Botany Webquest
advertisement
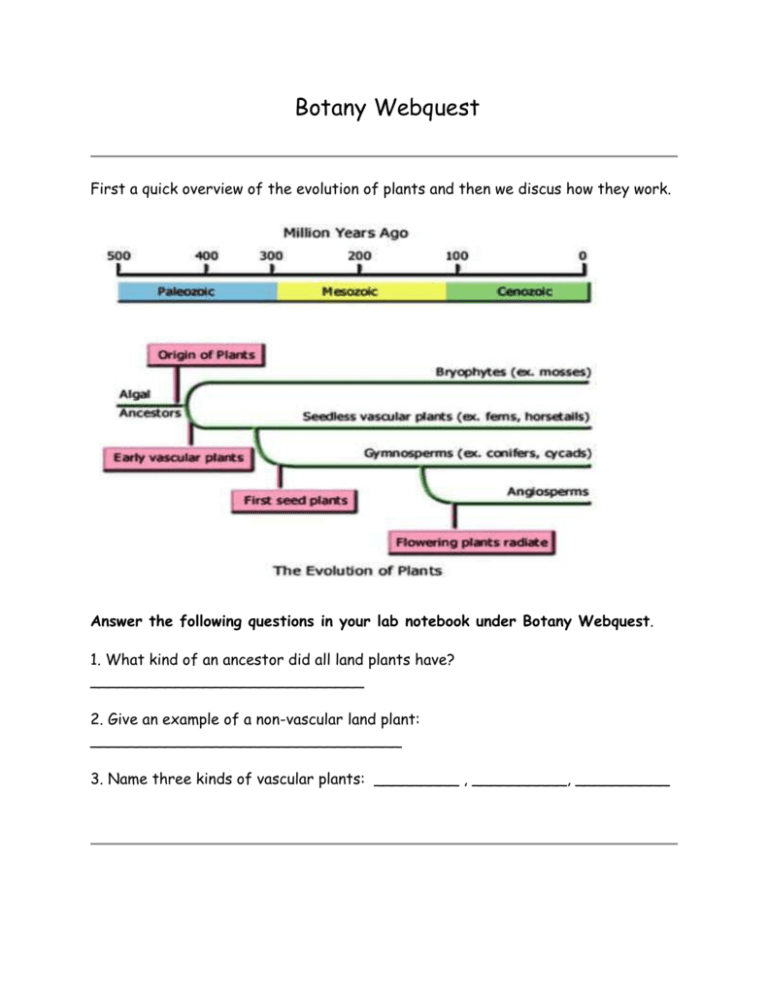
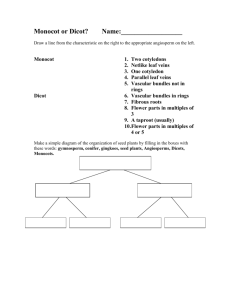
Botany Webquest First a quick overview of the evolution of plants and then we discus how they work. Answer the following questions in your lab notebook under Botany Webquest. 1. What kind of an ancestor did all land plants have? _____________________________ 2. Give an example of a non-vascular land plant: _________________________________ 3. Name three kinds of vascular plants: _________ , __________, __________ All of the more general questions about plant phyla can be found at: http://www.perspective.com/nature/plantae/index.html or within your biology textbook. 4. Botanists still have to get their act together! There are at least four competing classification systems in use. Classification is typically done according to__________________, ___________________ or ___________________ 5. Mosses and Allies belong to the phylum ____________________________ 6. Non-vascular means ____________________________________________ 7. Besides mosses, what are two other nonvascular plants?_______& _______ 8. Find a picture of the life cycle of any plant. Name the plant and tell which part of the life cycle is dominant (gametophyte or sporophyte)? Like all plants, mosses alternate generations. 9. Which generation is dominant? 10. Which generation is parasitic? 11. Ferns and Allies (Pteridophyta and allies) in phylum _______are a huge evolutionary jump over mosses! They have a primitive ________so they can grow much larger. Ferns prefer to grow in ___ light and relatively high ___. 12. Which generation is now dominant? _____________ 13. What chromosome stage is the fern gametophyte in?____________ 14. Conifers and Allies are in the phylum ___________________ Try this website: http://biology.clc.uc.edu/Courses/bio106/gymnospr.htm 15. The gymnosperms add the next level of complexity to plant evolution: they reproduce from _______; however, they are "naked.” Seeds generally contain three parts: ____, _____, and _____. The seed is formed on a pine ______ rather than in the ovary of a flower. Some conifers, such as the Yew and Ginko, produce their seeds inside a _________________ structure. 16. Flowering Dicot Plants are in phylum ______ and class _______. Try this website: http://www.nhptv.org/NATUREWORKS/nwep14f.htm 17. Angiosperms add the final improvement to plant reproduction: they grow their seeds inside ___________which is the base of a ___________. After it is fertilized, the flower falls away and the ovary swells to become ___________. 18. Angiosperms in the class Dicotyledoneae grow two ___________ (cotyledons). 19. In addition, foliage leaves typically have a ______________ originating at the base of the leaf blade, or three or more main veins that diverge from the base. 20. Are most of the planet’s plants dicot or monocot? 21. Monocots start with _____. The main veins of their foliage leaves are usually _________. 22. Monocots provide us with our primary sources of nutrition, such as, ____, ____, and ____. Take a look at this site: http://waynesword.palomar.edu/ww0602.htm#carrion 23. What is a carrion flower? 24. Why do Dutchman’s Pipe flowers trap gnats? 25. What flower smells like fresh dog poop and why? 26. What flower smells like a skunk? 27. What is the scientific name of the corpse flower? 28. What is the largest, worst smelling flower in the world? 29. Choose one of the carnivorous plants found at the following website: http://waynesword.palomar.edu/carnivor.htm. Write a short paragraph that describes how that plant catches insects.