421 (2) 50117456 Office: 3rd floor office no. 332 B Faculty of Management, Comenius University in Bratislava Ul. Odbojárov 10 820 05 Bratislava 25 |Slovak republic Web: http://www.fm.uniba.sk E-Mail: andrea.studenicova@fm.uniba.sk