Transformations and Illusions - California State University, Long Beach
advertisement

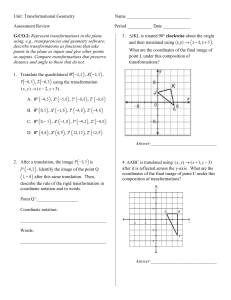
Transformations and Illusions1 Students will have the opportunity to explore geometric transformations in a piece of M.C. Escher’s artwork after learning to identify and draw reflections, translations, and rotations of figures. Suggested Grade Range: 7-12 Approximate Time: 1 hour State of California Content Standards: Mathematics Content Standards Grades 8-12: Geometry 2.2 Know the effect of rigid motion on figures in the coordinate plane and space, including rotations, translations, and reflections. Relevant National Content Standards: Mathematics Common Core State Standard: 8.G 1. Verify experimentally the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations. Lesson Content Objectives: Identify and draw rotations, reflections and translations of angles, polygons, and other figures. Investigate rotations, reflections and translations of figures in a drawing by M.C. Escher. Describe transformations using correct mathematical vocabulary. Materials Needed: Lined or white paper Rulers Three colored pencils per student or pair One copy per student of M.C. Escher’s Angels and Devils drawing (included) One copy per student of the “Transformation Practice” sheet (included) Mirrors (optional) One copy per student of the “Transformation STEM Extension” (included) 1 An early version of this lesson was adapted and field-tested by Monica D. Williams-Davis and Layla Nourbakhsh, participants in the California State University, Long Beach Foundational Level Mathematics/General Science Credential Program. STEM Activities for Middle and High School Students Transformations and Illusions 2-1 Summary of Lesson Sequence Introduce the lesson by providing a copy of M.C. Escher’s Angels and Devils drawing (included) for students to view and discuss. Lead students through compiling Cornell Notes on the vocabulary for the lesson including transformation, reflection, translation, and rotation. Model writing letters and their transformations, providing an example of each. Guide students through their own practice drawing transformations of letters. Check for students’ understanding by allowing students to identify and color figures from Escher’s Angels and Devils that are reflections, translations, and rotations. Allow groups to develop a way to teach the rest of the class how to reflect, rotate, and translate a letter or polygon. To close the lesson, students may discuss in small groups examples of transformations that may be observed inside the classroom or outside, then report to the whole class. For independent practice, students will complete an included activity sheet. Provide the optional Transformation Extension activity sheet and allow students to find designs where transformations of shapes are used. Assumed Prior Knowledge Prior to this lesson students should know how to identify, draw, and measure shapes and angles, and be familiar with the quadrants of the coordinate plane. Classroom Set Up Students will be asked to work in small groups for portions of this lesson. Lesson Description Introduction Provide students with a copy of M.C. Escher’s Angels and Devils (included) and allow students to view and discuss the piece. Generate discussion by using probing questions: What elements of the piece are repeated to form a pattern? Are there angles that are congruent? What is different about the angles (direction and position)? Input Lead students through taking notes of the key vocabulary for the lesson: transformation, reflection, translation, and rotation: Transformation: a change. A transformation changes the position of a shape on a coordinate plane. The shape moves from one place to another when it is transformed. STEM Activities for Middle and High School Students Transformations and Illusions 2-2 Reflection: a flip. A reflection takes place when a shape is flipped across a line and faces the opposite direction. A shape and its reflection are mirror images of each other. Demonstrate a reflection using an object in the classroom and a mirror. Translation: a slide. An object is translated when it moves in one direction from the starting point to the end. Demonstrate a translation by sliding an object in the classroom across a table. Rotation: a turn. An object that is rotated turns on a point to face another direction like the hand turning on the face of a clock. Demonstrate a rotation with an object in the classroom or by directing students’ attention to a clock with rotating arms. Model Demonstrate a reflection, translation, and rotation of the letter E. Provide another example if necessary without taking from students’ opportunity to explore transformations during the guided practice. Be careful to choose a letter, which has some asymmetry or students will not easily see that it has been changed. Guide Students Through Their Practice Move around the classroom checking students’ progress and allowing students to assist each other after assigning the following transformations: Reflect: p, m, T, nap, and their name. Translate: S, V, e, and a square. Rotate: L, w, C, and a triangle. Check for Understanding Using their copy of M.C. Escher’s Angels and Devils, ask students to color one of the figures in the picture (an angel or devil). Have them find a reflection of that shape and color it in as well. Have students hold up their papers to check their understanding. STEM Activities for Middle and High School Students Transformations and Illusions 2-3 Ask students to use a different color to indicate another figure and its translation. Using a third color, ask students to color a third figure and its rotation. Student Team Teach Allow students time to discuss a method for teaching how to perform a transformation on a polygon. Assign a polygon and a transformation to each group, and after allowing time to prepare, call on representatives of each group to teach the class how to perform the transformation on their polygon. Independent Practice Provide students with the Transformation Practice activity sheet (included) to complete independently. Closure Allow students to discuss in small groups examples of transformations that they observed in the classroom or outside of the classroom and share with the whole class. Students may be permitted to show with their own body a reflection, translation or rotation. Ask students: Can you think of a situation where the result of a reflection may be the same as the result of a rotation? (A 180 rotation yields the same result as a reflection; you can point out that the term “180” is used in skateboarding, etc.). Suggestions for Differentiation and Extension Explain to students that symmetry is commonly found in engineering and architectural designs and allow students to share examples of designs they are familiar with that have an element of symmetry. Provide students with the Transformation Extension activity sheet (included) so that they may explore symmetry in designs on their own. Encourage students to use a digital camera or cellular phone to take a photograph of a symmetric design they encounter so that they may share it in class. STEM Activities for Middle and High School Students Transformations and Illusions 2-4 Transformation Practice 1. A translation ... flips a shape slides a shape turns a shape 2. A reflection ... flips a shape slides a shape turns a shape 3. What rotation would turn the capital letter Z into a capital N? 360 degrees 90 degrees 180 degrees 4. A triangle on a grid is rotated 90 degrees about the centre of the grid. The distance between the tip of the triangle and the centre of the grid ... increases stays the same decreases 5. A drawing of a stick-man is reflected in a mirror line. The eye of the reflected man is ... the same distance from the mirror line as the original shape. further from the mirror line than the original shape. nearer the mirror line than the original shape. 6. A dot at position (4,3) on a grid is translated four squares to the right. What are its new coordinates? (0,3) (4,3) (8,3) 7. A dot at position (0,0) on a grid is translated one square to the right and two squares up. What are its new coordinates? (0,0) (2,1) (1,2) 8. Which of these techniques can transform the letter b into the letter d? Reflection Rotation Translation 9. Which of these techniques can NOT transform the letter M into the letter W? Reflection Rotation Translation STEM Activities for Middle and High School Students Transformations and Illusions 2-5 Transformation Extension Engineers, architects, and inventors often design objects that make use of transformed shapes. Find a building, a machine, or any other man made object for which you can identify a transformed shape in the design. 1. If possible, take a digital photograph of the object you found so that you may refer to it to answer the next questions and so that you may share your findings with the class. 2. Draw a simple diagram of the object you found. Label the shape and its transformation or transformations. 3. Explain how the transformed shape contributes to the design of the object. STEM Activities for Middle and High School Students Transformations and Illusions 2-6