The Eukaryotic Cell (plant and animal cells) Eukaryotes: Organisms
advertisement

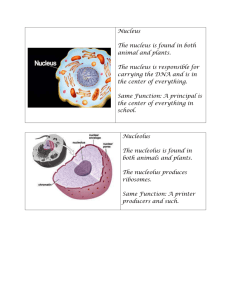
The Eukaryotic Cell (plant and animal cells) Eukaryotes: Organisms whose cells contain a _____________ and membrane-­‐bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are different from prokaryotic (bacteria) cells: -­‐ ____________________ (typically) -­‐ contains a ____________________ -­‐ contains ____________________ (specialized subunits within a cell that performs a specialized function – is usually enclosed within its own lipid bilayer) -­‐ ______________ are different from the ribosomes in prokaryotes (usually larger in eukaryotes) -­‐ includes single OR ____________________ organisms Cell structure Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Ribosomes Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Vesicle Description/Function -­‐ made of a phospholipid bilayer Functions: * involved with enzymatic activity * involved with cell identification -­‐ is considered the “gatekeeper” of cell because it controls what goes in and out -­‐ cytosol = the _________ of the cell (mostly water and molecules and ions) -­‐ cytoplasm = cytosol + ___________________ -­‐ a lot of chemical reactions take place here -­‐ it’s like the “_______________ floor” -­‐ framework of micro_____________ and micro ______________ -­‐ constantly shifting due to cell’s needs Function: provides _____________, _____________, traffic flow -­‐ similar to the framework inside a building that keeps it together -­‐ made up of ______(rRNA specifically) and proteins Function: assembles amino acids into ______________ (main “product” produced and needed for the cell) -­‐ like the “____________ worker” -­‐ looks like folded ________________ studded with ribosomes (hence the “rough look”) Function: makes, modifies, and ________________ proteins -­‐ similar to an “____________ line” for the ribosomes to work on -­‐ looks like folded membranes with ____ ribosomes (hence “smooth”) Function: makes __________ -­‐ similar to an assembly line (like the rough ER) but it’s just making a different product -­‐ looks like flattened sacs of membranes Function: sorts, packages, and _____________ substances for transport -­‐ similar to a “_______________ center” -­‐ small membrane enclosed _____ Function: transports substances made by the _______ apparatus -­‐ like a “____________ service” In Animal (A) or Plant (P) cells? A & P Lysosome Vacuole Nucleus Nuclear Membrane Nucleolus Mitochondria Centrioles Cilia and/or Flagella Cell Wall Plastids -­‐ membrane bound sacs of digestive _______________ Functions: * breaks down old ________________ * breaks down ________ items * induces cell death if needed -­‐ it’s technically a specialized vesicle -­‐ like a “_______________ crew” for the cell -­‐ membrane bound sacs that hold substances Function: serves as _____________ for food, water, wastes, etc. -­‐ similar to a “______________ cupboard” -­‐ Plants have one ___________ vacuole for storage AND support -­‐ Animal cells have many small vacuoles for different purposes -­‐ membrane bound organelle that contains the genetic information (DNA) of the cell -­‐ also contains parts and enzymes needed for DNA replication and transcription (you’ll learn about this later) -­‐ contains the nucleolus Function: stores and protects the DNA -­‐ is like the “control center” or “_________” of the cell -­‐ double lipid bilayer that serves as the physical barrier to separate the contents of the nucleus from the cytosol -­‐ also called the Nuclear _______________ -­‐ contains holes called the Nuclear ________ that allows the transport of certain molecules -­‐ looks like a large blob inside the nucleus Function: makes the ribosomes -­‐ like the “factory parts generator” or the “HR department” that hires the employees -­‐ double membrane bound organelle Function: performs aerobic respiration which makes __________ (ATP) and also detoxifies oxygen -­‐ considered the “Generator” or “__________ house” of the cell -­‐ cylindrical bundles of _____________________ (looks like churro sticks!) Function: assists with cell _________________ -­‐ Cilia = __________ hair-­‐like structures (usually more numerous) -­‐ Flagella = ___________ hair-­‐like structure (usually fewer) Function: used for _____________ (swimming) and creates currents to sweep objects towards or away from the cell -­‐ made of ______________ in plants (chitin in fungi) -­‐ different from bacteria cell walls (although serves a similar purpose) Function: Support for the cell (______________) -­‐ Leucoplasts: store _____________ -­‐ Chromoplasts: store ________________ -­‐ Chloroplasts: * organelle of _____________________: the process by which plants convert sunlight and water into sugar and oxygen In this ANIMAL cell, locate and label the: nucleus, nucleolus, rough ER, smooth ER, mitochondria, golgi complex, centrioles, cell membrane, nuclear membrane, nuclear pore In this PLANT cell, locate and label the: nucleus, nucleolus, rough ER, smooth ER, mitochondria, golgi complex, vacuole, cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplast