G e r s t e i n
S c i e n c e
I n f o r m a t i o n
C e n t r e
Metabolism & Nutrition
Introduction to Health Informatics
Winter 2005
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
Health Informatics
CanMeds 2000
2. Use the Gerstein web site
1
www.library.utoronto.ca
2
3. Case of the week #1: The Thirsty Patient
3
4. MEDLINE® and PubMed
5
5. PubMed
5
6. Ovid MEDLINE
Tips
Structure
Example
6
7. Review Questions
8
Contacts
ask.gerstein@utoronto.ca
Rea Devakos, rea.devakos@utoronto.ca
Carla Hagstrom, carla.hagstrom@utoronto.ca
Sandra Langlands, s.langlands.melvin@utoronto.ca
Gerstein Science Information Centre, University of Toronto
2004. Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto. Do not copy, print, cut or reproduce without the written
permission of the authors. All rights reserved. Use of any material, in whole or in part is expressly forbidden without
prior written consent.
IIN
R
O
D
U
C
N
O
H
E
A
H
O
R
M
A
S
W
E
R
IN
NTTTR
RO
OD
DU
UC
CTTTIIO
IO
ON
NTTTO
OH
HE
EA
ALLLTTTH
HIIN
IN
NFFFO
OR
RM
MA
ATTTIIC
IC
CS
S... W
WIIN
IN
NTTTE
ER
R222000000555
Health Informatics…
…”concerns itself with the cognitive,
information processing and
communication tasks of medical
practice, education and research,
including the information science and
the technology to support these tasks.”
Greenes RA. Shortliffe EH.
JAMA 1990 Feb 23; 263(8):1114-20.
Informatics Skills
A number of the roles and objectives outlined in CanMeds 2000 relate to and
encompass the informatics training and education of the medical graduate:
•As Medical Expert / Skilled Clinical Decision Maker the medical graduate
will be able to “retrieve, analyze, and synthesize relevant and current data and
literature, using information technologies and library resources, in order to help
solve a clinical problem.”
•As Manager the medical graduate will be able to “apply a broad base of
information to the care of patients in ambulatory care, hospitals and other
health settings.”
•As Health Advocate / Community Resource the medical graduate will be
able to “gather information about a population in order to better serve its needs”
and “utilize best evidence” to participate in community activities directed at
improving health.
•As Scholar the medical graduate will “be able to pose a research question”
and “demonstrate the ability to engage in life-long, self directed learning and
critical inquiry.”
Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada. (1996). Skills for the New Millennium: Report of the Societal
Needs Working Group. CanMEDS2000 Project. [Online] 1996. [cited 2003 Jan 08]; Available from:
URL:http://rcpsc.medical.org/publications/index.php#canmeds
2004. Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto. Do not copy, print, cut or reproduce without the written
permission of the authors. All rights reserved. Use of any material, in whole or in part is expressly forbidden without
prior written consent.
IIN
R
O
D
U
C
N
O
H
E
A
H
O
R
M
A
S
W
E
R
IN
NTTTR
RO
OD
DU
UC
CTTTIIO
IO
ON
NTTTO
OH
HE
EA
ALLLTTTH
HIIN
IN
NFFFO
OR
RM
MA
ATTTIIC
IC
CS
S... W
WIIN
IN
NTTTE
ER
R222000000555
2. Use the Gerstein Web Site
www.library.utoronto.ca/gerstein
1.1 Books and journals
e-journals
Journals
Books
1.3 Science databases
Web of Science
1.4 How-to
1.2 Medical databases
MEDLINE
PubMed
Databases by Subject a-z
Find it on the Internet
Information Guides
2004. Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto. Do not copy, print, cut or reproduce without the written
permission of the authors. All rights reserved. Use of any material, in whole or in part is expressly forbidden without
prior written consent.
3. Case of the Week #1: The Thirsty Patient
A 45 year old woman has a 10 year history of amenorrhea and galactorrhea, and more recently, has
developed headaches and defects in her visual field. She is admitted to the neurosurgery ward for
resection of a tumour.
She underwent uneventful surgery to resect the tumour. Twelve hours post-operatively, the nurse
noted that she was passing large volumes of urine (600 ml/hour). The urine osmolality was 75
mOsm/kg. At this time, the patient was slightly drowsy, recovering from her anesthetic. Although the
woman's pre-operative serum sodium concentration was 140 (normal = 135 - 145 mmol/L), it rose to
150 mmol/L twelve hours post-operatively.
Questions
1.
What structures appear to be involved in leading to this patient’s complaints? Why does the
woman have both amenorrhea and galactorrhea?
2.
Assessment of pre-operative hormone levels in this woman would likely reveal:
Prolactin
LH/FSH response
to GnRH
A)
High
Low
Low
Low
B)
High
Low
High
High
C)
High
Normal
Low
Normal
D)
Normal
High
Low
High
E)
Low
Low
High
Low
Should biochemical tumour markers have been measured in this patient?
3.
LH/FSH GnRH
4.
What is polyuria? What is the differential diagnosis of polyuria? What is the likely cause of
the polyuria in this case? How would you prove the diagnosis?
5.
Predict the changes in ECF and ICF volumes in this patient 12 hours post-operatively.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
ECF
Increased
Increased
Normal
Decreased
Decreased
ICF
Decreased
Increased
Decreased
Increased
Normal
6.
Why did the patient become hypernatremic? (There are two components to the answer!)
7.
If her polyuria did not resolve spontaneously, what would be the best agent for chronic
treatment? What other treatment might this woman require?
Hands on Topics
Question Categories
Gerstein Tools
Pituitary Tumour
Galactorrhea
Amenorrhea
Urine Osmolality
Conditions
Tests
Drug Therapy
e-Books
2004. Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto. Do not copy, print, cut or reproduce without the written
permission of the authors. All rights reserved. Use of any material, in whole or in part is expressly forbidden without
prior written consent.
IIN
R
O
D
U
C
N
O
H
E
A
H
O
R
M
A
S
W
E
R
IN
NTTTR
RO
OD
DU
UC
CTTTIIO
IO
ON
NTTTO
OH
HE
EA
ALLLTTTH
HIIN
IN
NFFFO
OR
RM
MA
ATTTIIC
IC
CS
S... W
WIIN
IN
NTTTE
ER
R222000000555
4. MEDLINE and PubMed
MEDLINE is the premier index to journal articles in clinical and research medicine.
The database contents, citations from over 4,000 journals, are sold to a variety of
interface producers – including Ovid.
PubMed is the National Library of Medicine’s (NLM) interface to MEDLINE with the
following additions:
Out-of-scope citations (e.g., articles on business theory, plate tectonics or
astrophysics) from certain MEDLINE journals
Citations that precede the date that a journal was selected for MEDLINE
indexing
Some additional life science journals that submit full text to
PubMedCentral and receive a qualitative review by NLM.
NCBI's Entrez integrated molecular biology databases. These databases
contain DNA and protein sequences, 3-D protein structure data,
population study data sets, and assemblies of complete genomes
In Process Citations - PREMEDLINE
PubMed's in-process records provide basic citation information and
abstracts before the citations are indexed. New records are added to
PubMed daily and are identified by: the notation: [PubMed - in process].
After indexing, the identifier is removed.
5.
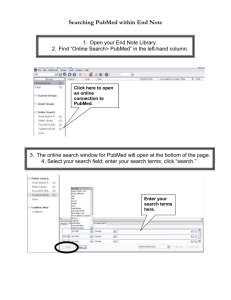
PubMed
Access from Gerstein homepage
Tips
Use natural language, as you would in a search engine – PubMed
translates it into Boolean statements
Play with your wording to alter your search results
Click on DETAILS to discover how your search was translated and modify
if necessary
Use related search, clinical queries and systematic reviews judiciously…
Sophisticated searches may be easier to manipulate in OVID MEDLINE
2004. Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto. Do not copy, print, cut or reproduce without the written
permission of the authors. All rights reserved. Use of any material, in whole or in part is expressly forbidden without
prior written consent.
IIN
R
O
D
U
C
N
O
H
E
A
H
O
R
M
A
S
W
E
R
IN
NTTTR
RO
OD
DU
UC
CTTTIIO
IO
ON
NTTTO
OH
HE
EA
ALLLTTTH
HIIN
IN
NFFFO
OR
RM
MA
ATTTIIC
IC
CS
S... W
WIIN
IN
NTTTE
ER
R222000000555
6. Ovid MEDLINE
Access from the Gerstein homepage
Tips
Write a search question which describes your topic
Identify main concepts
Note synonyms, alternate spelling, truncation for each concept.
Search each concept separately
Where possible, choose terms from database thesaurus, i.e. MeSH (Medical
Subject Headings)
Consider explodes
Use subheadings cautiously
Link concepts with Boolean operators
Consider adding limits at the end of your search
Structure
Databases use controlled language or natural language to index data. Medical
indexing terms , also called MeSH headings, can be found in the MeSH Subject
Headings field.
Each record is composed of fields, which can be searched individually.
Find information on field codes in OVID’s HELP files:
Example: You can search for an author by entering matthews s:.au. or any
institution with “toronto” in its name by typing toronto.in.
Use Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) to combine search terms or statements
Sample Record
2004. Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto. Do not copy, print, cut or reproduce without the written
permission of the authors. All rights reserved. Use of any material, in whole or in part is expressly forbidden without
prior written consent.
IIN
R
O
D
U
C
N
O
H
E
A
H
O
R
M
A
S
W
E
R
IN
NTTTR
RO
OD
DU
UC
CTTTIIO
IO
ON
NTTTO
OH
HE
EA
ALLLTTTH
HIIN
IN
NFFFO
OR
RM
MA
ATTTIIC
IC
CS
S... W
WIIN
IN
NTTTE
ER
R222000000555
Example:
Search Question:
"What postoperative complications may arise from pituitary tumour surgery?"
Main Concepts:
Pituitary tumour
Complications following surgery
Resulting Search Statement:
Pituitary Neoplasms and
Postoperative Complications
MeSH Subject Headings:
Pituitary Neoplasms
Postoperative Complications
( a ) and
(b)
Limits:
Human
English
Year of Publication
Three Boolean operators:
a AND b
AND
OR
a NOT b
NOT
a OR b
2004. Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto. Do not copy, print, cut or reproduce without the written
permission of the authors. All rights reserved. Use of any material, in whole or in part is expressly forbidden without
prior written consent.
IIN
R
O
D
U
C
N
O
H
E
A
H
O
R
M
A
S
W
E
R
IN
NTTTR
RO
OD
DU
UC
CTTTIIO
IO
ON
NTTTO
OH
HE
EA
ALLLTTTH
HIIN
IN
NFFFO
OR
RM
MA
ATTTIIC
IC
CS
S... W
WIIN
IN
NTTTE
ER
R222000000555
7.
Review Questions
REVIEW
• Each article in MEDLINE has a record composed of
___________ which can be searched separately, if
necessary.
• The subject matter/content of each article in MEDLINE is
described by 10 to 25 _________ terms chosen from the
_________ thesaurus, the controlled vocabulary for the
database.
• When preparing a search strategy first write out a
____________ ______________.
• Where possible, choose search terms from the
__________ thesaurus.
• A Scope Note provides a ______________ for a term
and gives its history as a controlled vocabulary term.
• “When in doubt, explode.” Exploding a subject heading
retrieves results that contain the subject heading in
combination with all of its narrower, more specific terms
indented below it in the hierarchical list of
____________.
• Search the concepts in the strategy _____________ for
maximum flexibility and ease of further strategy revision.
• Apply limits such as english, human or full text as a
____________ step in the search strategy.
2004. Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto. Do not copy, print, cut or reproduce without the written
permission of the authors. All rights reserved. Use of any material, in whole or in part is expressly forbidden without
prior written consent.