Lesson Plan
Section 3 Curved Mirrors
PACING
Regular Schedule:
Block Schedule:
with lab(s): N/A
with lab(s): N/A
without lab(s): 2 days
without lab(s): 1 day
OBJECTIVES
1. Calculate distances and focal lengths using the mirror equation for concave and
convex spherical mirrors.
2. Draw ray diagrams to find the image distance and magnification for concave and
convex spherical mirrors.
3. Distinguish between real and virtual images.
4. Describe how parabolic mirrors differ from spherical mirrors.
NATIONAL SCIENCE EDUCATION STANDARDS
UCP 1: Systems, order, and organization
UCP 2: Evidence, models, and explanation
UCP 3: Change, consistency, and measurements
UCP 4: Evolution and equilibrium
UCP 5: Form and function
SAI 1:
Abilities to do scientific inquiry
SAI 2:
Understanding about scientific inquiry
ST 1:
Abilities of technological design
ST 2:
Understanding about science and technology
HNS 1: Science as a human endeavor
FOCUS (5 minutes)
__ Overview Review the objectives listed in the Student Edition. (GENERAL)
MOTIVATE (5 minutes)
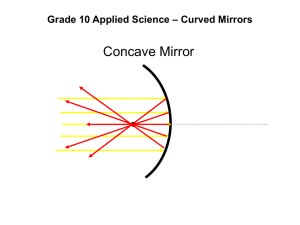
__ Demonstration, Image Formed by a Concave Mirror, TE This demonstration uses
flexible polyester film with reflective coating to show that changing the curvature of a
concave mirror produces different images. (GENERAL)
KEY SE = Student Edition TE = Teacher Edition ANC = Ancillary Workbook OSP = One-Stop Planner
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Physics
1
Chapter 13
Lesson Plan
__ Visual Strategy, Figure 11, TE Students compare the photo to the drawing and discuss
what each of the parts represents. (GENERAL)
TEACH (70 minutes)
__ PowerPoint® Resources Use the customizable presentation to help students master the
concepts in this section. (GENERAL)
__ Transparency 64, Image Formation by a Concave Spherical Mirror This
transparency illustrates that the rays from an object converge to form an image in front of
a concave mirror.
__ Transparency 65, Images Created by Concave Mirrors This transparency shows how
concave mirrors create images in different configurations.
__ Transparency 66, Image Formation by a Convex Spherical Mirror This transparency
illustrates how a virtual image is formed by a convex mirror.
__ Transparency 67, Spherical Aberration and Parabolic Mirrors This transparency
illustrates why spherical aberration occurs and how spherical aberration is avoided in
parabolic mirrors.
__ Transparency Master 46A, Sign Conventions and Rules for Drawing Reference Rays
This transparency master summarizes the sign conventions and rules for drawing reference
rays.
__ Transparency Master 47A, Sign Conventions for Mirrors This transparency master
summarizes the sign conventions for all mirrors.
__ Quick Lab, Curved Mirrors, SE Students observe the reflection of a pencil in both sides
of a spoon. (GENERAL)
__ Demonstration, Focal Point of a Concave Mirror, TE This demonstration uses a light
source, ray filter, concave mirror, and white paper to show that rays parallel to the
principle axis are reflected through the focal point. (GENERAL)
__ Demonstration, Beams Reflected from a Concave Mirror, TE This demonstration uses
a light source, ray filter, and concave mirror to demonstrate the formation of a virtual
image. (BASIC)
__ Sample Set B, Imaging with Concave Mirrors, SE This sample and practice problem
set covers imaging with concave mirrors. (ADVANCED)
__ Classroom Practice, Imaging with Concave Mirrors, TE Use these problems as a
teamwork exercise or for demonstration at the board or on an overhead projector.
(GENERAL)
__ Demonstration, Convex Mirror, TE This demonstration helps students see that parallel
beams reflected by convex mirrors are diverging. (BASIC)
__ Visual Strategy, Table 5, TE Students answer questions about the signs of different
symbols as applied to images formed by convex and concave mirrors. (BASIC)
__ Sample Set C, Convex Mirrors, SE This sample and practice problem set covers convex
mirrors. (GENERAL)
KEY SE = Student Edition TE = Teacher Edition ANC = Ancillary Workbook OSP = One-Stop Planner
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Physics
2
Chapter 13
Lesson Plan
__ Classroom Practice, Convex Mirrors, TE Use these problems as a teamwork exercise
or for demonstration at the board or on an overhead projector. (GENERAL)
__ Visual Strategy, Figure 14, TE Students discuss how the angle of incidence varies when
the incoming ray is farther away from the principal axis of a spherical mirror.
(ADVANCED)
CLOSE (10 minutes)
__ Section Review, SE Students answer review questions, critical-thinking questions, and
interpreting-graphics questions that assess their understanding of the section objectives.
(GENERAL)
__ Study Guide, Curved Mirrors, ANC Use this worksheet to review the main concepts
presented in the section. (GENERAL)
__ Section Quiz, ANC Use this quiz to assess students' understanding of the section.
(BASIC)
OTHER RESOURCE OPTIONS
__ Holt Online Learning Students can access interactive problem-solving help and active
visual concept development with the Holt Physics Online Edition available at
go.hrw.com.
__ Interactive Tutor, Module 14, Reflection This interactive activity gives students a fun
way to extend their knowledge of this physics concept and to further develop their
problem-solving skills. (GENERAL)
__ Interactive Tutor, Module 14, Worksheet This worksheet assesses students’
comprehension of the concepts covered in the corresponding CD-ROM activity.
(GENERAL)
__ Problem Workbook, Sample Set B: Imaging with Concave Mirrors, ANC This
worksheet provides an additional example problem and several practice problems that
cover imaging with concave mirrors. (GENERAL)
__ Problem Bank, Sample Set B: Imaging with Concave Mirrors, OSP This worksheet
provides a third example problem and several practice problems that cover imaging with
concave mirrors. (GENERAL)
__ Problem Workbook, Sample Set C: Convex Mirrors, ANC This worksheet provides
an additional example problem and several practice problems that cover convex mirrors.
(GENERAL)
__ Problem Bank, Sample Set C: Convex Mirrors, OSP This worksheet provides a third
example problem and several practice problems that cover convex mirrors. (GENERAL)
__ SciLinks, Online Students can visit www.scilinks.org to find internet resources related
to the chapter content.
Topic: Telescopes
SciLinks Code: HF61500
KEY SE = Student Edition TE = Teacher Edition ANC = Ancillary Workbook OSP = One-Stop Planner
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Holt Physics
3
Chapter 13