Civil Liberties and Civil Rights
advertisement
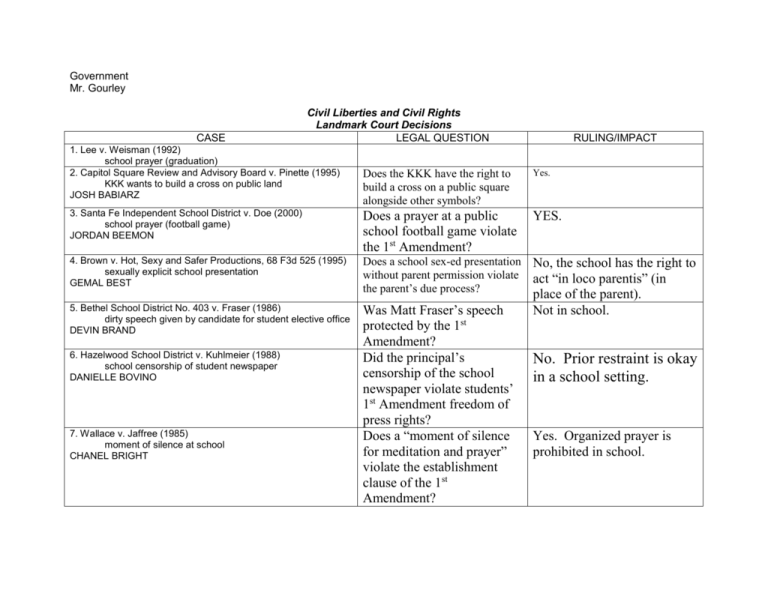
Government Mr. Gourley CASE Civil Liberties and Civil Rights Landmark Court Decisions LEGAL QUESTION 1. Lee v. Weisman (1992) school prayer (graduation) 2. Capitol Square Review and Advisory Board v. Pinette (1995) KKK wants to build a cross on public land JOSH BABIARZ RULING/IMPACT Does the KKK have the right to build a cross on a public square alongside other symbols? Yes. 3. Santa Fe Independent School District v. Doe (2000) school prayer (football game) JORDAN BEEMON Does a prayer at a public school football game violate the 1st Amendment? YES. 4. Brown v. Hot, Sexy and Safer Productions, 68 F3d 525 (1995) sexually explicit school presentation GEMAL BEST Does a school sex-ed presentation without parent permission violate the parent’s due process? 5. Bethel School District No. 403 v. Fraser (1986) dirty speech given by candidate for student elective office DEVIN BRAND Was Matt Fraser’s speech protected by the 1st Amendment? Did the principal’s censorship of the school newspaper violate students’ 1st Amendment freedom of press rights? Does a “moment of silence for meditation and prayer” violate the establishment clause of the 1st Amendment? No, the school has the right to act “in loco parentis” (in place of the parent). Not in school. 6. Hazelwood School District v. Kuhlmeier (1988) school censorship of student newspaper DANIELLE BOVINO 7. Wallace v. Jaffree (1985) moment of silence at school CHANEL BRIGHT No. Prior restraint is okay in a school setting. Yes. Organized prayer is prohibited in school. 8. Tinker v. DesMoines School District (1969) antiwar protest at school LONZIE CARTER 9. Furman v. Georgia (1972) death penalty 10. Schenk v. United States (1919) encouragement of draft resistance 11. New York Times v. United States (1971) government censorship of stolen secret materials (prior restraint) 12. Feiner v. New York (1951) freedom of speech and disorderly conduct GWEN DAVIS 13. Miller v. California (1973) what constitutes pornography/obscenity 14. United States v. O’Brien (1968) burning of draft cards 15. Gregory v. Chicago (1969) protest march in front of mayor’s home ERIK DIAZ 16. Widmar v. Vincent (1981) use of public facilities by religious group NICK DIXON 17. Chicago v. Morales (1999) anti-loitering law DONTREAL EVANS 18. United States v. Eichman (1990) flag burning ROB GILES Is wearing a black armband protected symbolic speech under the 1st Amendment? YES. Did Feiner’s arrest for breach of the peace violate his 1st amendment freedom of speech? No, because his speech was leading to violence and disrupting traffic. Was the demonstration protected under 1st Amendment freedom of assembly? YES. Did Chicago’s antiloitering ordinance violate the 1st Amendment freedom of association? YES. Laws cannot criminalize one’s right to associate with others on public property. Is flag burning protected symbolic speech under the 1st YES, if not a 19. Agostini v. Felton (1997) public school teachers in private schools 20. Reno v. ACLU (1997) freedom of speech on the internet TIERRA WILLIAMS 21. Gideon v. Wainwright (1963) right to counsel MICHAEL GREEN 22. Mapp v. Ohio (1961) search and seizure JASON GUTIERREZ 23. Regents of California v. Bakke (1978) race-based admissions policy MALLORY JABAAY Amendment? clear & present danger Are people guaranteed representation under the 6th Amendment in a non-capital trial? Was the search of Mapp’s suitcase permitted by the 4th Amendment? YES, in any CRIMINAL case, one’s right to an attorney cannot be taken. No. The exclusionary rule doesn’t allow illegally obtained evidence into court. Race cannot be the SOLE Does a racial quota for college admission violate factor in an admission decision. 14th Amendment equal protection? 24. U.S. v. Nixon (1974) executive privilege/confidentiality 26. RIAA v. Verizon Internet Services (2003) internet downloads / privacy 27. Korematsu v. United States (1944) Japanese war internments 28. Brandenbyrg v. Ohio (1969) political advocacy 29. Schechter Poultry Corporation v. United States (1935) federal government and intrastate trade 30. Heart of Atlanta Motel, Inc. v. United States (1964) discrimination in public accommodation LATRELL JONES Can a hotel owner discriminate on the basis of NO. If a business is 31. Board of Education v. Earls drug testing in schools JACOB KOLWYCK 32. Boy Scouts of America v. Dale (2000) prohibition against gay scouts JUSTIN LEVY 33. Cohen v. California (1971) f-word on a jacket CORNELIOUS LOWE 34. Hurley v. Irish American Gay, Lesbian, and Bisexual Group of Boston (1995) inclusion/exclusion in a parade MARLENE MILES 35. Church of the Lukumi Babalu Aye v. Hialeah ritual animal slaughter KHYREE PIERCE 36. Oncale v. Sundowner Offshore Services (1998) same-sex sexual harassment MONTSERRAT RAMIREZ-PERALTA 37. McDonald v. City of Chicago (2010) handgun ban JAMES ROBERTS race? “open” it can’t discriminate. Does a random drug test of student athletes violate the 4th Amendment freedom from unreasonable search? Was Dale’s freedom of association violated when the Boy Scouts excluded him for being gay? Is the f-word protected speech in a public place? Does exclusion from a Catholic parade violate GLIB’s 1st amendment freedom of speech? Did the City ordinance banning animal sacrifice violate the church’s 1st Amendment freedom of religion? Can sexual harassment occur between members of the same gender? Did the Chicago handgun ban violate the 2nd Amendment right to bear arms? Drug tests are okay if done randomly. No. Boy Scouts represents religious values and is a private organization. YES. NO. Not if the parade is religious. YES. YES. People may now register handguns within the city. 38. Graham v. Florida (2010) death penalty for non-homicide juveniles PATRICK ST. JOHN 39. South Dakota v. Dole (1987) federal highway funds and state drinking age MICHAEL TAPLEY 40. Federal Communications Commission v. Pacifica Foundation (1978) banned words on TV/radio ABREYA TAYLOR 41. Arizona v. Gant (2009) police searches of automobiles DOMINIQUE THOMAS 42. Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission (2010) Campaign contributions and free speech PAIGE WILSON-COLEMAN Can Congress take away highway funds from a state over its drinking age? Is the FCC’s regulation of radio waves protected by the 1st Amendment? Is a search conducted after handcuffing a defendant a violation of 4th Amendment search and seizure? Are campaign advertisements protected by the 1st Amendment? YES. “banned words case” YES. No probable cause existed. Yes. Corporations can buy political ads. Landmark Court Case Brief DUE FRIDAY (50 PTS). Must be typed/hand written. Plagiarized is an automatic zero. I. The Facts a. Who, what, when, where? II. Legal Issue(s) before the Court a. What questions of law does the case raise? b. What part(s) of the Constitution and/or amendments apply? III. The Holding (Decision) of the Court (Outcome- 9-0, 5-4) a. majority/unanimous (EVERY CASE WILL HAVE ONE. TELL ME WHICH Justice wrote it, what it stated etc.) b. Concurring- agree with majority but for different reason (Think about pizza example) If there is one tell me same info as majority. Dissenting- disagrees with decision of the case. If there is one tell me same info as majority. IV. Significance of the Case (Case Law) 1. Why is this case important? Significance. 2. Answer the legal question that you wrote down from packet. answer it using your opinion based off research. HELPFUL WEB ADDRESSES: www.law.cornell.edu www.findlaw.com