Final Exam Review- Connected Biology Chapter 5 What is the cell
advertisement

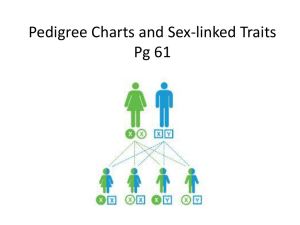
Final Exam Review- Connected Biology Chapter 5 1. What is the cell Cycle? 2. What are the main parts that make up the cell cycle? 3. Draw a diagram of the cell cycle. 4. Define Mitosis. 5. Draw and define interphase. 6. Draw and define prophase. 7. Draw and define metaphase. 8. Draw and define anaphase. 9. Draw and define telophase. 10. Draw and define cytokinesis. Chapter 6 11. Define meiosis. 12. What are the stages of meiosis? 13. What is the definition of a trait? 14. What are three examples of traits? 15. What is the definition of genetics? 16. Who is the father of genetics? 17. What is the definition of purebred? 18. What is a cross? 19. What is the name given to the first generation of plants? 20. What is the name given to the first set of “children”? 21. What are the 2 parts of the law of segregation? 22. What is the definition of gene? 23. What is the definition of allele? 24. How many alleles are there for each gene? 25. What is the definition of homozygous? 26. What is the definition of heterozygous? 27. What is a genotype? 28. What is a phenotype? 29. What is the definition of dominant? 30. What is the definition of recessive? 31. What is going to be the result of a homozygous-homozygous cross? 32. What is going to be the result of a heterozygous- heterozygous cross? 33. What is going to be the result of a heterozygous -homozygous cross? 34. What does the law of independent assortment say? 35. What is the advantage of sexual reproduction? Chapter 7 36. What causes many genetic disorders? 37. What is a carrier? 38. What is the definition of sex-linked genes? 39. Why are males responsible for having boys or girls? 40. Which chromosome has more influence over phenotype? Why is that? 41. What is the definition of incomplete dominance? What is an example of incomplete dominance? 42. What is the definition of codominance? What is an example of codominance? 43. What is the definition of a polygenic trait? What are 2 examples of polygenic traits? 44. Explain how a female can be a carrier for a sex-linked trait. 45. Why are there no male carriers for sex-linked traits? 46. What are the 6 symbols on a pedigree? 47. What is the definition of karyotype? Chapter 8 48. What are nucleotides? 49. What are the three parts of the nucleotides? 50. What is the DNA structure called? 51. What are the nucleotides joined together by? 52. What are the steps in the process of replication? 53. What is the central dogma biology? 54. What is replication? 55. What is transcription? 56. What is translation? 57. Where do they occur? 58. What is the definition of RNA? 59. What are the three ways that RNA and DNA differ? 60. What are the three basic steps in transcription? 61. What are the three types of RNA? 62. Codons are made of how many nitrogen bases? 63. Where are proteins made in the cell? 64. What is the definition of mutation? Chapter 10 65. Define Evolution. 66. Who is considered to be the father of the modern evolutionary theory? 67. Define Natural selection. 68. Define adaptation 69. Explain 6 forms of evidence for evolution. Chapter 11 70. What is a gene pool? 71. What is genetic equilibrium (Hardy Weinberg) and what has to happen for a population to be in equilibrium? 72. Distinguish between convergent and divergent evolution 73. What is a gene pool? 74. What are 5 factors that lead to Evolution 75. Explain the different types of isolation and how they affect populations. Chapter 13 76. Define Ecology 77. Define Ecosystem 78. Define biotic factors. Give 3 examples 79. Define abiotic factors. Give 3 examples