doc
advertisement

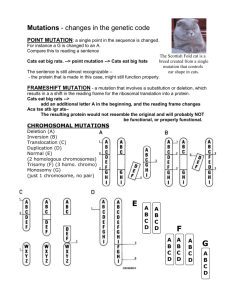
Study Questions: Mutations Part I 1) What is a point mutation? What is the difference between a silent mutation, a nonsense mutation and a missense mutation? 2) What effect would a single base pair deletion within a gene coding sequence have on the resultant protein? What if the deletion was big (like 1000 bp)? Could you get a suppressor mutation? 3) If E. coli was growing without any extra mutagens, would you expect its genome to have any mutations? How do chemical mutagens change this? 4) Describe three different types of chemical mutagens. What kinds of mutations would each cause, and how? 5) How does the Ames test work? If the original his- mutation is a point mutation how would the test change if the starting mutation was a whole gene deletion? 6) You are working with a copper resistance gene chromosomal gene locus in E. coli. After repeated streak isolation of the strain you resequenced the copper resistance gene and noticed that the gene was reversed with respect to the promoter. Do you expect this mutant to be resistant or sensitive to copper? Why? What kind of mutation is this? 7) You are studying mutation rates of the antibiotic rifampicin in E. coli. You carried out the fluctuation test and here are the results. The final cell amount in each culture was about 108. Calculate the mutation rate for rifampicin. Culture # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Rifampicin Resistant colonies/plate 1 5 0 20 0 50 0 0 0 100