Toxic Plants " mouse party "
advertisement

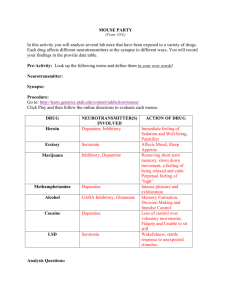
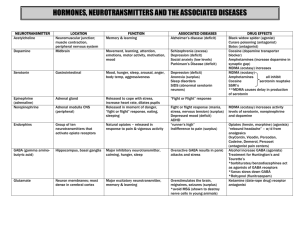
Toxic Plants " mouse party " Heroin Before heroin enter the system , inhibitory neurotransmitter are the active in the synapse which inhibit dopamine from being released . When the body natural opiate activate opiate receptor the release of Nu is shut down . without inhibition dopamine can be released. Heroin mimics natural opiate and bind to opiate receptor , turning off dopamine inhibition . dopamine allowed to flood the synapse producing immediate feeling of sedation and well-being . Neuron with opiate receptor are in part of brain responsible for transmission of pain signal ,stress response and emotional attachment . Our body opiate are natural painkillers , effective when we have sustained massive injury . this is why morphine ( a drug related to heroin ) is used as pain killer . Cocaine Dopamine transporter are responsible for removing dopamine from the synaptic cleft after they have done their job. Cocaine block those receptors leaving dopamine trapped in the synaptic cleft . as a result dopamine bind again and again to the receptor over stimulating the cell . cocaine concentrate in the reward pathway. And active in the part of brain controlling voluntary movement . this why cocaine abusers are fidgety and unable to be still . LSD LSD act almost exclusively on serotonin neurons , LSD chemically resemble serotonin and elicit its effect by binding to serotonin receptor .There are several serotonin receptors in the brain each one for specific function. LSD interact with particular receptor , but not always in the same day. Sometime LSD inhibit them sometime its excite them. This is one reason why LSD has complex sensory effect. LSD excite locus coeruleus LC in the brain which is responsible for feeling wakefulness and evoking a startle response to unexpected stimulus. Marijuana Before marijuana enter the system inhibitory NT are active in the synapse . these NT inhibit dopamine from being released. When activated by own body cabnnabinoid , cabnnabinoid receptor turn off the release of inhibitory NT . without inhibition dopamine can be released. THC active chemical in marijuana mimics anandamide and bind to cabnnabinoid receptor. Inhibition turned off and dopamine is allowed to squirt into the synape . Anandamide is known to be involved in removing unnecessary short term memories, and slowing down movement , make us feel relaxed and calm. Unlike THC, Anandamide break down quickly in the body. That explain why Anandamide doesn’t produce perpetual natural high . Methamphetamine Dopamine transporter are responsible for removing dopamine from the synaptic cleft. Coz meth mimic dopamine it’s taken into the cell by dopamine transporter and enter dopamine vesicle forcing the dopamine out . the excess dopamine in the cell causes the transporter to start working in reverse actively pumping dopamine out of the cell and into the synapse. The excess dopamine become in the trapped in the synaptic cleft as a result it start to bind again and again to thereceptor over stimulating the cell . Meth is highly addictive because its work directly in the brain reward pathway making the user feel intense pleasure and exhilaration . Ecstasy Serotonin transporter are responsible for removing serotonin from synaptic cleft after they done their job . Ecstasy mimics serotonin and is taken up by serotonin transporter , in fact Ecstasy Is more rapidly taken than serotonin . interaction with Ecstasy alter the transporter and become temporally confused and start to work in reverse by transporting serotonin out of the cell and trapped in synaptic cleft and bind again and again to the receptor over stimulating the cell . Ecstasy affect serotonin pathway responsible for mood, sleep , perception and appetite . and interact indirectly with reward pathway . the excess serotonin stimulat a milder dopamine release in reward pathway diving Ecstasy slightly addictive properties . Alcohol GABA inhibitory NT are active throughout the brain act to control neural activity along many brain pathways . another brain NT called glutamate act as brain general purpose excitatory NT . When alcohol enter the brain it deliver a double sedative punch . first it interact with GABA receptor to make them more inhibitory . second it bind to glutamate receptor preventing them from exciting the cell. Alcohol affect areas of brain involved in memory formation , decision making and impulse controlling . To understand see this link : Mouse Party Link http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/mouse/ Good luck






![[1] Edit the following paragraph. Add 4 prepositions, 2 periods](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007214461_1-73dc883661271ba5c9149766483dcfed-300x300.png)