Ch. 19
advertisement
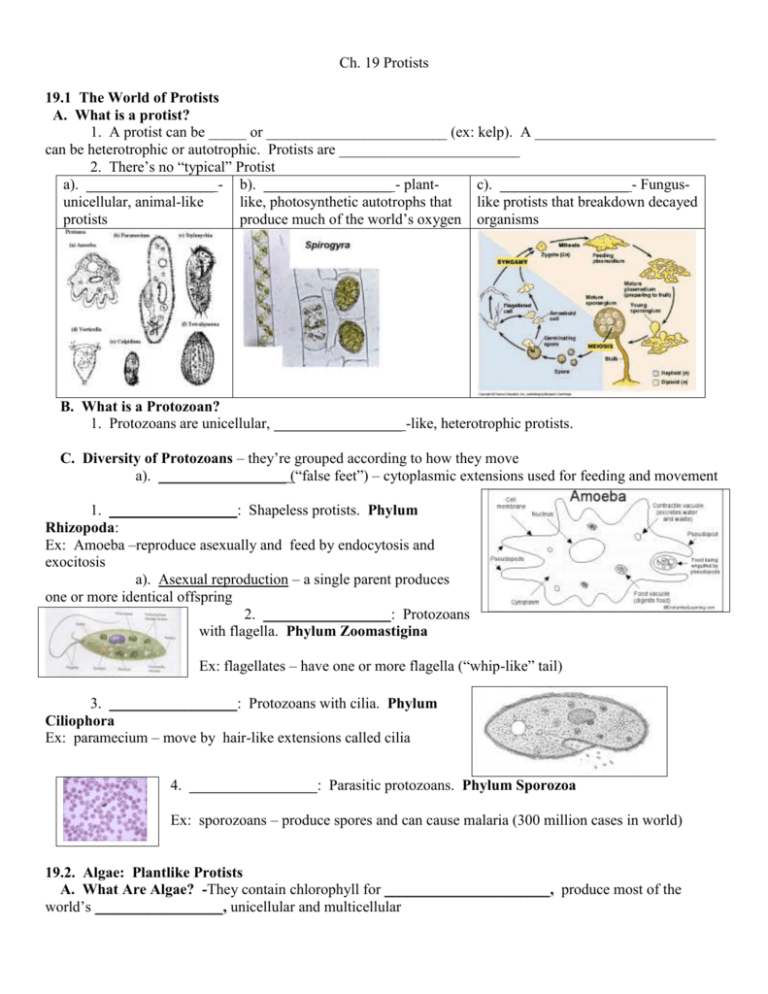
Ch. 19 Protists 19.1 The World of Protists A. What is a protist? 1. A protist can be _____ or ________________________ (ex: kelp). A ________________________ can be heterotrophic or autotrophic. Protists are ________________________ 2. There’s no “typical” Protist a). _________________ - b). _________________ - plantc). _________________ - Fungusunicellular, animal-like like, photosynthetic autotrophs that like protists that breakdown decayed protists produce much of the world’s oxygen organisms B. What is a Protozoan? 1. Protozoans are unicellular, _________________ -like, heterotrophic protists. C. Diversity of Protozoans – they’re grouped according to how they move a). _________________ (“false feet”) – cytoplasmic extensions used for feeding and movement 1. _________________: Shapeless protists. Phylum Rhizopoda: Ex: Amoeba –reproduce asexually and feed by endocytosis and exocitosis a). Asexual reproduction – a single parent produces one or more identical offspring 2. _________________: Protozoans with flagella. Phylum Zoomastigina Ex: flagellates – have one or more flagella (“whip-like” tail) 3. _________________: Protozoans with cilia. Phylum Ciliophora Ex: paramecium – move by hair-like extensions called cilia 4. _________________: Parasitic protozoans. Phylum Sporozoa Ex: sporozoans – produce spores and can cause malaria (300 million cases in world) 19.2. Algae: Plantlike Protists A. What Are Algae? -They contain chlorophyll for ______________________, produce most of the world’s _________________, unicellular and multicellular B. Diversity of Algae.- Six major algae phyla 1. __________________: Autotrophs and heterotrophs: Phylum Euglenophyta a. Contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis but no cell wall b. Can ingest food when light is not found c. Contain a “whip-like” flagella for moving 2. _________________: The golden algae. Phylum Bacillariophyta Ex: Diatoms – autotrophs with hard shells of silica, reproduce asexually then sexually 3. _________________: The spinning algae. Phylum Dinoflagellata Ex: Dinoflagellates – have 2 flagella and cell wall, some produce toxins and cause red tides. 4. _________________ _________________. Phylum Rhodophyta Ex: Red algae – Red, multicellular marine seaweed a. Thallus – seaweed body that lacks roots 5. ________________________. Phylum Phaeophyta Ex: Brown algae – Brown, multicellular kelp 6. _________________________. Phylum Chlorophyta Ex: Green algae - grow in moist areas a. Algae can grow in a _________________ – a group of cells that live together. Ex: Volvox b. Algae can reproduce asexually via _________________ – an individual breaks into pieces and each piece becomes a new individual C. _________________ of _________________ – life cycle in which organisms alternates between haploid (N) and diploid (2N) generations 1. _________________ – haploid stage, makes gametes 2. _________________ – Diploid stage, makes spores 19.3. Slime Molds, Water Molds, and Downy Mildews A. The fungus-like phylums: 1. _________________ – plasmodial slime 2. _________________ – 3. _________________ – molds are animal-like but reproduce with Cellular slime molds water and downy mildew spores (fungi) a. Plasmodium – a mass of keep their haploid cells appear fuzzy and grow in cytoplasm that contains diploid nuclei but no moist places cell walls