Chapter 4 intro to psy

Chapter 4
1.
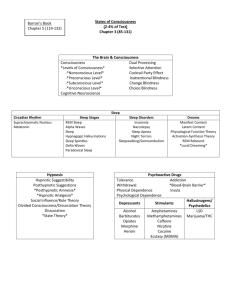
Circadian Rhythm: The pattern of fluctuations in bodily processes that occur regularly each day.
2.
Hypnosis: An altered state of consciousness characteristics by focused attention, deep, relaxation, and heightened susceptibility to suggestion.
3.
REM sleep: The stage of sleep that involves rapid eye movements and that is most closely associated with periods of dreaming.
4.
Stimulants: A drug that activates the nervous system, such as cocaine or nicotine.
5.
Consciousness: A state of awareness of ourselves and of the world around us.
6.
Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep, remaining asleep, or returning to sleep after nighttime awakenings.
7.
Psychoactive drugs: Chemical substances that affect a person’s mental or emotional state.
8.
Hallucinogens: Drugs that alter sensory experiences and produce hallucinations.
9.
Narcolepsy: A disorder characterized by sudden unexplained sleep attacks during the day.
10.
Tolerance: A form of physical habituation to a drug in which increased amounts are needed to achieve the same effect.
11.
Depressants: Drugs, such as alcohol and barbiturates that dampen central nervous system activity.
12.
Latent Content: True underlying meaning of the dream, disguised in the form of dream symbols.
13.
Manifest Content: Refers to events that occur in the dream.
14.
Sleep Apnea: Temporary cessation of breathing during sleep. (causes people to snore because of airways been too narrow)
15.
Opioids: Are narcotics, addictive drugs that have pain-relieving and sleepinducing properties. (morphine, heroin)
16.
Activation-synthesis hypothesis: The proposition that dreams represent the brain’s attempt to make sense of the random discharges of electrical activity that occurs during REM sleep.
17.
Drug dependence: A severe drug-related problem characterized by impaired control over the use of the drug.
18.
Physiological dependence: A state of physical dependence on a drug caused by repeated usage that changes body chemistry.
19.
Biofeedback: A method of learning to control one’s bodily functions by monitoring one’s own brain waves, blood pressure, degree of muscle tension.
20.
Psychological Dependence: A patterns of compulsive or habitual us of a drug to satisfy a psychological need.
21.
Withdrawal Syndrome: A cluster of symptoms associated with abrupt withdrawal from a drug.
22.
Sleepwalking disorder: A sleep disorder characterized by repeated episodes of sleepwalking.
23.
Altered states of consciousness: State of awareness that differ from one’s usual waking state.
24.
Drug Abuse: Maladaptive or dangerous use of a chemical substance.
25.
Lucid dreams: Dreams in which the dreamer is aware that he or she is dreaming.
26.
Daydreaming: A form of consciousness during a waking state in which one’s mind wanders to dreamy thoughts or fantasies.
27.
Narcotics: Addictive drugs that have pain-relieving and sleep inducing properties.
28.
Alcoholism: A Chemical addiction characterized by impaired control over the use of alcohol and physiological dependence on it.
29.
Posthypnotic suggestion: A hypnotist’s suggestion that the subject will respond in a particular way following hypnosis.
30.
Neodissociation theory: A theory of hypnosis based on the belief that hypnosis represents a state of dissociated consciousness.
31.
Hidden Observer: Hilgard’s term for a part of consciousness that remains detached from the hypnotic experience but aware of everything that happens during it.
32.