EpicenterLocLabAdv09 - Holicong9thGradeScience
advertisement

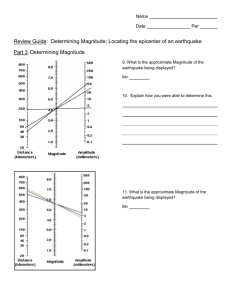
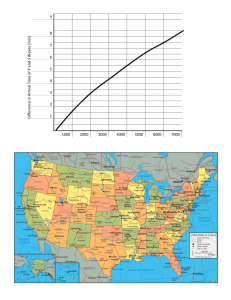
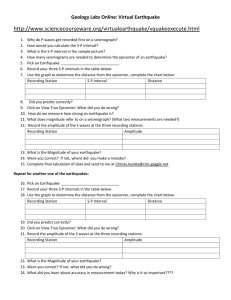
Advanced Ninth Grade Science When an earthquake occurs, different types of waves are generated. These waves carry the energy from the earthquake and travel at different speeds, so their times of arrival at a recording station will differ. As waves travel farther, the difference between the arrival times of the p and s waves increases. This difference in arrival time can tell us how far away the earthquake occurred, but not in which direction. Seismologists can use these properties of certain types of seismic waves to find the epicenter of an earthquake. Standards: 1.4 1.5 2.3 2.5 Write in various modes in all content areas Produce writing of high quality Understand & apply concepts related to measurement & estimation Select and communicate appropriate problem-solving techniques 3.5.10.A Relate Earth features and processes that change the Earth Objective: To determine the location of an earthquake epicenter 1. Use the chart provided to determine the S-P interval or S-P lag time for each of the cities that experienced the earthquake waves. Fill this in on your data chart. 2. Determine how far these distances would be on your compass, using the scale provided. Remember, 1cm=50 km, so to determine how wide to stretch your compass, you would divide your distance by 50 and this would give you’re your compass distance. 3. Draw the circles on your map. Mark an X on the spot where all 3 intersect. This is the epicenter. Label it with the letter A. 4. Repeat steps 1-4, finding the epicenters for data B on the same map (you may wish to use color pencils to help separate circles for epicenter A from epicenter B. 5. Find the epicenters for C, and D on the 2nd map. Analysis Questions: 1. Which earthquake waves are the first to reach a site affected by the quake? 2. Describe the motion of each type of earthquake wave. 3. Which wave causes the most amount of damage on land? Why? 4. What is the location of the earthquake at epicenter A according to your estimates? 5. What problems would you face if you had data from only two recording stations? 6. Suppose an earthquake occurred in San Francisco. What would be the difference in arrival time between the p and s waves at Las Vegas? How did you determine this? Conclusion: What is the relationship between S-P intervals and the distance to the epicenter? Describe the triangulation process that you used to determine the epicenter of an earthquake? What information do you have to have to find the epicenter? City Carson City, NV Sacramento, CA Monterey, CA S-P Lag time (seconds) 36 31 46 Distance (km) Distance (cm) Find the location of epicenter B if the stations below report the following data: City Elko, NV S-P Lag time (seconds) 31 Klamath Falls, OR 46 Reno, NV 52 Distance (km) Distance (cm) (D in km/50) Find the location of epicenter C if the stations below report the following data: City Medford, OR S-P Lag time (seconds) 42 Monterey, CA 33 Boise, ID 55 Distance (km) Distance (cm) (D in km/50) Find the location of epicenter D if the stations below report the following data: City Klamath Falls, OR S-P Lag time (seconds) 46 Las Vegas, NV 62 Ely, NV 66 Distance (km) Distance (cm) (D in km/50)