DRUGS, BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR Mid
advertisement

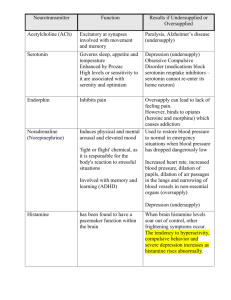
DRUGS AND BEHAVIOR Exam 2 Autumn, 2010. 1. Drug-induced supersensitivity a. is due to a loss of synaptic terminals b. is produced primarily by pharmacological antagonists c. is produced primarily by pharmacological agonists d. is not reversible e. none of the above NAME:__________________ 2. The side effects of the some drugs include increased pulse rate and blurred vision due to dilation of the pupil. These symptoms are due to what pharmacological action of the drugs? a. catecholamine depletion throughout the brain b. blockade of post-ganglionic parasympathetic muscarinic receptors c. antagonism of dopamine and serotonin receptors d. competitive antagonism at post-ganglionic sympathetic receptors e. partial agonism of muscarinic receptors in the autonomic nervous system 3. A few hours after taking a drug that produces euphoria you then become dysphoric (sad). This is called a. rebound effects b. REM depression c. Law of Initial Value d. euphoric coefficient ratio 4. The half-life of 10 mg of zolpidem is 6 hours. If you only take 5 mg of this drug then the half-life is now ____ hours. a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 d. 6 5. The rate-limiting enzyme, and also the first enzyme, in the synthesis of catecholamines is a. tyrosine hydroxylase. b. aromatic acid decarboxylase. c. dopamine beta-hydroxylase. d. DOPA. 6. Which of the following most accurately represents the synthesis of the catecholamines? a. DOPA → tyrosine → dopamine → norepinephrine b. Tyrosine → DOPA → dopamine → norepinephrine c. Tyrosine → dopamine → DOPA → norepinephrine d. DOPA → dopamine → tyrosine → norepinephrine 7. The _______ and _______ dopamine pathways have been implicated in drug abuse and schizophrenia. a. nigrostriatal; mesocortical b. mesocortical; mesolimbic c. mesolimbic; nigrostriatal 1 d. laterodorsal; medial 8. Selective blockade of terminal autoreceptors for DA would lead to a(n) a. decrease in DA release. b. increase in DA release. c. decrease in cell firing. d. increase in cell firing. 9. Hypofrontality is a condition that a. appears in the motor cortex of patients with Parkinson’s disease b. is associated with normal performance of the card sorting task c. is seen in schizophrenic patients only when trying to perform the card sorting task d. is seen in schizophrenic patients both when trying to perform the card sorting task and when they are at rest 10. Depressed people a. have a shortened REM latency, i.e. the time it takes them to enter dream sleep. b. increased total REM sleep c. do not respond well to sleep deprivation d. all of the above 11. The permissive theory of depression and mania states that a. both NE and 5-HT function must be depressed to be manic b. both NE and 5-HT function must be elevated to be manic c. 5-HT is depressed and NE is elevated to be manic d. 5-HT function is elevated and NE is depressed to be depressed 12. Amphetamine or MDMA use is associated with a. constricted pupils b. decreased heart rate c. hyperthermia and tachycardia d. loss of bladder control e. excessive yawning 13. Which of the following drugs is an antagonist at its receptor site? a. amphetamine b. ibogaine c. MDMA, ecstacy d. Scopolamine 14. Hyperarousal in schizophrenics may be due to too many of these neurons in the brainstem. a. dopamine b. norepinephrine c. serotonin d. both dopamine and norepinephrine e. acetylcholine 2 15. The actions of amphetamine include all of the following except: a. a post-synaptic receptor antagonist b. inhibition of MAO c. release of dopamine d. blockade of reuptake of norepinephrine 16. Long-term, i.v. amphetamine use is associated with permanent vascular damage in the brain because. a. amphetamine itself is quite toxic to the brain tissue b. there is an abrupt increase in blood pressure in the small vessels of the brain c. amphetamine induces the release of dopamine, which causes the vascular damage d. this statement is incorrect, amphetamine does not injury the vascular supply of the brain. 17. Which of the following conditions would induce depression? a. withdrawal from amphetamine use b. stopping smoking c. reserpine use d. all of the above 18. Stimulation of the serotonin neuronal autoreceptor, 5HT1A, would cause a. increased serotonergic neuronal activity, similar to that produced by the action of LSD b. decreased neuronal activity, similar to that produced by the action of LSD c. increased production of serotonin d. drowsiness if you were awake at the time 19. The euphoriant properties of cocaine could probably be significantly reduced by taking: a. an amphetamine-like drug b. a norepinephrine receptor agonist c. an acetylcholine receptor antagonist d. a dopamine receptor antagonist 20. The side effects of the some drugs include increased pulse rate and blurred vision due to dilation of the pupil. These symptoms are due to what pharmacological action of the drugs? a. catecholamine depletion throughout the brain b. blockade of post-ganglionic parasympathetic muscarinic receptors c. antagonism of dopamine and serotonin receptors d. competitive antagonism at post-ganglionic sympathetic receptors 21. Which of the following is false about Psilocybin? a. Psilocybin is the active ingredient in the Amanita muscaria mushroom b. Psilocybin use is associated with anti-cholinergic side effects such as dry mouth and dilated pupils. c. The hallucinations associated with psilocybin use are recognized as unreal by the user d. Overdose of psilocybin is associated with panic reactions, tachycardia, mydriasis and hyperthermia. 22. Which of the following statements about LSD is true? a. LSD is extremely potent and is not metabolized by the body 3 b. Tolerance develops very slowly to LSD c. The psychological effects of LSD far outlast its presence in the brain. d. LSD initially increases the firing rate of serotonergic raphe cells e. LSD use is associated with greater sensitivity to pain. 23. The peripheral symptoms due to stimulation of the post-ganglionic sympathetic nervous system would not include: a. Bradycardia b. Tachycardia c. pyrexia d. tremors e. increased repiration 24. After eating a mushroom, you find that now sounds have colors and visual images make sounds. This is known as… a. formication b. obfuscation c. anesthesia d. synesthesia e. eructation 25. Amphetamine or MDMA use is associated with a. constricted pupils b. decreased heart rate c. hyperthermia and tachycardia d. loss of bladder control 26. Which neurotransmitter system is destroyed by abuse of the amphetamine analog 3,4methylenedioxymethamphetamine, MDMA (a.k.a., Ecstasy)? What is the mechanism of this destruction? a. dopamine and serotonin due to formation of free radicals and peroxides b. serotonin and acetylcholine due to formation of free radicals and peroxides c. serotonin only due to depletion of energy stores in the cell body d. norepinephrine only due to formation of free radicals and peroxides 27. Dopamine neurons are clustered within this nucleus. a. locus coeruleus b. raphe c. substantia nigra d. striatum 28. The projection of neurons out of the locus coeruleus into the spinal cord control… a. the autonomic nervous system b. pain signals flowing into the brain c. feeding behaviors d. the experience of euphoria 29. Dopamine is… 4 a. produced from tryptophan b. produced in the cytoplasm and then transported into synaptic vesicles c. produced from norepinephrine inside synaptic vesicles d. required to maintain pain gating from the spinal cord 30. Reserpine produces which of the following? a. slowed heart rate b. increased heart rate c. euphoria d. enhanced pain due to a loss of pain gating 31. Genuine smiles a. are initiated within the motor cortex that controls the facial muscles b. are initiated by the action of acetylcholine neurons in the basal forebrain c. are related to the increased action of norepinephrine neurons d. are initiated by dopamine-dependent activity in the basal ganglia/striatum areas of the brain 32. Euphoria seems to be related to activity in which pathway? a. the substantia nigra input to the forebrain motor areas b. the norepinephrine projection to the nucleus accumbens c. the mesolimbic/mesocortical pathway from the VTA d. the acetylcholine pathway from the basal forebrain 33. Virtually all of the currently prescribed drugs to treat the symptoms of schizophrenia block which neurotransmitter receptor? a. dopamine b. acetylcholine c. norepinephrine d. serotonin 34. PET studies suggest that people with ADHD a. release too little acetylcholine in their frontal cortex b. release too much serotonin in the frontal cortex c. release too much dopamine in the caudate nucleus/striatum area d. release too little dopamine in the caudate nucleus/striatum area 35. Which of the following increase the activity of norepinephrine neurons? a. serotonin b. glutamate c. sleep d. opiates 36. What do mescaline, MDMA, MDA and DOM have in common? a. they all share a structural similarity to the amino acid tyrosine b. they all share a structural similarity to acetylcholine c. they all share a structural similarity to dopamine 5 d. they all have the ability to enhance activity of the parasympathetic nervous system 37. The metabolism of MDMA is saturable, meaning… a. the half-life is constant even though you’ve taken a very large dose b. higher doses are just as toxic as lower doses of the drug c. the metabolism is slower at lower doses of the drug d. the metabolism slows down when higher doses of the drug are taken 38. With regard to the effects of MDMA on the body… a. hyperthermia is due to activation of a mitochondrial uncoupling protein b. the bradycardia can be life-threatening c. caffeine is neuroprotective d. elevated intake of Vitamin E is not relevant 39. The memory problems that MDMA users experience are likely related to… a. impaired function of forebrain acetylcholine neurons b. too little release of dopamine in their hippocampus c. an ongoing sleep disturbance d. elevated body temperatures during the waking hours 40. According to the permissive theory of depression, the reason that a person becomes depressed after ingesting Reserpine is because… a. they have depleted their vesicular stores of norepinephrine and serotonin b. they have inhibited MAO c. they have induced an increase in norepinephrine release d. their dopamine levels are too low 41. The “cheese effect” is due to the ingestion of… a. tryptophan b. tyrosine c. tyramine d. glycine 42. The “cheese effect” is most often seen when drugs… a. inhibit MAO b. release too much dopamine c. block reuptake of serotonin d. prevent the actions of acetylcholinesterase 43. Depressive symptoms can be treated by either preventing the reuptake of serotonin, or… a. blocking dopamine receptors b. blocking serotonin receptors c. blocking acetylcholine receptors d. blocking reuptake of choline 44. With regard to depression, the hormone BDNF… 6 a. is inversely related to the amount exercise one gets b. stress increases the level of this hormone in the hippocampus c. levels increase with anti-depressant therapy d. is responsible for the feelings of guilt and suicide 45. Lithium treatment appears to require the activation of signaling by which of the following neurotransmitters? a. BDNF b. IGF c. insulin d. VGF 46. Cocaine’s ability to act as local anesthetic is due to… a. the blockade of sodium channels b. the blockade of potassium channels c. the slowed release of serotonin on pain gating pathways in the spinal cord d. the increased release of norepinephrine on sensory inputs 47. Why was combining cocaine with wine such an economic success for Angelo Mariani? a. in order to reduce the gastric irritation when consumed b. their combined flavor was enhanced c. the addiction tendency for both drugs was reduced d. in order to decrease the unpleasant aspects of cocaine use 48. Which of the following drugs would likely reduce the euphoriant effects of cocaine? a. the anti-psychotic drug, thorazine b. LSD c. mescaline d. scopolamine 49. Which of following is a rebound symptom of cocaine abuse? a. insomnia b. hyperphagia (eating a lot) c. euphoria d. very boring dreams 50. The principle actions of cocaine are… a. the blockade of acetylcholine muscarinic receptors b. the stimulation of serotonin and dopamine receptors c. the blockade of reuptake of serotonin and dopamine receptors d. the inhibition of serotonin and dopamine catabolism by MAO 51. Taking cocaine leads to stimulation of 5HT1A receptors. Why? a. because it can act directly as an agonist at this serotonin receptor site b. because of the elevation of synaptic levels of serotonin c. due to the long term inhibition of MAO 7 d. due to the indirect actions of dopamine upon this site 52. Chronic exposure to cocaine results in a time-dependent and transient reorganization of a. glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens b. serotonin receptors in the raphe c. dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbens d. dopamine and serotonin receptors in the nucleus accumbens 53. The most active ingredient in Khat is a. scopolamine b. reserpine c. cathinone d. mescaline 54. Asarone acts similar to which of the following drugs? a. scopolamine b. reserpine c. amphetamine and mescaline d. LSD 55. Blocking the voltage-dependent Na+-dependent channels on neurons probably is the reason that Kavin is able to produce which of these effects? a. anxiety b. convulsions c. analgesia d. nightmares 56. Consuming a lot of tryptophan will allow the serotonin neurons in your brain to… a. produce more serotonin, but not necessarily release more serotonin b. produce no more, no less, serotonin than usual c. tryptophan is too water soluble to get across the brain, nothing happens d. reduce the production of dopamine 57. Consuming a diet that contains no tryptophan at all will produce which of the following emotional responses? a. fear b. sadness c. euphoria d. hyperfrontality 58. If you have too few 5HT-1A receptors (i.e. a rather specific birth defect), what emotional symptom might you express? a. heart palpitations and depressed respiration b. sadness with hyperphagia c. euphoria and mania d. anxiety 8