5 Components of Comms
advertisement
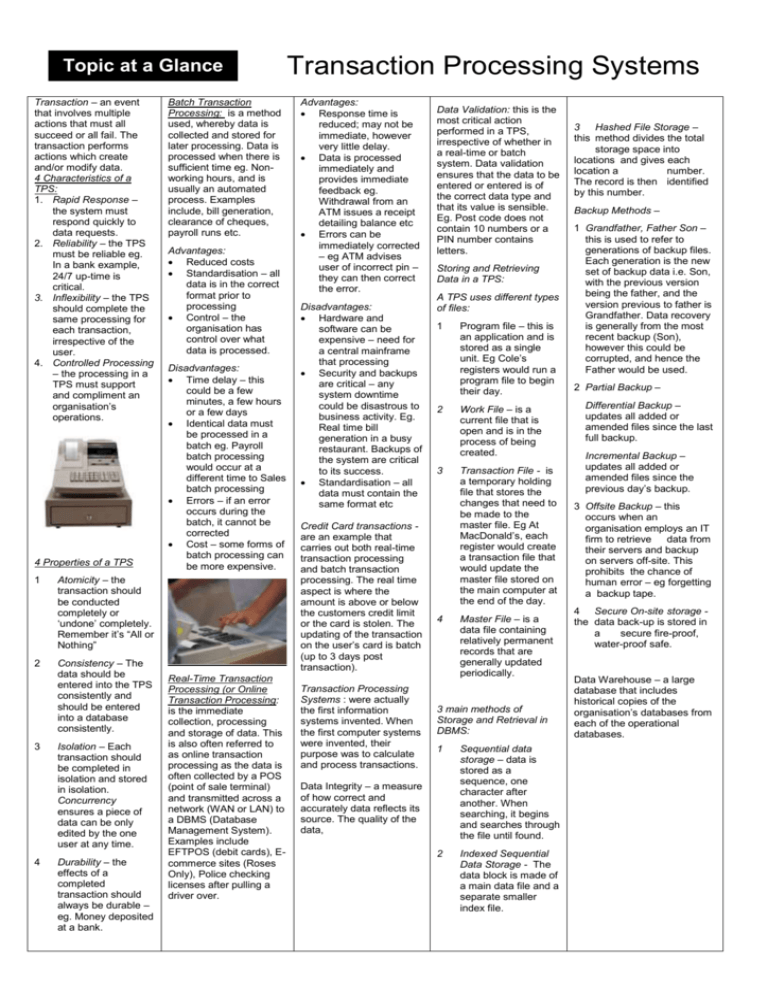
Topic at a Glance Transaction – an event that involves multiple actions that must all succeed or all fail. The transaction performs actions which create and/or modify data. 4 Characteristics of a TPS: 1. Rapid Response – the system must respond quickly to data requests. 2. Reliability – the TPS must be reliable eg. In a bank example, 24/7 up-time is critical. 3. Inflexibility – the TPS should complete the same processing for each transaction, irrespective of the user. 4. Controlled Processing – the processing in a TPS must support and compliment an organisation’s operations. 4 Properties of a TPS 1 2 3 4 Batch Transaction Processing: is a method used, whereby data is collected and stored for later processing. Data is processed when there is sufficient time eg. Nonworking hours, and is usually an automated process. Examples include, bill generation, clearance of cheques, payroll runs etc. Advantages: Reduced costs Standardisation – all data is in the correct format prior to processing Control – the organisation has control over what data is processed. Disadvantages: Time delay – this could be a few minutes, a few hours or a few days Identical data must be processed in a batch eg. Payroll batch processing would occur at a different time to Sales batch processing Errors – if an error occurs during the batch, it cannot be corrected Cost – some forms of batch processing can be more expensive. Atomicity – the transaction should be conducted completely or ‘undone’ completely. Remember it’s “All or Nothing” Consistency – The data should be entered into the TPS consistently and should be entered into a database consistently. Isolation – Each transaction should be completed in isolation and stored in isolation. Concurrency ensures a piece of data can be only edited by the one user at any time. Durability – the effects of a completed transaction should always be durable – eg. Money deposited at a bank. Real-Time Transaction Processing (or Online Transaction Processing: is the immediate collection, processing and storage of data. This is also often referred to as online transaction processing as the data is often collected by a POS (point of sale terminal) and transmitted across a network (WAN or LAN) to a DBMS (Database Management System). Examples include EFTPOS (debit cards), Ecommerce sites (Roses Only), Police checking licenses after pulling a driver over. Transaction Processing Systems Advantages: Response time is reduced; may not be immediate, however very little delay. Data is processed immediately and provides immediate feedback eg. Withdrawal from an ATM issues a receipt detailing balance etc Errors can be immediately corrected – eg ATM advises user of incorrect pin – they can then correct the error. Disadvantages: Hardware and software can be expensive – need for a central mainframe that processing Security and backups are critical – any system downtime could be disastrous to business activity. Eg. Real time bill generation in a busy restaurant. Backups of the system are critical to its success. Standardisation – all data must contain the same format etc Credit Card transactions are an example that carries out both real-time transaction processing and batch transaction processing. The real time aspect is where the amount is above or below the customers credit limit or the card is stolen. The updating of the transaction on the user’s card is batch (up to 3 days post transaction). Transaction Processing Systems : were actually the first information systems invented. When the first computer systems were invented, their purpose was to calculate and process transactions. Data Validation: this is the most critical action performed in a TPS, irrespective of whether in a real-time or batch system. Data validation ensures that the data to be entered or entered is of the correct data type and that its value is sensible. Eg. Post code does not contain 10 numbers or a PIN number contains letters. Storing and Retrieving Data in a TPS: A TPS uses different types of files: 1 Program file – this is an application and is stored as a single unit. Eg Cole’s registers would run a program file to begin their day. 2 Work File – is a current file that is open and is in the process of being created. 3 Transaction File - is a temporary holding file that stores the changes that need to be made to the master file. Eg At MacDonald’s, each register would create a transaction file that would update the master file stored on the main computer at the end of the day. 4 Master File – is a data file containing relatively permanent records that are generally updated periodically. 3 main methods of Storage and Retrieval in DBMS: 1 Sequential data storage – data is stored as a sequence, one character after another. When searching, it begins and searches through the file until found. 2 Indexed Sequential Data Storage - The data block is made of a main data file and a separate smaller index file. Data Integrity – a measure of how correct and accurately data reflects its source. The quality of the data, 3 Hashed File Storage – this method divides the total storage space into locations and gives each location a number. The record is then identified by this number. Backup Methods – 1 Grandfather, Father Son – this is used to refer to generations of backup files. Each generation is the new set of backup data i.e. Son, with the previous version being the father, and the version previous to father is Grandfather. Data recovery is generally from the most recent backup (Son), however this could be corrupted, and hence the Father would be used. 2 Partial Backup – Differential Backup – updates all added or amended files since the last full backup. Incremental Backup – updates all added or amended files since the previous day’s backup. 3 Offsite Backup – this occurs when an organisation employs an IT firm to retrieve data from their servers and backup on servers off-site. This prohibits the chance of human error – eg forgetting a backup tape. 4 Secure On-site storage the data back-up is stored in a secure fire-proof, water-proof safe. Data Warehouse – a large database that includes historical copies of the organisation’s databases from each of the operational databases.