BIO-302 Final 2003
advertisement

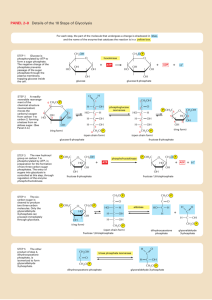
BIO302 Biochemistry II Final Examination, June 6, 2003 Question a) The major energy storage compound of animals is fats (except in muscles). Why would this be advantageous? b) Why don’t plants use fats/oils as their major energy storage compound? Answer: for mobile organisms weight can be a critical actor, and packing the most energy into the least weight is decidedly advantageous. B) for immobile plants, weight is not a critical factor, and it costs more energy to make fat/oil than starch. Question In fatty acid synthesis malonyl-CoA is used as a “condensing group” rather than acetyl-CoA. Suggest a reson for this. Answer: Energy is needed to condense an acetyl group to the growing fatty acid. In theory, such could be done with acetyl;CoA, using ATP. In practice, the ATP is used to convert acetyl-CoA to malonylCoA, the condensation of the acetyl moiety of malonyl-CoA is driven in part of the accompanying decarboxylation and requires no additional energy. Another possible reason is to avoid a metabolic confusing of pathways particularly in uncompartmented prokaryotes. Malonyl-CoA says “synthesis”, acetyl-CoA says “degradation”. Question Match hexokinase and glucokinase with the descriptions from the right column that are appropriate a) hexokinase 1) is found in the liver b) glucokinase 2) requires ATP for reaction 3) is specific for glucose 4) has a broad specificity for hexoses 5) has a high KM value for glucose 6) is inhibited by glucose 6-phosphate b) glucokinase shows sigmoidal kinetics in contrast to other hexoses which obeys Michaelis-Menten kinetics. Is this an advantage? Answer: 1 a, b, 2 a, b, 3 b, 4 a, 5 b, 6 a Question Which of the following conversions take place in a metabolic situation that requires much more NADPH than ribose 5-phosphate, as well as complete oxidation of glucose 6-phosphate to CO2? a) glucose 6-phosphate ribulose 5-phosphate b) ribose 5-phosphate fructose 6-phosphate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate c) fructose 6-phosphate glucose 6-phosphate d) fructose 6-phosphate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate ribose 5-phosphate e) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate pyruvate Answer: a, b, c Question Liver synthesizes fatty acids and lipids for export to other tissues. Would you expect the pentose phosphate pathway to have a low or a high activity in this organ.? Explain your answer. Answer: NADPH is required for reductive biosynthesis. Therefore pentose phosphate pathway is high in the liver. Question Which of the following statements about the hormonal regulation of glycogen synthesis and degradation are correct? a) Insulin increases the capacity of the liver to synthesize glycogen. b) Insulin is secreted in response to low levels of bood glucose. c) Glucagon and epinephrine have opposing effects on glycogen metabolism. d) Glucagon stimulates the breakdown of glycogen, particularly in the liver. e) The effects of all three of the regulating hormones are mediated by cyclic AMP. Answer: a, d Wnite down the open chemical formula for oleic acid (C18:1 cis-9). Answer: CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7CO2H Explain thermogenesis. (How heat is generated to maintain body temperature).