Document
advertisement
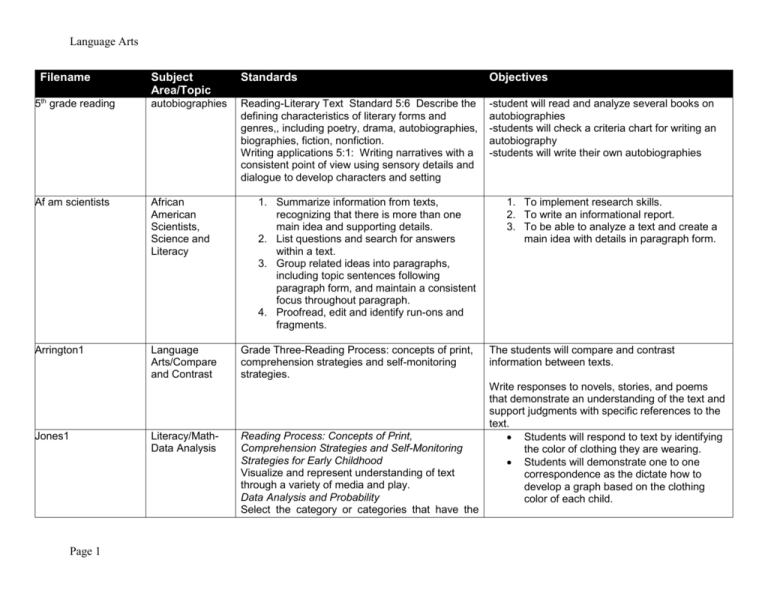
Language Arts Filename Subject Area/Topic Standards Objectives 5th grade reading autobiographies Reading-Literary Text Standard 5:6 Describe the defining characteristics of literary forms and genres,, including poetry, drama, autobiographies, biographies, fiction, nonfiction. Writing applications 5:1: Writing narratives with a consistent point of view using sensory details and dialogue to develop characters and setting -student will read and analyze several books on autobiographies -students will check a criteria chart for writing an autobiography -students will write their own autobiographies Af am scientists African American Scientists, Science and Literacy 1. Summarize information from texts, recognizing that there is more than one main idea and supporting details. 2. List questions and search for answers within a text. 3. Group related ideas into paragraphs, including topic sentences following paragraph form, and maintain a consistent focus throughout paragraph. 4. Proofread, edit and identify run-ons and fragments. 1. To implement research skills. 2. To write an informational report. 3. To be able to analyze a text and create a main idea with details in paragraph form. Arrington1 Language Arts/Compare and Contrast Jones1 Literacy/MathData Analysis Page 1 Grade Three-Reading Process: concepts of print, comprehension strategies and self-monitoring strategies. Reading Process: Concepts of Print, Comprehension Strategies and Self-Monitoring Strategies for Early Childhood Visualize and represent understanding of text through a variety of media and play. Data Analysis and Probability Select the category or categories that have the The students will compare and contrast information between texts. Write responses to novels, stories, and poems that demonstrate an understanding of the text and support judgments with specific references to the text. Students will respond to text by identifying the color of clothing they are wearing. Students will demonstrate one to one correspondence as the dictate how to develop a graph based on the clothing color of each child. Language Arts Filename Subject Area/Topic Architecture Architecture, Social Studies and Literacy Author study Literacy, Author Study Page 2 Standards most or fewest objects in a floor or table graph. 1. Determine the meanings and pronunciations of unknown words by using dictionaries, thesauruses, glossaries, technology, and textual features, such as definitional footnotes or sidebars. 2. Establish and adjust purposes for reading, including to find out, to understand, to interpret to enjoy and to solve problems. 3. Compare the geographic and social characteristics of the river civilizations of the Tigris and Euphrates (Mesopotamia), the Nile (Egypt), the Huang Ho (China) and the Indus (Pakistan) before 1000 B.C., including the location, government, religion, agriculture, and cultural/scientific contributions. 1. Analyze techniques authors use to describe characters, including narrator or other characters’ point of view, characters’ own thoughts, words or actions. 2. Identify the features of setting and explain their importance in texts. 3. Identify the main and minor events of the plot and explain how each incident gives rise to the next. 4. Explain first, third and omniscience points of view and explain how voice affects text. 5. Identify recurring themes, patterns and symbols found in literature from different eras and cultures. 6. Explain defining characteristics of literary forms and genres. 7. Distinguish how an author establishes mood and meaning through word choice, figurative language and syntax. Objectives 1. Students will create a dictionary to use for researching different types of architecture from different periods of history, including, but not limited to, the river civilizations in the Tigris. Euphrates (Mesopotamia), the Nile, the Huang Ho, and the Indus Valley. 2. Students will create a model of a home from one of the above mentioned river civilizations, writing a descriptive paragraph explaining how it relates to the standards. 1. Students will read a minimum of 3 books by the same author, analyzing each text for the standards listed. 2. Students will create a thesis statement that evaluates the author’s writing and includes an understanding of the texts read. 3. Students will submit their publications to literary criticism magazines. Language Arts Filename Grade 3 descriptive paragraph Grade 3 birthday invitation Ecosystems Page 3 Subject Area/Topic Writing Habits and Processes. Follow-up lesson to Grade 3 Social Studies Birthdays Lesson Writing Applications: Grade 3. A follow-up lesson to the previous third grade Social Studies and Writing Habits and Processes lesson. Ecosystems Research, Science and Literacy Standards 8.Estabish a thesis statement for informational writing or a plan for narrative writing. Write in response to an on-demand task. Use resources and reference materials, including dictionaries, to select more effective vocabulary. Write formal and informal letters that include important details and follow correct letter format. 1. Describe the role of producers in the transfer of energy entering ecosystems as sunlight to chemical energy through photosynthesis. 2. Explain how almost all animals’ food can be traced back to plants. 3. Trace the organization of a simple food chain and food webs. 4. Summarize that organisms can only survive in ecosystems in which their needs can be met. 5. Support how an organism’s patterns of behavior are related to the nature of that Objectives Students will write a paragraph describing a birthday celebration which combines traditions and customs from their family and the country which they researched for the previous Social Studies lesson. Students will use a thesaurus to choose effective vocabulary. Students will write an invitation to a birthday party describing the songs, games, food, and other activities will take place. 1. Students will research an ecosystem from a list of ecosystems (pond, lake, march, ocean, prairie, wetland, etc.) and answer a series of research questions, based on the stated standards. 2. Students will compose a research paper and present it to a peer or other grade level student. Language Arts Filename Subject Area/Topic Standards Objectives organism’s ecosystem, including the kinds and numbers of other organisms present, the availability of food and resources, and the changing physical characteristics of the ecosystem. Country research Colonization, Social Studies and Literacy Collaborative lesson plan template 2 literature Literature- Tall Tales Collaborative lesson plan template 2 language arts & science Language Arts / Science 1. Describe the lasting effects of Spanish, French and English colonization in North America including cultural patterns evident today such as language, food, traditions, and architecture. 2. Write informational essays or reports, including research that organize information with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion following common expository structure when appropriate and includes facts, details and examples to illustrate important ideas. 2. Generate a topic for research and develop a plan for gathering information. 3. Compare and contrast important findings and select sources to support central ideas, concepts and themes. Reading Process: Concepts of print Comprehension Strategies 1. Students will research the effects of French, Spanish and English colonization in North and South America, including, but not limited to Canada, Haiti, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Louisiana, Argentina, Venezuela. 2. Students will be asked to analyze how this colonization affected them directly and why. 3. Students will present their findings to families at a party. Writing Application *write a response to story showing interpretation of text. The student will -Summarize main ideas in text with supporting details. -Describe how organisms interact with one another and environment. -Write a friendly letter following correct format. Students answer literal questions to demonstrate Reading applications – Informational text Life science Writing applications Collaborative lesson Page 4 Helga Reading Process/ Comprehension Strategies The student will *summarize important information from text to demonstrate comprehension. Language Arts Filename plan Sheppard lesson 1 Collaborative lesson plan Sheppard 9 Subject Area/Topic Standards Objectives Sheppard/ Reading Comprehension Strategies/ Mouse Mess Sheppard/ Reading/ Comprehension Benchmark C: Identify the central ideas and supporting details of informational text comprehension of text Reading Applications: Literary Text Standard 2.3 Retell or re-enact a story that has been heard. Benchmark A: Compare and contrast plot across literary works. Reading Phonemic Awareness, Word Recognition and Fluency Standard KR1.2 Hear and say the separate phonemes in words, such as identifying the initial consonant sound in a word and blend phonemes to say words. Benchmark A: Use letter-sound correspondence knowledge and structural analysis to decode words. Reading Phonemic Awareness, Word Recognition and Fluency Standard R1.2 Identify and complete rhyming words and patterns. Benchmark A Use letter-sound correspondence knowledge and structural analysis to decode words. Reading Standard R: 1.1 Recognize, say and write common sound of letters Benchmark A. Use letter-sound correspondence knowledge and structural analysis to decode words Reading Standard R3.3 Identify favorite books and stories BenchmarkA: Compare and contrast plot across literary works. Students will tell beginning, middle and end of story. Students will act out the story. Collaborative lesson plan Sheppard 8 Sheppard/Phon emic Awareness/ CVC pattern Collaborative lesson plan Sheppard 7 Sheppard/ Reading/ Rhyme Collaborative lesson plan Sheppard 6 Sheppard/ Phonemic Awareness/Sou nds of Letters Collaborative lesson plan Sheppard 10 Page 5 Sheppard/ Reading/ Literary Text Students will decode CVC pattern words. To recognize rhyming words. Recognize letter sounds y, w, x and z Students will tell what authors and stories they like best and graph the results. Language Arts Filename Subject Area/Topic Standards Objectives Collaborative lesson plan literacy number 2 Collaborative lesson plan literacy 5 Literacy Concepts of Print, Comprehension Strategies, and Self- Monitoring Strategies. Phonemic Awareness, Word Recognition and Fluency Recall information from a story by sequencing pictures and events. Identify and complete rhyming words and patterns. Collaborative lesson plan diamonte poems Literacy Literacy 5-6:R2.1 Comprehend nonfiction, fiction, poetry, and drama using interpretive, critical, and evaluative processes. *** Analyze the qualities of characters and the actions that demonstrate those qualities. *** Determine the credibility of characters in a story, citing evidence to support conclusions about the characters. Collaborative lesson plans acrostic poems Literacy 5-6:R2.1 Comprehend nonfiction, fiction, poetry, and drama using interpretive, critical, and evaluative processes. *** Analyze the qualities of characters and the actions that demonstrate those qualities. *** Determine the credibility of characters in a story, citing evidence to support conclusions about the characters. Collaborative lesson plan 1 Jones2 Page 6 Literacy Phonemic Awareness Literacy/Readin g Comprehension K:R1.1 Recognize, say and write common sounds of letters. Reading Process: Concepts of Print, Comprehension Strategies and Self-Monitoring Strategies Begin to represent text sequences through media and play. K:R1.2 After reading chapter the book entitled, The Chocolate Touch by Patrick Skene Catling as well as reading the Greek myth entitled, King Midas and the Golden Touch students will analyze and compare the actions of the characters. After reading chapter the book entitled, The Chocolate Touch by Patrick Skene Catling as well as reading the Greek myth entitled, King Midas and the Golden Touch students will analyze and compare the character traits of the two characters. To recognize the relationship between letters and sounds. Students will create their own mask of a character from The Mitten. Students will participate in a re-enactment of the story The Mitten. Language Arts Filename Subject Area/Topic Math&altasgr4 Grade 4: Math/Social Studies/Literacy Adaptable grades 3 - 6 Literacy social stdy lesson plan Literacy / Social Studies Lesson plan 9 Writing/Campbel l/Grade 6 Linda Winegar/ Language Arts/Writing/ Write friendly Lesson plan 9 winegar Page 7 Standards Reading Applications: Literary Text Retell or re-enact events from a story through a variety of media and play events. Math: Measurement: Write, solve and verify solutions to multi-step problems involving measurement Social Studies: Geography: Use a linear scale to measure the distance between places on a map. ELA: Research: Identify information found in sources… Social Studies Skills and Methods #2 Locate information in a variety of sources using key words, related articles and cross-references. Reading Process#4 Summarize information in texts, recognizing that there may be several important ideas rather than just one main ides and supporting details. #6 Select, create and use graphic organizers to interpret textual information. Reading applications #1 Use text features, such as chapter titles, headings and subheadings: parts of books including the index and table of contents and online tools to locate information. Writing Processes #8 Group related ideas into paragraphs, including topic sentences following paragraph form, maintain a consistent focus across paragraphs Writing Conventions #11 Use conjunctions Communication #8 Deliver informational presentations 6WA6 Produce informal writings (e.g. journals, notes and poems for various purposes. English Language Arts-1 Writing Benchmark C: Write a friendly letter Indicator 3: Write friendly letters or invitations that follow a simple letter format. Objectives Math: Solve and verify solutions to multi-step problems involving measurement. Social Studies: Use the scale and a ruler to determine distances on a map. ELA: Use an atlas as an information source. Students will listen to the reading of a biography trade book of MLK (in the media center) as a spring-board to using the writing process to generate a research report on a famous black American. Students will write their own poems using different formats Students will fill out a web to organize their ideas. Students will refer to their web as they write. Students write a friendly letter using at least three complete sentences. Language Arts Filename Lesson plan 8 Lesson plan 8 winegar Lesson plan 7 Lesson plan 7 winegar Lesson plan 6w Page 8 Subject Area/Topic letter to a character in a story. Reading/Campb ell/Grade 3 Linda Winegar/ English Language Arts1/Introduction to Alphabetical Order Language Arts/Acrostic Poetry/Campbell /Grade 6 Linda Winegar/ English Language Arts 1 Writing Write a descriptive paragraph about your best friend. Linda Winegar/ English Language Arts1/Writing Poetry Standards Objectives Students will listen as others are reading. 3RA1 Use the table of contents, chapter headings, glossary, index, captions and illustrations to locate information and to comprehend texts. Acquisition of Vocabulary Benchmark E: Use resources to determine the meanings and pronunciation of unknown words. Indicator 9: Determine the meaning of unknown words using a beginner’s dictionary. Students will: -identify text features and their use -select representative features -demonstrate findings in group presentations Listen and discuss the story The Z was Zapped Determine the meaning of the unknown words using a beginner’s dictionary. WA 6 Produce informal writings(e.g. journals, notes and poems) for various purposes. -Students will construct acrostic poems. -Students will determine character traits. =Students will use synonyms. Writing Process Standard Benchmark C: Use organizers to clarify ideas for writing assignments. Benchmark D: Use revision strategies and resources to improve ideas and content, organization, word choices and detail. Establish a purpose for reading Create and use graphic organizers such as Venn diagrams or webs, with teacher assistance, to demonstrate comprehension. Use legible handwriting, spell high frequency words correctly, use strategies to spell unfamiliar words, correct capitalization, use nouns, verbs, and adjectives (descriptive words) Students will listen and discuss numerous stories about friendship Listen and discuss the story The Giving Tree by Shel Silverstein. Write responses to stories that include simple judgments about the text. Create phonetically-spelled written work that can usually be read by the writer and others. Use adjectives (descriptive word) appropriately. Writing Conventions Standard Benchmarks A, B, and C. Indicators 1-7 Writing Applications Standard Benchmark B: Compose writings that convey a clear message and include well chosen details. Indicator 2: Write responses to stories that include simple judgments about the text. Writing Conventions Standard Benchmark D: Use grammatical structures in Language Arts Filename Lesson plan 6 Lesson plan 6 winegar Lesson plan 5 Lesson plan 4 Lesson plan 3 Lesson plan 11 Page 9 Subject Area/Topic Reading/Writing/ Campbell/Grade 6 Language Arts/ Contractions/Wi negar Poetry/Cinquain/ Abi-Ezzi/Grade 5 Reading: Finding and summarizing main idea and supporting details in a paragraph/AbiEzzi/Grade 5 Literacy/Writing/ Science Reading/Campb ell/Grade 6 Standards Objectives written work. Indicator 8: Use nouns, verbs, and adjectives (descriptive words). Communication: Oral and Visual Standard Benchmark D: Speak clearly and at an appropriate pace and volume. Indicator 6: Speak clearly and understandably. WA 6 Produce informal writings(e.g. journals, notes and poems) for various purposes. Speak clearly and understandably. Deliver brief informal presentation Acquisition of Vocabulary Gr.1 To recognize contractions and common abbreviations. Reading and Writing grade 5: R:2.1 Comprehend nonfiction, fiction, poetry and drama using interpretive, critical and evaluative processes. Grade 5:W1.1 Develop writing through a process which includes initial plans and multiple drafts. -Students will be able to define characteristics of cinquain poetry -Students will write a cinquain using a graphic organizer. -Students will edit poems and present to class. -Students will write a winter cinquain. -Students will identify and summarize main idea and supportive details in a paragragh. -Students will delete information not relative to the main idea -Students will rewrite information in their own words. 5:2 Gathering meaning: Students read with accuracy to comprehend a variety of texts Life Science #8 Compare Ohio animals during different seasons describing changes in behavior and body coverings. Writing/Research #4 Identify important information 6RALT6 Explain the defining characteristics of literary forms and genres including poetry, drama, -Students will review the concept of metaphor -Students will apply writing extended metaphors -To research an animal of their choice. -Visit an animal website. -To write an informational report. Students will: -recognize similes and metaphors Language Arts Filename Lesson plan 10w Lesson plan 10 Lesson plan 1 Lesson 5 – letter recognition Jones5 Subject Area/Topic Linda Winegar Literacy/ Introductory Lesson for Sequencing Parts of a Story Writing/Campbel l/Grade 6 Writing/Health/S ocial Studies/Masylk/ Grade 2 Literacy: Phonemic Awareness, Word Recognition, and Fluency: Introducing letter G Literacy/Math/S cience Page 10 Standards Objectives myths, biographies, autobiographies, fiction and nonfiction. English Language Arts-1 Writing Process Benchmark C. Use organizers to clarify ideas for writing assignments Indicator 5: Organize writing to include a beginning, middle, and end. -explain the inferential meaning 6WA2 Write responses to novels, stories, poems and plays that provide an interpretation, critique or reflection and support judgments with specific references to text. Writing Applications #3 Write letters that include information and follow letter format Students will -analyze two poems -identify literary devices -critique literary merit of poems To list ways to keep a community clean. To write a friendly letter. Literacy Standard Grade K: Phonemic Awareness Benchmark A: Use letter-sound correspondence knowledge and structural analysis to decode words. Indicators: 4: Distinguish and name all upper-and lower-case letters. 5: Recognize, say and write common sounds of letters. Reading Applications: Informational, Technical and Persuasive Text Use pictures and illustrations to aid comprehension. Tell the topic of a selection that has been read aloud (e.g., What is the book about?). Patterns, Functions and Algebra Identify, copy, extend and create simple patterns or sequences of sound, shapes and motions in The children will identify the given letter in upper and lower case form. The students will recognize and say the sound of the given letter. The students will identify and write and/or draw two objects that start with the identified letter. The students will listen and discuss a story read by the teacher. The students will write three sentences using a graphic organizer telling about the beginning, middle and end of a story. Students will determine what seeds need to grow as outlined in text. Students will design a garden using pictures of plants. Students will create a pattern in the “garden” with the pictures of plants. Language Arts Filename Subject Area/Topic Jones4 Literacy/Math Jones3 Literacy/Social Studies Mathlitconnectiongr3l Page 11 Grade 3: Standards the context of daily activities and play. Life Sciences Standard Observe and begin to recognize the ways that environments support life by meeting the unique needs of each organism (e.g., plant/soil, birds/air, fish/water) Reading Applications: Informational, Technical and Persuasive Text Gain text information from pictures, photos, simple charts and labels. Research Share findings of information through retelling, media and play. Data Analysis and Probability Data Collection Gather, sort and compare objects by similarities and differences in the context of daily activities and play. Acquisition of Vocabulary Name items in common categories (e.g., animals, food, clothing, , etc.). Writing Applications Dictate stories or produce simple stories using pictures, mock letters or words. Scientific Ways of Knowing Standard Recognize the difference between helpful and harmful actions toward living things. Economics Standard Demonstrate an understanding of the concepts of production, distribution and consumption through play (e.g., food from the farm, to the grocery store) and concrete experiences (e.g., food purchased from the store and cooked at home). Math: Number, Number Sense and Operations: Objectives Students will respond to text. Students will, given a set of animal pictures, sort pictures using a dichotomous key (farm animals or not farm animals). Students will orally state what they know about farm animals. Students will identify common object that could be considered “gifts”. Using the story as a model, students will use pictures to create their own story. Students will demonstrate a minimal understanding of some of the sources for common objects. Math: Model division and translate contextual Language Arts Filename Subject Area/Topic Standards Objectives esson Math/Literacy/ Adaptable grades 2-5 situation involving division into conventional mathematical symbols. ELA: Listen to a story and identify the main idea of division and the details of sharing equally. Mathlitconnectiongr5l esson Grade 5: Math/Literacy/ Adaptable gr. 57 Model, represent and explain division; e.g., sharing equally, repeated subtraction, rectangular arrays and area model. Example: a. translate contextual situations involving division into conventional mathematical symbols. b. explain how a remainder may impact an answer in a realworld situation. ELA: Communication: Identify the main idea, supporting details…. Math: Measurement: Draw circles, and identify and determine relationships among the radius, diameter, center, and circumference. ELA: Literacy: Demonstrate active listening strategies… Winegar lesson plan 13 Language Arts/er/- est endings/ Winegar Winegar lesson plan 11 Language Arts/Beginning, middle and end/Winegar Vocab lesson Literacy Poetry lesson Literacy / Writing Page 12 Acquisition of Vocabulary Gr.1 Benchmark C: Apply structural analysis skills to build and extend vocabulary and to determine word meaning. Indicator 8: Read root words and their inflectional endings. (e.g., walk, walked, walking) Reading Applications-Literary Text Gr.1 Benchmark B: Use supporting details to identify and describe main ideas, characters and setting. Indicator 3: Retell the beginning, middle and ending of a story including its important events. Acquisition of Vocabulary: #2 Use context clues to determine the meaning of synonyms and antonyms #6 Apply Knowledge of prefixes, suffixes and roots and their various inflections to analyze the meanings of words. Writing Processes #1 Generate writing ideas through discussions with others and from printed Math: Determine the diameter and circumference of a given circle using string. Measure string lengths. Identify the relationship (that ratio is an approximation of pi.) ELA: Listen to a story focusing on visual contact and language clues to determine word meaning in a non-conventional way. Students will be able to demonstrate an understanding of the difference between -er and – est endings. The students will listen to a story and then identify and retell the beginning, middle and end. To expose students to root words and affixes and synonyms and antonyms, using library reference materials. The Media Center sponsored poetry reading of Lyrical Poetess Sara Holbrook; then students Language Arts Filename Subject Area/Topic Standards Objectives material. #3 Vary language and style as appropriate to the audience and purpose Writing Applications #5 Produce informal writings (journals, notes and poems) for various purposes. Penpal Subject: Language Arts participated in a writing workshop with her. She explained that her goal was to make poetry an enjoyable experience for children. She also explained that her house was always chaotic while her neighbors seemed to have the perfect house and children. So, her goal and ours was to write a poem with a humorous look at a less than perfect event in a child’s life. 3: W2.1 Students will write in a variety of genres for Focus: Students will learn the different parts of a a variety of purposes. friendly letter, while writing to a “Pen Pal.” writing and autobiographical. Performance Indicator: Write formal and informal letters (e.g., thank you notes, letters of request) that include relevant information and date, proper salutation, body, closing and signature. Mathtechnologygr3les son Grade 3: Math/Technolog y Adaptable grades 3-5 Winegar lesson plan 6 Language Arts/ Contractions/Wi negar Page 13 Purpose: Students will write a friendly letter to a “Pen Pal.” while sharing events through and stories through narrative Math: Measurement: Identify and select Math: Identify temperatures using degrees appropriate units for measuring….d. temperature-- Fahrenheit and compare those temperatures degrees (Fahrenheit or Celsius) Number, Number using symbols <, >, =. Technology ELA: Use a Sense, and Operations: Use mathematical website to gather timely temperature information language and symbols to compare and order; e.g., less than, greater than, at most, at least, <,>,=, ≤, ≥. Technology ELA: Research Acquire information from multiple sources Acquisition of Vocabulary Gr.1 To recognize contractions and common abbreviations.







