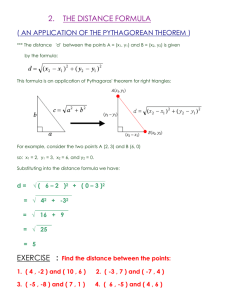
Applications: Pythagorean Theorem Notes
advertisement
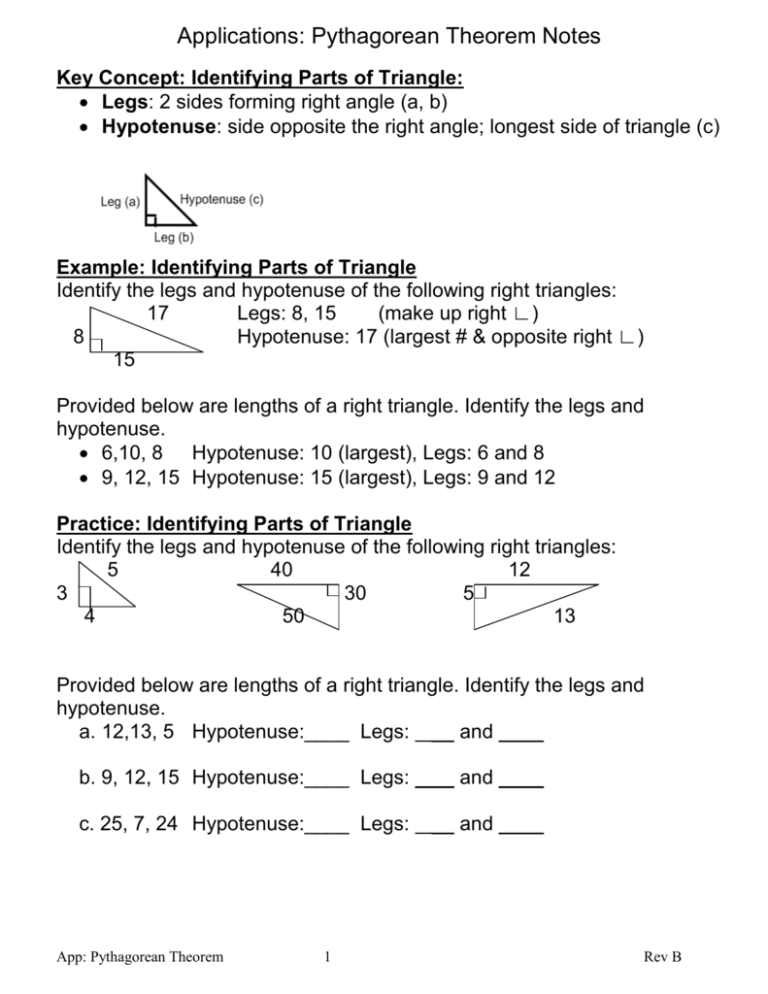
Applications: Pythagorean Theorem Notes Key Concept: Identifying Parts of Triangle: Legs: 2 sides forming right angle (a, b) Hypotenuse: side opposite the right angle; longest side of triangle (c) Example: Identifying Parts of Triangle Identify the legs and hypotenuse of the following right triangles: 17 Legs: 8, 15 (make up right ∟) 8 Hypotenuse: 17 (largest # & opposite right ∟) 15 Provided below are lengths of a right triangle. Identify the legs and hypotenuse. 6,10, 8 Hypotenuse: 10 (largest), Legs: 6 and 8 9, 12, 15 Hypotenuse: 15 (largest), Legs: 9 and 12 Practice: Identifying Parts of Triangle Identify the legs and hypotenuse of the following right triangles: 5 40 12 3 30 5 4 50 13 Provided below are lengths of a right triangle. Identify the legs and hypotenuse. a. 12,13, 5 Hypotenuse:____ Legs: __ and ____ b. 9, 12, 15 Hypotenuse:____ Legs: __ and ____ c. 25, 7, 24 Hypotenuse:____ Legs: __ and ____ App: Pythagorean Theorem 1 Rev B Applications: Pythagorean Theorem Notes Key Concept: Pythagorean Theorem Pythagorean theorem: a2 + b2 = c2 (for right angles) Pythagorean Theorem is used to find the length of a side of a right triangle when the lengths of the other 2 sides are known. if a2 + b2 = c2 then = √c2 = c or if a2 = c2 - b2 then a = √a2 = if 32 + 42 = 52 then or 2 if 3 = 52 - 42 then 3 = √32 = = √52 = 5 Examples: Solve for Missing Side Using the Pythagorean Theorem, solve for the missing side: 6 x 8 x Step 1: Identify legs & hypotenuse Hypotenuse: c = x, Legs: a=6, b=8 Step 2: Plug in values in a2 + b2 = c2 and solve 62 + 82 = x2 36 + 64 = x2 100 = x2 10 = x 17 15 App: Pythagorean Theorem Step 1: Identify legs & hypotenuse Hypotenuse: c = 17, Legs: a=x, b=15 Step 2: Plug in values in a2 = c2 - b2 and solve x2 = 172 - 52 x2 = 289 -225 x2 = 64 x =8 2 Rev B Applications: Pythagorean Theorem Notes Practice: Solve for Missing Side Using the Pythagorean Theorem, solve for the missing side: 1. Solve for a 15 a 12 2. Solve for c 10 3. Solve for b 24 2 6 c b 4. Solve for a 10 a 8 5. Solve for c 5 6. Solve for b 12 4 6 c b Key Concept: Determining if lengths are sides of right triangle When given 3 sides, identify your hypotenuse and legs with the hypotenuse being the largest number. Plug in values into the Pythagorean Theorem: a2 + b2 = c2 If the equation is true, then you have a right triangle If a2 + b2 > c2 then you have an acute triangle If a2 + b2 < c2 then you have an obtuse triangle Examples: Determining if lengths are sides of right triangle Determine whether the given lengths are sides of a right triangle. a. 3, 9, 7 b. 6,10, 8 hypotenuse: 9; legs: 3, 7 hypotenuse: 10; legs 6, 8 2 2 2 3 +7 =9 62 + 82 = 102 9 + 49 = 81 36 + 64 = 100 58 ≠ 81 100 = 100 No, obtuse triangle Yes App: Pythagorean Theorem 3 Rev B Applications: Pythagorean Theorem Notes Practice: Determining if lengths are sides of right triangle Determine whether the given lengths are sides of a right triangle. a. 20, 21, 29 b. 16,30,34 c. 7, 24, 25 d. 24, 60, 66 e. 23,18,14 f. 9, 12, 15 Key Concept: Pythagorean Triples There are many common sets of 3 whole numbers that satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem. Memorize the following Pythagorean Triples. They come in handy and help save you time. 3, 4, 5 5, 12, 13 7, 24, 25 8, 15, 17 9, 40, 41 NOTE: The largest number must be the hypotenuse in order for these to work. Key Concept: Special Right Triangles App: Pythagorean Theorem 4 Rev B