Chapter 3 Notes - new
advertisement
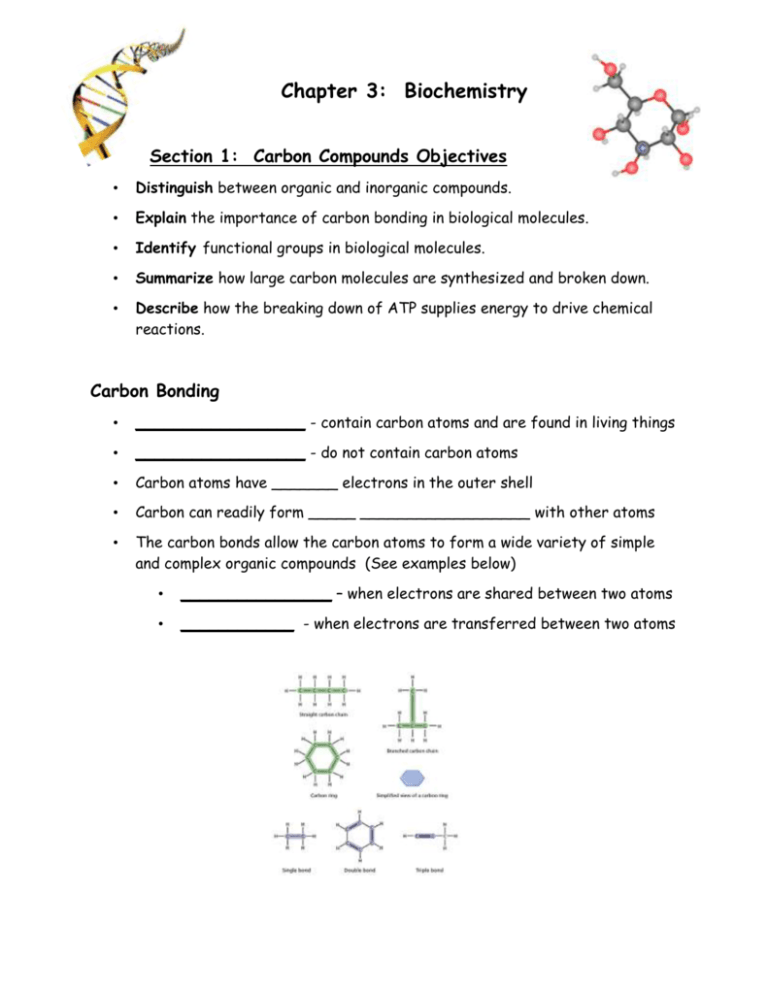
Chapter 3: Biochemistry Section 1: Carbon Compounds Objectives • Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. • Explain the importance of carbon bonding in biological molecules. • Identify functional groups in biological molecules. • Summarize how large carbon molecules are synthesized and broken down. • Describe how the breaking down of ATP supplies energy to drive chemical reactions. Carbon Bonding • __________________ - contain carbon atoms and are found in living things • __________________ - do not contain carbon atoms • Carbon atoms have _______ electrons in the outer shell • Carbon can readily form _____ __________________ with other atoms • The carbon bonds allow the carbon atoms to form a wide variety of simple and complex organic compounds (See examples below) • ________________ – when electrons are shared between two atoms • ____________ - when electrons are transferred between two atoms Functional Groups • ____________________ - groups of atoms that influence the properties of molecules and the chemical reactions in which the molecules participate • See Table 3-1 (page 52) Large Carbon Molecules • __________ – a molecule that consists of repeated, linked units • _____________________ – large polymers • _______________ – small simple molecules • ________________________ - join __________ to form __________ • • Releases ___________ as a by-product • Example: Monomer + Monomer Polymer + Water _____________________ - water is used to split polymers into monomers • Example: Polymer + Water Monomer + Monomer Energy Currency • Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) - stores and releases energy during cell processes, enabling organisms to function Section 2: Molecules of Life Objectives • Distinguish between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. • Explain the relationship between amino acids and protein structure. • Describe the induced fit model of enzyme action. • Compare the structure and function of each of the different types of lipids. • Compare the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. Carbohydrates • Composed of: • ________, ______________, and _________ in a ratio of about • ______ carbon to _______ hydrogen to _______ oxygen • Monomer = _______________________ • Our main source of _________________ • Used as _______________ ___________________ in organisms Carbohydrate # of Monosaccharides Example Monosaccharide Glucose (blood), fructose (fruit), galactose (milk) Disaccharide Sucrose, lactose, maltose Polysaccharide Glycogen(liver + muscle), starch (plants), cellulose (cell walls), chitin (exoskeletons of arthropods) Proteins • Composed of: • ___________, ____________, __________, and _____________ • Monomer = ________________ • Make up 50% of your ______ _______________ • Functions including structural, defensive, and catalytic roles • Examples: • • • Enzymes: amylase, catalase, maltase • Structural: collagen • Contractile: actin, myosin (found in muscles) • Transport: hemoglobin (transports oxygen in the blood) • Storage • Hormones: insulin Amino Acids • Proteins are made up of monomers called amino acids • The sequence of amino acids determines a protein’s shape and function Dipeptides and Polypeptides – Two amino acids are joined by __________ bonds to form a dipeptide – A long chain of amino acids is called a __________________ • Amino acid diagram • Enzymes – ______________ chemical reactions – Bind to specific _______________ (aka reactants) – The binding of a substrate with an enzyme causes a change in the enzyme’s shape and reduces the activation energy of the reaction – Typically named for the substrate they work on + “-ase” – The enzyme sucrase works on sucrose – Factors that affect enzymes: _________________ or ______ Lipids • ________________ molecules that store energy • _______________ in water • Include triglycerides, phosolipids, steroids, waxes, and pigments • Twice the energy stored in lipids than in the same amount of carbs • Monomer = _____________________ • _______________________ • • Most lipids contain fatty acids, unbranched carbon molecules that have a hydrophilic end (head) and a hydrophobic end (tail) _______________________ • = _______________ • Consist of _____ fatty acids and _____ molecule of glycerol • ______________ = hard at room temperature (butter, lard) • ___________ bonds between carbon atoms • ______________ = liquid at room temperature (vegetable oil) • • • • Some ________________ bonds between carbon atoms _______________________ • Make up _________________________ • Consist of ______ fatty acids and _____ glycerol molecule • _______ bilayer = Hydrophilic end (head) and a hydrophobic end (tail) _______________________ – Made of one long fatty acid chain joined to one long alcohol – Waterproof – Form protective coating on plant leaves _______________________ – Composed of four fused carbon rings – Examples = animal hormones, cholesterol Nucleic Acids • Large and complex organic molecule • Stores and transports information • Monomer = __________________ • Structure of Nucleic Acids • Deoxyribonucleic acid (______) - contains genetic information that determines the characteristics of an organism and directs cell activities • Ribonucleic acid (______) - plays many key roles in building of proteins and can act as enzymes. • ____________________ = monomer of nucleic acids • Three main components • _______________________ • _______________________ • _______________________