Fall 2006 – BIO 234 Final Exam Study Guide
advertisement

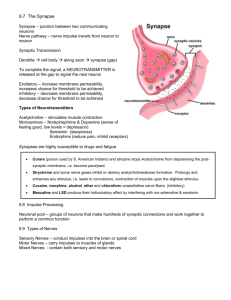
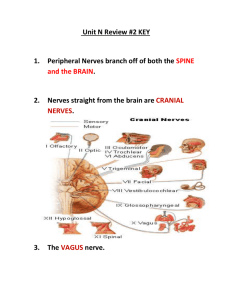
BIO 234 Exam III Study Guide - Spring 2009 Ch 12 o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o CNS vs. PNS – subdivisions of each Types of neurons & variation – (sensory, interneurons, motor; unipolar, bipolar, multipolar) Structure of neuron (dendrites, axon, body, etc) Axonal transport – anterograde, retrograde and axoplasmic flow – describe each. Neuroglial cells – types and function Myelin sheath – how is it formed, nodes of Ranvier o Neurilemma, basal lamina, Synapses – know structure of a synapse axodendritic, axoaxonic, axosomatic know physiology of synaptic transmission Neurotransmitters- cholinergic, adrenergic, GABA – excitatory vs. inhibitory EPSPs and IPSPs. Temporal vs. spatial summation of local potentials. What is presynaptic inhibition? Neuronal circuits – converging, diverging and reverberating circuits What is synaptic plasticity? Mechanisms of signal modification and cessation Ch 13 o o o o o o o o o o Anatomy of spinal cord (cauda equina, conus medularis, cervical enlargement, etc) What level does it extend to? Meninges White (columns) and gray (horns) matter of spinal cord. Know direction of tracts (SPINOreticular vs. ReticuloSPINAL tract) – which is ascending/descending, afferent/efferent?, motor/sensory) Know FUNCTION, origin and destination of gracilis & cuneatus fasciculi (tracts) Nerve anatomy – epineurium, perineurium, endoneurium, axoplasm, dendrites, soma, axon, etc. Review spinal nerve anatomy – DRG, roots, rami Somatic reflexes – stretch (myotatic) withdrawal, crossed-extensor o What is reciprocal inhibition? Know anatomy and function of stretch receptors (muscle spindles) Ch 14 o embryonic origins of adult brain structures o 3 primary vesicles (prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon o 5 secondary (telencephalon, diencephalons, mesencephalon, metencephalon, myelencephalon o Brain – know general anatomy (lobes, hemispheres, gyri, sulci, brainstem, midbrain, cerebellum, etc) o Meninges: dura (2 parts, venous sinuses; falx cerebri, cerebelli, tentorum cerebelli), arachnoids, pia; meningitis o Ventricular system and CSF – functions and pathway of flow of CSF o Chorid plexus, ependymal cells (fct?) o Blood brain and Blood-CSF barriers – structure, location and functions. – CVO’s? o Functional regions of cerebral cortex o o o o o o o Know the location and function of primary and association areas for: Voluntary motor, somatosensory, visual, auditory, vestibular, olfactory, gustatory & visceral sensory areas. Know the 2 language areas – Broca’s and Wernicke’s (what is their fct?) Sensory and motor homunculi– what are they? and where are they located? - (pre and postcentral gyri) – what do the distorted pictures mean? o What are multimodal association areas? (Don’t worry about locations) Cerebral lateralization – in general (left vs. right brain functions) Types of white matter tracts in brain (projection, association, commissural) Basal nuclei – location and General functions Limbic system – what is it? 2 main components. (amygdala & hippocampus) Brainstem o Diencephalon – thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus – know function of each o Midbrain – which CN, other fcts o Pons o Cerebellum o Medulla How do scientists/researchers learn about the functional regions of the brain? Ch 15 o Know the function of the ANS and its 2 subdivisions: sympathetic and parasympathetic NS o Where are nuclei/preganglionic cell bodies of the SympatheticNS located? \Parasympathetic? o What is Autonomic tone? o Explain visceral reflexes o What are the sympathetic chain ganglia? What are 3 possible pathways for sympathetic nerves that enter the chain? - spinal nerve pathway, sympathetic nerve pathway, splanchnic nerve pathway… o White and gray communicating rami. o What are splanchnic nerves? o Which cranial nerves involved w/ parasympathetics?/ Sacral nerves? - Know chart on slide 15 o What ganglia/plexuses do they go to/ what organs/glands do they innervate? Function? o How are their pathways different from sympathetic pathways?/From somatic pathways? (hint: length of preganglionics vs. postganglionics?/Where are the ganglia located) o Sympathetic NS: abdominal aortic plexus …celiac, sup and inf mesenteric ganglia) o What is the enteric nervous system? o Adrenal medulla – autonomic function? o Review neurotransmitters (Ach and NE) and where they are secreted in the ANS. o Ach receptors: muscarinic vs. nicotinic o NE receptors: alpha-adrenergic and beta-adrenergic o Dual innervation – give example of cooperative and antagonistic