Problem Set 3
advertisement
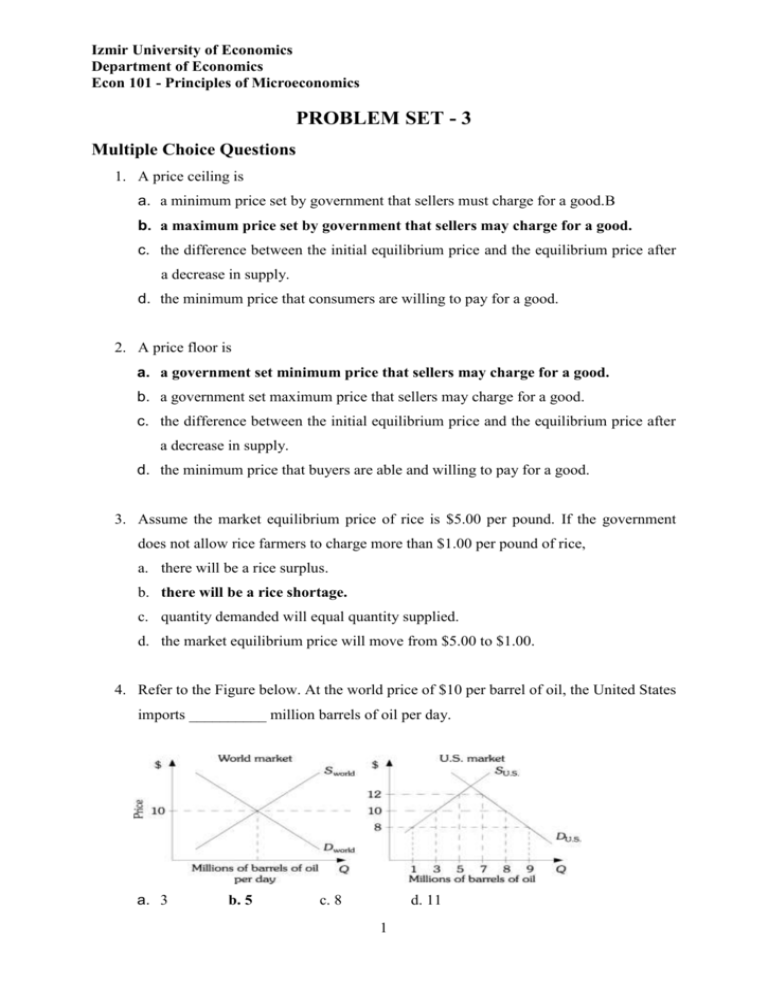
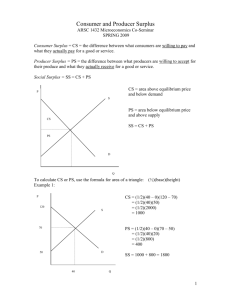
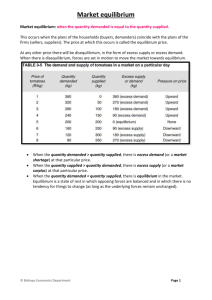
Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics PROBLEM SET - 3 Multiple Choice Questions 1. A price ceiling is a. a minimum price set by government that sellers must charge for a good.B b. a maximum price set by government that sellers may charge for a good. c. the difference between the initial equilibrium price and the equilibrium price after a decrease in supply. d. the minimum price that consumers are willing to pay for a good. 2. A price floor is a. a government set minimum price that sellers may charge for a good. b. a government set maximum price that sellers may charge for a good. c. the difference between the initial equilibrium price and the equilibrium price after a decrease in supply. d. the minimum price that buyers are able and willing to pay for a good. 3. Assume the market equilibrium price of rice is $5.00 per pound. If the government does not allow rice farmers to charge more than $1.00 per pound of rice, a. there will be a rice surplus. b. there will be a rice shortage. c. quantity demanded will equal quantity supplied. d. the market equilibrium price will move from $5.00 to $1.00. 4. Refer to the Figure below. At the world price of $10 per barrel of oil, the United States imports __________ million barrels of oil per day. a. 3 b. 5 c. 8 d. 11 1 Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics 5. The difference between the maximum amount a person is willing to pay for a good and its current market price is known as a. producer surplus. b. profits. c. revealed preferences. d. consumer surplus. 6. You would be willing to pay a maximum of $50 to attend a concert, and you can buy a ticket for $30. Your consumer surplus is a. $10 b. $20 c. $30 d. $50 7. The difference between the minimum amount a firm is willing to accept for a good and its current market price is known as a. the paradox of value. b. profits. c. producer surplus. d. consumer surplus. Refer to the information provided in Figure 1 below to answer the questions that follow. Figure 1 2 Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics 8. Refer to Figure 4.5. Which of the following areas represents consumer surplus? a. A b. B c. C d. E 9. Refer to Figure 4.5. Which of the following areas represents producer surplus? a. A b. B c. C d. E Refer to the information provided in Figure 2 below to answer the questions that follow. Figure 2 10. Refer to Figure 2. Which areas amount to a deadweight loss? a. Areas B+E b. Areas C+D c. Areas A+B d. Areas E+F 11. Refer to Figure 2. Which price maximizes the sum of consumer and producer surplus? a. 1.50 b. 2.50 c. 3.70 d. Any price greater than 3.75 3 Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics Essay Questions 1. Explain how the price system eliminates a shortage and a surplus. A shortage means that quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied. This will lead to upward pressure on price. As price rises, quantity demanded falls and quantity supplied rises. This will continue until quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. A surplus means that quantity demanded is less than quantity supplied. This will lead to downward pressure on price. As price falls, quantity demanded rises and quantity supplied falls. This will continue until quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. 2. List and briefly define some types of non-price rationing systems. (1.) Queuing: Waiting in line as a means of distributing goods and services. (2.) Favored customers: Those who receive special treatment from dealers during situations of excess demand. (3.) Rationing coupons: Tickets or coupons that entitle individuals to purchase a certain amount of a given product per month. 4