10-6A-Nationalism
advertisement
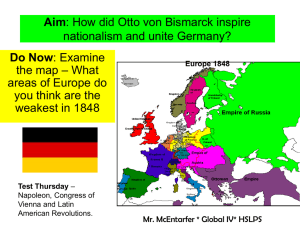
10th Grade Semester One Unit 6a: Nationalism Stage 1: Desired Outcomes Topic / Unit Title: Nationalism * How can nationalism be used as a unifying force? NYS Content Standards Key Idea 1: The study of world history requires an understanding of world cultures and civilizations, including an analysis of important ideas, social and cultural values, beliefs, and traditions. This study also examines the human condition and the connections and interactions of people across time and space and the ways different people view the same event or issue from a variety of perspectives. Key Idea 2: Establishing timeframes, exploring different periodizations, examining themes across time and within cultures, and focusing on important turning points in world history help organize the study of world cultures and civilizations. Key Idea 3: Study of the major social, political, cultural, and religious developments in world history involves learning about the important roles and contributions of individuals and groups. Key Idea 4: The skills of historical analysis include the ability to investigate differing and competing interpretations of the theories of history, hypothesize about why interpretations change over time, explain the importance of historical evidence, and understand the concepts of change and continuity over time. Understandings: Common Core Skills Reading-Social Studies (RH) 2. Determine the main idea of a document 3. Use information/ideas to determine cause and effect 4. Use source information/ideas to differentiate and understand political, social and economic trends 6. Compare and contrast various points of view 8. Identify and analyze evidence Writing (W) 1. Write an argument to support claims 3. Write narratives using effective techniques 4. Produce writing appropriate to task, purpose and audience 9. Draw evidence from informational text Speaking and Listening (SL) 1. Initiate and participate in collaborative discussion 2. Accurately use multiple sources of information 4. Clearly present appropriate information and evidence Language (L) 1. Demonstrate appropriate grammar usage in writing and speaking (sentence complexity) 4. Build vocabulary and expand word choice 5. Understand and interpret figures of speech and nuances in word meanings Essential Questions: Nationalism, Unification, Franco-Prussian War, Otto von Bismarck, “Blood and Iron,” Prussia, German Confederation, Young Italy, Red Shirts, Mazzini, Cavour, Garibaldi Assess the weakness of the German confederation and Italian peninsula divided. Locate Italy and Germany on a map, both before and after unification. Analyze how newly unified Germany and Italy changed the balance of power in Europe. Analyze the goals and methods of Otto von Bismarck and assess how he used nationalism to unify Germany. How was nationalism a driving force in both the unification of Italy and Germany? How did Bismarck use war to unify Germany? How did the methods of strong leaders lead to the unification of both Italy and Germany? How did these leaders use nationalism as the driving force of unification? How did newly unified Germany and Italy change the balance of power in Europe? Stage 2: Assessments and Tasks Common Core Literacy Task Write a one page newspaper article with a date and headline about the future of Europe after the unification of Germany and Italy, including the key terms. Write an “interview” with one of the nationalistic leaders of unification, such as Bismarck, Cavour or Garibaldi, using the key terms, in which they explain their goals for their respective nation. Write an essay about the power of nationalism in the 19th century. Performance Task(s) – Other Evidence Discuss the goals and methods of Otto von Bismarck, Mazzini, Cavour and Garibaldi and analyze the role that nationalism played in each leader’s actions. Create a poster showing the ideas and goals of one of the leaders of Italy’s unification. Discuss the consequences of newly unified Germany and Italy on all of Europe and make predictions for Europe’s future. How will students reflect upon and self-assess their learning? Class room discussion of essential questions. Exit tickets, answering essential questions. Homework assignments. Presentation of posters and newspaper articles (see common core literacy task and performance task) Stage 3: Learning Plan Instructional Activities and Materials (W.H.E.R.E.T.O.) Aim: Was nationalism a positive, unifying force in the 19th century? Identify/define: Mazzini, Cavour, Garibaldi, Risorgimiento, young Italy, Bismarck, blood and iron. Compare and contrast maps of Italy and Germany both before and after unification. Describe and compare and contrast the methods used by the Italian leaders and by Bismarck to unify their countries. Discuss how Cavour and Bismarck used their positions of power in Sardinia and Prussia s points of departure for unification. Assess whether or not Germany and Italy benefited from unification. Evaluate whether the methods and efforts of these nationalist leaders were justified. Evaluate whether nation building can take place without strong/great leaders. Teacher Reflection for Future Planning Teacher Reflection for Future Planning Student responses to class discussions. Exit tickets with feedback, answering the essential questions Exam Homework assignments with feedback for students. Read student work – newspaper articles, essays, posters, etc.