Final Exam Study Guide
advertisement

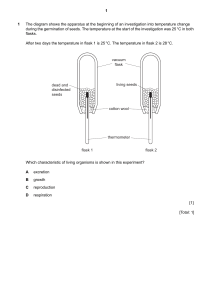
Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 12 1. Which domain contains all organisms that have a nucleus? 2. How do scientist hypothesize how cyanobacteria changed early Earth? Chapter 17 3. List the levels of classification from broadest (contains the most organisms) to the narrowest (contains the least number of organisms. 4. What does Linnaean taxonomy use the name and classify organisms? Chapter 13 5. What is a biotic factor? Give some examples. 6. What is a food web? How would the loss of one animal disrupt the web? 7. Give an example of a food chain. How would the loss of one animal disrupt the chain? Chapter 14 8. Describe an organism’s niche. 9. Define: a. Parasitism b. Commensalism c. Competition d. Mutualism Chapter 15 10. Traveling from the coniferous region to the tundra region you would most likely see a _____________ in biodiversity. 11. What characteristics do all deserts have in common? 12. Contrast weather and climate. 13. If a cell contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, it is ______________. Chapter 16 14. Thousands of acres of tropical rain forest are cut down each year, primarily for farming and wood products. Identify two negative consequences of rain forest destruction. Explain the negative impact of each consequence. Chapter 18 15. How do bacteria and archea differ? 16. What is the major role(s) of bacteria in the environment? 17. All viruses are made of proteins and ____________. Chapter 19 18. A protist is any organism that is not a plant, animal, fungus or __________________. 19. What are the major characteristics of fungi? Chapter 20 20. Plants use sunlight to drive this process _________________________. 21. What are the major characteristics of plants? 22. Without plants, _______________ could not live on land. Chapter 21 23. A seed plant is anchored in the ground by its ___________________. 24. Vascular tissue in plants consists of ______________ and _____________. 25. What are the functions of a stem? 26. Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse in and out of a leaf through the _____________. 27. What is the difference between monocot and dicot stems? Chapter 22 28. This structure contains a plant embryo, a food supply, and a protective covering _______________________. 29. Pollen grains are produced by ________________. 30. The gametophytes of gymnosperms (pine trees) live inside reproductive structures called _________________________. 31. Angiosperms (flowering plants) produce seeds inside protective structures called ______________________. 32. A ripened ovary that contains seeds is called a _________________. 33. What are characteristics of seeds that are dispersed by wind and water? Chapter 23 34. Contrast plant and animal cells. 35. What are the characteristics of all animals? 36. Any animal with a spinal cord is a ______________________. 37. How do sponges get food? 38. The body of an annelid (earthworm) has ________________ Chapter 24 39. In what habitats do you find arthropods? Chapter 25 40. Fish obtain oxygen from water through these structures. 41. Why can the eggs of amphibians dry out easily? Chapter 26 42. Where can reptiles NOT live? 43. What are the general characteristics of birds? 44. What are the general characteristics of mammals?