Transformations (The Parent Trap) Lesson Plan
advertisement

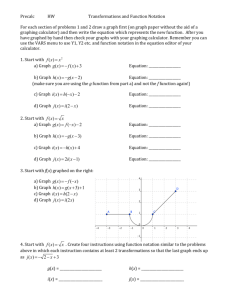
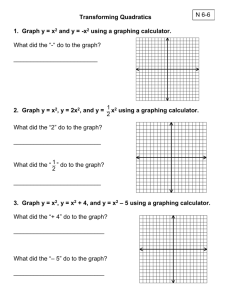
Project AMP Dr. Antonio R. Quesada – Director, Project AMP The Parent Trap The graphs are twins, but not identical, what’s the difference? What transformed two similar objects into two different looks? Lesson Summary In this lesson, students will start by graphing a simple exponential function by using a table. In the graphs that follow, students will be graphing more exponential functions with various transformations. The students will be asked to analyze the graph and make conjectures on what they think happens to the graph with alterations to the parent function. The students will be using a graphing calculator to check their graphs and their hypothesis on other parent functions and their transformations. To conclude the inquiry lesson, students will be given a parent function and a transformed graph and be asked to write the equation of the graph. As a challenge, students will be asked to graph will multiple transformations. As an extension to this activity, students will be able to generalize transformation rules to use with other functions. Key Words Exponential Function Transformations Project AMP Dr. Antonio R. Quesada – Director, Project AMP Graphing Background Knowledge Students will have knowledge of the following: Graphing exponential functions using a table Using a graphing calculator to graph functions Ohio Standards Benchmarks Geometry and Spatial Sense 8-10: F: Represent and model transformation in a coordinate plane and describe the results. Patterns, Functions and Algebra 8-10: B: Identify and classify functions as linear or nonlinear and contrast their properties using tables, graphs or equations. 8-10: C: Translate information from one representation (words, table, graph or equation) to another representation of a relation or function. Standards Patterns, Functions and Algebra Grade 9: #5: Describe and compare characteristics of the following families of functions: linear, quadratic, and exponential functions; e.g. general shape, number of roots, domain, range, rate of change, maximum or minimum. Grade 11: #11: Describe how a change in the value of a constant in an exponential, logarithmic or radical equation affects the graph of the equation. Learning Objectives Students will use inquiry to determine how changes to a parent function affect its graph. Students will analyze transformed graphs and be able to generate the function that matches the graph given the equation of the parent function. Project AMP Students will use a transformations. Dr. Antonio R. Quesada – Director, Project AMP graphing calculator to test their findings about Learning Goals Students will be able to sketch exponential graphs. Students will be able to sketch exponential graphs based on transformations given to the parent function. Students will be able to analyze transformations in graphs. Students will be able to look at new graphs and develop equations given the equation of the parent graph. Student will be able to generalize transformation rules and apply them to various functions. Materials Pencil Graphing Calculator Activity Sheets Assessment At the end of this lesson, a transformed function will be put on the board. Then students will be asked to sketch and describe the parent function. Then given a parent function students will have to perform various transformations and write the related equations.