Alg 2 1st 9 Weeks
advertisement

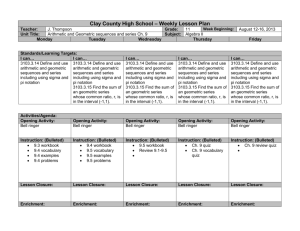
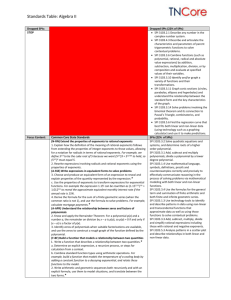
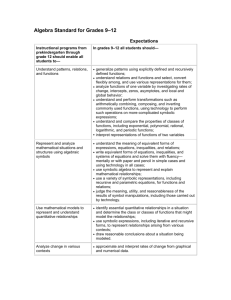
Recurring Themes Throughout the Course CLE: CLE 3103.1.1 Use mathematical language, symbols, definitions, proofs and counterexamples correctly and precisely in mathematical reasoning. CLE 3103.1.2 Apply and adapt a variety of appropriate strategies to problem solving, including testing cases, estimation, and then checking induced errors and the reasonableness of the solution. CLE 3103.1.3 Develop inductive and deductive reasoning to independently make and evaluate mathematical arguments and construct appropriate proofs; include various types of reasoning, logic, and intuition. CLE 3103.1.4 Move flexibly between multiple representations (contextual, physical, written, verbal, iconic/pictorial, graphical, tabular, and symbolic), to solve problems, to model mathematical ideas, and to communicate solution strategies. CLE 3103.1.5 Recognize and use mathematical ideas and processes that arise in different settings, with an emphasis on formulating a problem in mathematical terms, interpreting the solutions, mathematical ideas, and communication. CLE 3103.1.6 Employ reading and writing to recognize the major themes of mathematical processes, the historical development of mathematics, and the connections between mathematics and the real world. CLE 3103.1.7 Use technologies appropriately to develop understanding of abstract mathematical ideas, to facilitate problem solving, and to produce accurate and reliable models. CLE 3103.2.4 Understand the capabilities and limitations of technology when performing operations, graphing, and solving equations involving complex numbers. Checks for Understanding 3103.1.5 Determine the accuracy and reliability of a mathematical model. 3103.1.9 Translate the syntax of technology to appropriate mathematical notation for nonlinear and transcendental functions. 3103.1.10 Interpret the results of mathematical modeling in various contexts to answer questions. 3103.1.1 Create and analyze scatter-plots of non-linear and transcendental functions. 3103.1.2 Compare and contrast sampling techniques and identify the best technique for a given situation. 1 State Performance Indicators SPI 3103.1.4 Use mathematical language, symbols, definitions, proofs and counterexamples correctly and precisely to effectively communicate reasoning in the process of solving problems via mathematical modeling with both linear and non-linear functions. SPI 3103.1.1 Move flexibly between multiple representations (contextual, physical, written, verbal, conic/pictorial, graphical, tabular, and symbolic) of nonlinear and transcendental functions to solve problems, to model mathematical ideas, and to communicate solution strategies. SPI 3103.1.2 Recognize and describe errors in data collection and analysis as well as Assessments Instructional Resources Connections A classroom set of TI84s or TI-spires. School-to-career Masters http://www.algebra2.com/careers or resource kit kutasoftware.com has several worksheets for various topics Science and Mathematics Lab Manual (Glencoe Resource Kit) http://www.glencoe.com/se c/math/algebra/algebra2/al gebra2_05/extra_examples /index.php4/tn http://www.regentsprep.or g/Regents/math/ALGEBR A/mathALGEBRA.htm#Equations _and_Inequalities__ http://education.ti.com/edu cationportal/activityexchan ge/activity_list.do?cid=us http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/007873830x/ 3103.1.4 Identify the weaknesses of calculators and other technologies in representing nonlinear data, such as graphs approaching vertical asymptotes, and use alternative techniques to identify these issues and correctly solve problems. 3103.1.3 Use calculators to identify regression equations for nonlinear data. 3103.1.5 Determine the accuracy and reliability of a mathematical model. 3103.1.9 Translate the syntax of technology to appropriate mathematical notation for nonlinear and transcendental functions. identifying representations of data as being accurate or misleading. SPI 3103.1.3 Use technology tools to identify and describe patterns in data using non-linear and transcendental functions that approximate data as well as using those functions to solve contextual problems. student_view0/chapter7/les son7/personal_tutor.html http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078884829/ student_view0/chapter7/les son1/personal_tutor.html http://www.purplemath.co m/modules/ http://www.onlinemathlear ning.com/unit-circle.html http://teachers.henrico.k12. va.us/math/HCPSAlgebra2 / www.Mathorama.com http://www.fkss.ca/courses /math/PMa12/index.html Online Assessment with instant feedback: http://education.jlab.org/so lquiz/index.html Scavenger Hunt: Tool to find resources, located in each chapter of Glencoe Algebra 2 http://www.glencoe.com/sec/mat h/algebra/algebra2/algebra2_05/p dfs/Algebra2Scavenger.pdf Reading to Learn Mathematics: Vocabulary for each chapter of Glencoe Algebra 2 (activity sheets) Reading & Writing in the Mathematics Classroom (Glencoe Resource Kit) 2 eGlossary-Math http://www.glencoe.com/apps/e Glossary612/landing.php Online Algebra 2 Lessons: http://yourteacher.com/browselessons Teaching Mathematics with Foldables, Dinah Zike Resource CDs in kit: Alge2Pass Tutorials, Electronic Text Book, Worksheets and Enrichment Vocabulary Help: http://mathwords.com CLE 3103.2.4 3103.2.11 Understand the capabilities and limitations of technology. Make estimations without a calculator to detect potential errors. 3 http://calculusapplets.com/graph errors.html Course: Algebra 2 1st Nine Weeks Unit 1: Characteristics of Functions CLE: Curriculum Guide Estimated Time: 4 Weeks CLE 3103.3.2 Understand, analyze, transform and generalize mathematical patterns, relations and functions using properties and various representations. CLE 3103.3.3 Analyze and apply various methods to solve equations, absolute values, inequalities, and systems of equations over complex numbers. CLE 3103.3.5 Use mathematical models involving equations and systems of equations to represent, interpret and analyze quantitative relationships, change in various contexts, and other real-world phenomena. Essential Questions: How do you use the characteristics of each family of functions to distinguish between absolute value, step, piece-wise, linear, or quadratic functions? How would you determine the domain and range of a relation and how do they relate to the relation's inverse? What methods would you use to solve contextual problems involving 2 and 3-variable systems of linear equations and inequalities? Unit Academic Vocabulary: Inverse of a relation, inverse function, piece-wise function, step function Prerequisite Skills: Graph linear equations, solve linear equations Checks for State Understanding Performance Assessments Indicators CLE 3103.3.2 3103.3.3 Determine and graph the inverse of a function with and without technology. 3103.3.4 Analyze the effect of changing various parameters on functions and their graphs. 3103.3.5 Graph piece-wise and step functions. 3103.3.11 Describe and articulate the characteristics and parameters of a parent function. 4 SPI 3103.3.5 Describe the domain and range of functions and articulate restrictions imposed either by the operations or by the contextual situations which the functions represent. SPI 3103.3.10 Identify and/or graph a variety of functions and their translations SPI 3103.3.7 Identify whether a function has an inverse, whether two functions are inverses of each other, and/or explain why their graphs are reflections over the line y = x. Daily formative assessments Unit test School-based common assessments District Benchmark Assessment? Instructional Resources Domain Representations Activity http://illuminations.nctm.org/LessonDetail.aspx?id=L6 21 Graphing Piecewise Functions(Calc): http://www.tc3.edu/instruct/sbrown/ti83/funcpc.htm Function Transformation Activities (Calc): 1. http://education.ti.com/educationportal/activi tyexchange/Activity.do?cid=US&aId=9797 2. http://education.ti.com/educationportal/activi tyexchange/Activity.do?cid=US&aId=11930 Quadratic Function Transformations (Calc): http://education.ti.com/educationportal/activityexchang e/Activity.do?cid=US&aId=9795 How to Find an Inverse (TI) http://education.ti.com/educationportal/activityexchang e/Activity.do?cid=US&aId=8211 Connections Cell Phone Plans (Step Functions) Finance: Graphing Inequalities related to dividend earnings, minimum projections, share values or other related economics topics ACT Standards: Read tables and graphs Manipulate data from graphs Solve real-world problems using first-degree equations Write equations and inequalities that require planning, manipulating, and/or solving Solve simple absolute value inequalities Analyze and draw conclusions based on information from graphs in the coordinate plane Determine when an expression is undefined CLE 3103.3.3 3103.3.8 Solve a three by three system of linear equations algebraically and by using inverse matrices and determinants with and without technology. 3103.3.18 Solve compound inequalities involving disjunction and conjunction and linear inequalities containing absolute values. 3103.3.19 Solve linear programming problems. SPI 3103.3.8 Solve systems of three linear equations in three variables. Escape from the Tomb (Answers the question “When am I ever going to use systems of equations?” http://illuminations.nctm.org/LessonDetail.aspx?id=L6 98 SPI 3103.3.9 Graph the solution set of two or three linear or quadratic inequalities. Talk or Text (Application of Systems) http://illuminations.nctm.org/LessonDetail.aspx?id=L7 80 Biology/Chemistry applications with Linear Programming Matrix Operations, Solving (Not Cramer's, Calc): http://mathbits.com/mathbits/tisection/precalculus/matr ices.htm Cramer's Rule: http://www.purplemath.com/modules/cramers.htm Linear Programming: http://teachers.henrico.k12.va.us/math/hcpsalgebra2/36.htm Systems of Linear Equations: http://teachers.henrico.k12.va.us/math/hcpsalgebra2/37.htm Linear Programming—Dirt Bike Dilemma http://illuminations.nctm.org/LessonDetail.aspx?id=L6 85 CLE 3103.3.5 SPI 3103.3.12 Interpret graphs that depict realworld phenomena. SPI 3103.3.13 Solve contextual problems using quadratic, rational, radical and exponential equations, finite geometric series or systems of equations. 5 Contextual Quadratic Project: http://www.glencoe.com/sec/math/algebra/algebra2/alg ebra2_05/webquest/unit2/webquest.php4/ny Social Studies Course: Algebra 2 1st Nine Weeks Unit 2: Algebraic Operations CLE: Curriculum Guide Estimated Time: 4 Weeks CLE 3103.3.1 Understand and apply properties of rational exponents and perform basic operations to simplify algebraic expressions. CLE 3103.3.5 Use mathematical models involving equations and systems of equations to represent, interpret and analyze quantitative relationships, change in various contexts, and other real-world phenomena. Essential Questions: How would you determine that a polynomial has been completely factored? How do you properly simplify fractions that include radicals? Unit Vocabulary: complete the square, rational function Prerequisite Skills: operations on rational numbers, properties of exponents, factor polynomials Checks for State Understanding Performance Assessments Instructional Resources Indicators CLE 3103.3.1 3103.3.1 Perform operations on algebraic expressions and justify the procedures. 3103.3.21 Factor polynomials using a variety of methods including the factor theorem, synthetic division, long division, sums and differences of cubes, and grouping. 6 SPI 3103.3.1 Add, subtract and multiply polynomials; divide a polynomial by a lower degree polynomial. SPI 3103.3.3 Add, subtract, multiply, divide and simplify rational expressions including those with rational and negative exponents. Daily formative assessments Polynomial operations: http://teachers.henrico.k12.va.us/math/hcpsal gebra2/5-1.htm Unit test Polynomial Modeling with Algebra Tiles School-based common assessments District Benchmark Assessment? Use graphing calculator to compare factored and un-factored forms to check for accuracy Factoring/Multiplying Polynomials Activity/Game http://www.regentsprep.org/Regents/math/A LGEBRA/AV3/GridPoly.htm Connections Cost Analyst Career Connection: Production Costs and Factors Medicine: Estimating populations during epidemics with equations Business Entertainment ACT Standards: Find and use the least common multiple Work with numerical factors Work with scientific notation Work with squares and square roots of numbers Work with problems involving positive integer exponents Work with cubes and cube roots of numbers Determine when an expression is undefined Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials Draw conclusions based on number concepts, algebraic properties, and/or relationships between expressions and CLE 3103.3.5 3103.3.6 Simplify expressions and solve equations containing radicals. 7 SPI 3103.3.12 Interpret graphs that depict real-world phenomena. Interpreting Graphs (with or without Tech): http://www.glencoe.com/sec/math/algebra/al gebra2/algebra2_05/usa_today/index.php4/n y numbers Write expressions that require planning and/or manipulating to accurately model a situation Economics Social Studies