out of class lesson - Danbo International Schools
advertisement
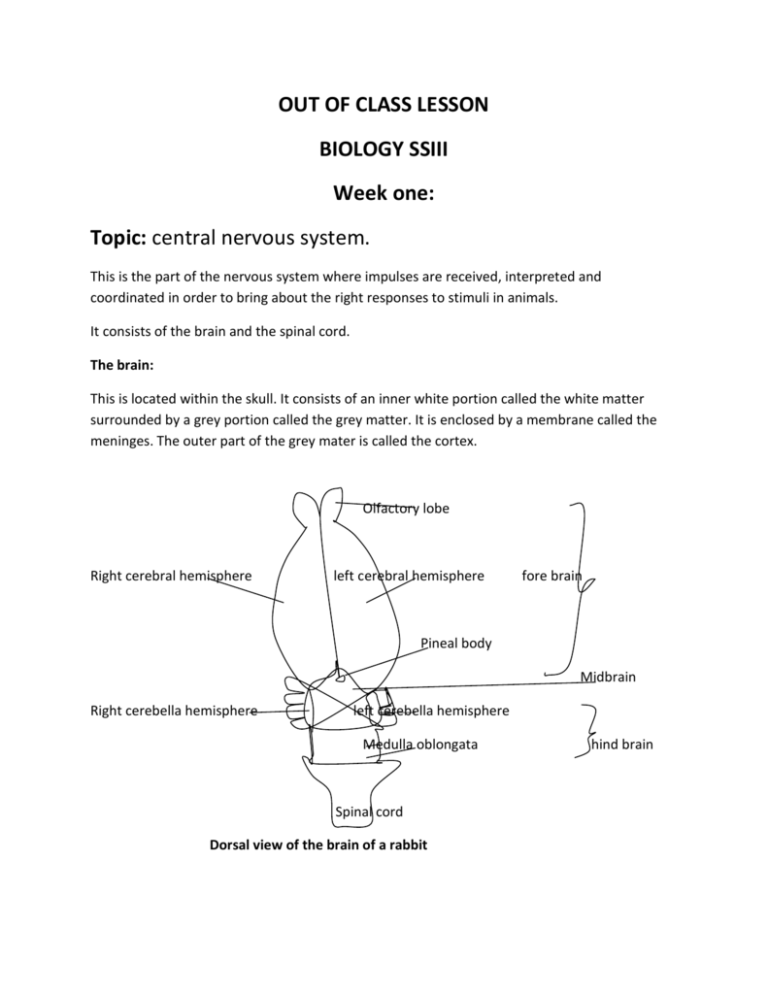
OUT OF CLASS LESSON BIOLOGY SSIII Week one: Topic: central nervous system. This is the part of the nervous system where impulses are received, interpreted and coordinated in order to bring about the right responses to stimuli in animals. It consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The brain: This is located within the skull. It consists of an inner white portion called the white matter surrounded by a grey portion called the grey matter. It is enclosed by a membrane called the meninges. The outer part of the grey mater is called the cortex. Olfactory lobe Right cerebral hemisphere left cerebral hemisphere fore brain Pineal body Midbrain Right cerebella hemisphere left cerebella hemisphere Medulla oblongata Spinal cord Dorsal view of the brain of a rabbit hind brain Above is the diagram of a typical mammalian brain. It can be divided into three major parts: The forebrain; The midbrain; And the hind brain as shown in the diagram above Parts of the brain and their functions: Parts of the mammalian brain Olfactory lobe Cerebrum(consisting of two cerebral hemispheres) Functions Interprets stimuli of smell - Receives, interprets and coordinates sensory impulses from various parts of the body. - Generates and sends motor impulses to muscles and glands for appropriate responses to stimuli. - It is the center of learning, reasoning, memory, imagination and creativity. Thalamus: oval shaped structures attached to - Receives and coordinate sensory lower surface of forebrain. impulses from various parts of the body. - Sends impulses to appropriate parts of the cerebral cortex for responses to different stimuli - Receives motor impulses from the cortex and relay them to appropriate muscles and glands for right responses to stimuli Hypothalamus: part of the forebrain below the - Controls homeostasis example thirst thalamus. and body temperature Cerebellum (consisting of two hemispheres as - Controls body posture and balance in diagram above) Medulla oblongata - Coordinate body reflexes like, heart beat, breathing, salivation and peristalsis Spinal cord: Long cylindrical organ located within the neural canal of the vertebral column, and extending from the base of the brain to the waist region of the body. In cross section, it consists of small narrow canal(spinal canal) surrounded by two layers of nerve tissues; an inner grey matter and an outer white matter enclosed in an envelope of membranous material called meninges. Below is a diagram of the cross section of a spinal cord. Dorsal root white matter grey matter Spinal canal Ventral root meninges Cross section of the spinal cord Parts of the spinal cord and their functions: Parts Spinal canal Functions Contains a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid which supplies the brain and spinal cord with oxygen and nutrients and drains it of waste like CO2. Path through which the sensory nerves enters the spinal cord Path through which motor nerves leaves the spinal cord Dorsal root Ventral root Functions of the spinal cord - Center of coordination of simple reflex actions like blinking of the eyes, knee jerk, etc - Connects the brain with the peripheral nervous system Assignment: 1. A) name two parts each of the i) Mammalian forebrain. ii) Mammalian hindbrain. b) State at least one function of each of the parts listed in 1a) above. c) Describe the function of the mammalian mid brain (use your text/browse) 2. Tabulate three differences and state two similarities between the brain and the spinal cord.







