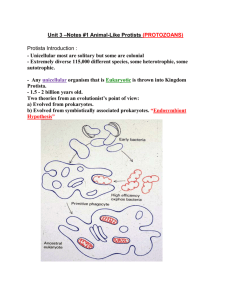
Unsegmented Worms I. 3 Types a. Phylum i. Flatworms ii
advertisement
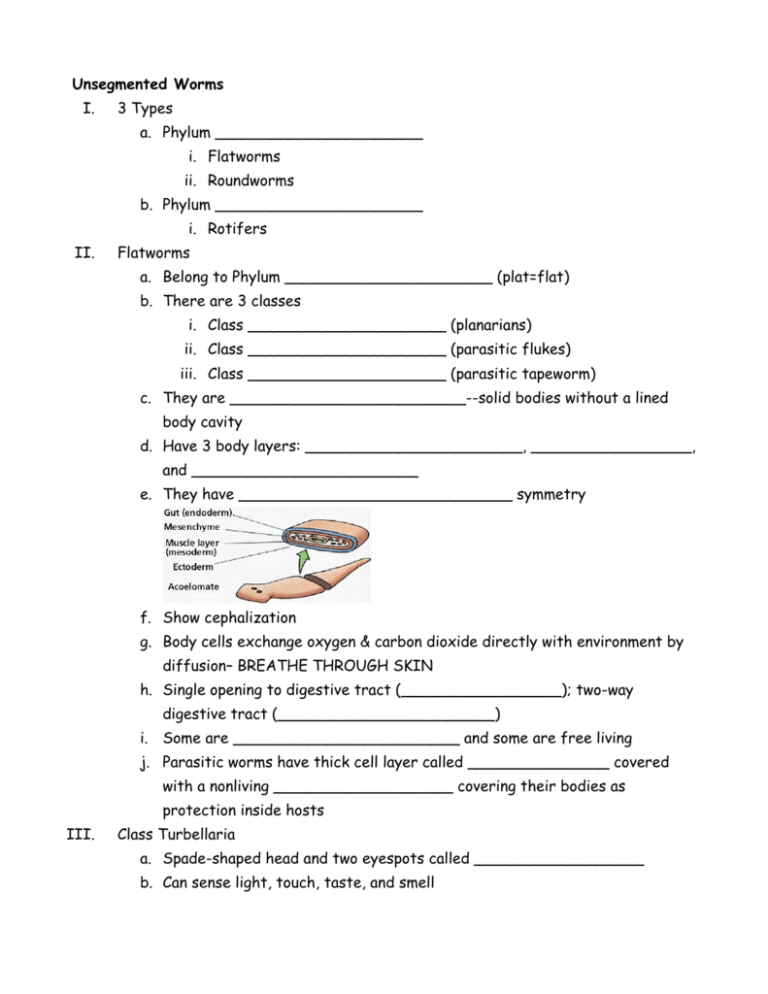
Unsegmented Worms I. 3 Types a. Phylum ______________________ i. Flatworms ii. Roundworms b. Phylum ______________________ i. Rotifers II. Flatworms a. Belong to Phylum ______________________ (plat=flat) b. There are 3 classes i. Class _____________________ (planarians) ii. Class _____________________ (parasitic flukes) iii. Class _____________________ (parasitic tapeworm) c. They are _________________________--solid bodies without a lined body cavity d. Have 3 body layers: _______________________, _________________, and ________________________ e. They have _____________________________ symmetry f. Show cephalization g. Body cells exchange oxygen & carbon dioxide directly with environment by diffusion– BREATHE THROUGH SKIN h. Single opening to digestive tract (_________________); two-way digestive tract (_______________________) i. Some are ________________________ and some are free living j. Parasitic worms have thick cell layer called _______________ covered with a nonliving ___________________ covering their bodies as protection inside hosts III. Class Turbellaria a. Spade-shaped head and two eyespots called __________________ b. Can sense light, touch, taste, and smell c. Have 2 clusters of nerve cells or ______________________ to form a simple brain d. Nervous system composed of a _________________ ___________ e. Capable of simple learning f. Move by timy hairs or _____________ over a mucus layer that they secrete g. Feed by scavenging for ________________________ (microscopic, unicellular organisms) h. Have a simple opening or mouth--_______________________ i. ___________________ ______________ remove waste j. Are _____________________________ (have male and female reproductive parts) k. Can reproduce asexually by ___________________________ l. Are free living IV. Class Trematoda a. Includes parasitic flukes b. Require a host to live c. Have suckers on both ends of body d. Can be ___________________________ (live inside a host) or __________________________ (live outside of a host) e. Nervous and excretory systems like turbellarians f. Hemaphrodites g. _________________________ (disease caused by parasitic blood flukes) i. Contracted by coming into contact with water contaminated with human urine or feces or touching certain snails that carry the blood fluke. ii. Worms can penetrate the skin. h. Blood Fluke Life Cycle The long and complex life-cycle of the fluke can be made easier to understand through the use of a nonsense mnemonic : Every - Egg Mirror - Miracidium (free-living in water) Spotted - Sporocyst (in snail) Red - Redia (in snail) Certainly - Cercaria (free-living in water/snail) Met - Metacercaria (in 2nd intermediate host) Approval - Adult V. Class Cestoda a. Includes tapeworms (parasite) b. Tough outer _____________________ prevents being digested by host c. Anterior end called ___________________ contains hooks and suckers for attachment to intestine of host d. Long, ribbon-like bodies e. Nervous system extends length of body but lacks sense organs f. Lacks mouth and digestive tract but absorbs digested nutrients from host g. Grows by making body segments called ________________________ h. Each _______________________ produces egg and sperm that ___________________ with other segments and also self-fertilize (hermaphrodites) i. Oldest, mature proglottids containing eggs at posterior end break off and pass out with feces j. Tapeworm Anatomy and Life Cycle Unsegmented Worms—Round Worms I. Roundworms belong to Phylum _________________________ a. __________________________ (Fluid filled body cavity) b. Slender bodies that taper on both ends c. Have ________________ and _______________ d. Can be free-living or parasitic e. Many types of roundworm eggs and larva live in soil, and can get into bodies when people get them on hands and transfer them to their mouths II. Examples of Roundworms a. ____________________ live in the human intestines—often get passed from child to child. i. Only live in humans—cannot get pinworms from pets. b. _______________________-- a disease from eating infected pork (cysts in pork contaminated with Trichinella species of worm) c. _______________________--live in small intestine of mammal host (such as human, dog, cat, etc.) i. suck blood and can cause anemia d. _______________________--parasitic roundworm that is spread from host to host through mosquito bites. i. Mosquitos spread the larva to the host, then the larva grow into adults in the heart and/or lungs of the host ii. Only spread through infected mosquitos. There must be an incubation period in the mosquito before another animal can be infected by it. iii. Usually affects dogs, cats, wolves, coyotes, etc. Rarely affects humans. Parasitic Worms Poster 1. Put all names of group members on the back. 2. Put the Common Name in the top center. 3. Include the full classification (Kingdom through Species). 4. How do humans and/or other animals contract it? 5. What are some symptoms and health concerns with this parasite? 6. How could the parasite be prevented? 7. How is the parasite treated? Parasitic Worms Poster 1. Put all names of group members on the back. 2. Put the Common Name in the top center. 3. Include the full classification (Kingdom through Species). 4. How do humans and/or other animals contract it? 5. What are some symptoms and health concerns with this parasite? 6. How could the parasite be prevented? 7. How is the parasite treated? Parasitic Worms Poster 1. Put all names of group members on the back. 2. Put the Common Name in the top center. 3. Include the full classification (Kingdom through Species). 4. How do humans and/or other animals contract it? 5. What are some symptoms and health concerns with this parasite? 6. How could the parasite be prevented? 7. How is the parasite treated?