Unit 11 Review Game—The Progressive Era
advertisement

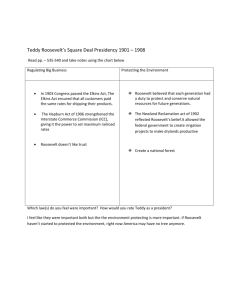
Unit 10 Review Game—The Progressive Era 1. As one progressive explained, the “real heart” of the progressive movement was to [A] to promote economic and social equality. [B] reinstate the policy of laissez-faire. [C] use the government as an agency of human welfare. [D] preserve world peace. [E] ensure the Jeffersonian style of government. 3. In regards to women, Progressivism [A] reflected the views of working-class women. [B] supported many reforms advocated by feminists. [C] offered little to the ever-growing women’s movement. [D] mirrored the women’s reform movements in Europe. [E] supported only the demand for woman suffrage. 4. What is a “muckraker”? [A] a monopolist. [B] an investigative journalist. [C] a politician who fought to end corruption. [D] a poor factory worker. [E] someone who advocated for the abolition of alcohol. 13. The progressive movement was instrumental in getting both the 17th and 18th amendments added to the Constitution. The 17th called for __, and the 18th called for __. [A] prohibition, woman suffrage [B] woman suffrage, income taxes [C] woman suffrage, direct election of senators [D] income taxes, direct election of senators [E] direct election of senators, prohibition 14. The settlement house and women’s club movements were crucial centers of female progressive activity because they [A] provided literary and philosophical perspectives on social questions. [B] introduced many middle-class women to a broader array of urban social problems and civic concerns. [C] became the launching pads for women seeking political office. [D] helped slum children learn to read Dante and Shakespeare. [E] broke down the idea that women had special concerns as wives and mothers. 5. Lincoln Steffens, in his book “The Shame of the Cities,” [A] laid bare the practices of the stock market. [B] unmasked the corruption of political machines. [C] attacked the United States Senate. [D] exposed the deplorable condition of blacks in urban areas. [E] uncovered deplorable facts of prostitution. 17. The most horrific example of the exploitation of workers during the Progressive era was the [A] Pullman Palace Car strike. [B] Ludlow Massacre. [C] Triangle Shirtwaist fire. [D] meatpacking conditions in Chicago. [E] anthracite coal miners. 7. Most muckrakers believed that their primary function in the progressive attack on social ills was to [A] devise solutions to society’s problems. [B] formulate a consistent philosophy of social reform. [C] explain the causes of social ills. [D] link up with movements for social justice. [E] make the public aware of social problems. 19. The progressive-inspired city-manager system of government [A] was started to remove corruption from city administration. [B] made giant strides under the leadership of Hiram Johnson. [C] was developed in Wisconsin. [D] opened urban politics to new immigrants. [E] brought democracy to urban dwellers. 9. Progressive reformers were mainly men and women from the [A] lower class [B] small towns. [C] upper class. [D] new wave of immigrants. [E] middle class. 21. While president, Theodore Roosevelt chose to label his reform proposals as the [A] Square Deal. [B] New Deal. [C] Fair Deal. [D] Big Stick. [E] Big Deal. 10. Political progressivism [A] emerged in both parties and at all levels of government. [B] was mainly a Republican reform movement. [C] began in Wisconsin. [D] died out shortly after Teddy Roosevelt left the presidency. [E] was more a minority movement than a majority mood. 12. progressives advocated all of the following except [A] initiative. [B] recall. [C] direct election of U.S. senators. [D] referendum. [E] socialism. 22. As a part of his reform program, Teddy Roosevelt advocated all of the following except [A] conservation of natural resources. [B] railroad regulation. [C] control of corporations. [D] consumer protection. [E] control of labor. 23. Teddy Roosevelt helped to end the 1902 strike in the anthracite coal mines by [A] helping the mine owners to import strike-breakers. [B] threatening to seize the mines and to operate them with federal troops. [C] using the military to force the miners back to work. [D] passing legislation making the miners’ union illegal. [E] appealing to mine owners’ and workers’ sense of the public interest. 24. One unusual and significant characteristic of the anthracite coal strike in 1902 was that [A] the owners quickly agreed to negotiate with labor representatives in order to settle their differences peacefully. [B] it generated widespread middle-class support. [C] for a time the mines were seized by the national government and operated by federal troops. [D] the national government did not automatically side with the business owners in the dispute. [E] the coal miners’ union was officially recognized as the legal bargaining agent of the miners. 25. The Hepburn Act dealt with the subject of [A] conservation of natural resources. [B] regulation of municipal utilities. [C] the purity of food and drugs. [D] women’s working conditions. [E] railroad regulation. 26. Teddy Roosevelt believed that trusts [A] were here to stay with their efficient means of production. [B] should be balanced by strong labor unions. [C] were too powerful to be regulated. [D] were greedy for power and wealth. [E] could be destroyed without damaging the economy. 27. The real purpose of TR’s assault on trusts was to [A] end vertical and horizontal integration. [B] prove that the government, not big business, ran the country. [C] inspire confidence in small business owners. [D] establish himself as a bigger “trustbuster” than Taft. [E] end all monopolies. 28. President Roosevelt believed that the federal government should adopt a policy of __ trusts. [A] dissolving [B] collusion with [C] ignoring [D] monitoring [E] regulating 29. When Upton Sinclair wrote The Jungle, he intended his book to focus attention on the [A] plight of workers in the meat-packing industry. [B] deplorable conditions in the drug industry. [C] unhealthy effects of beef consumption. [D] corruption in the United States Senate. [E] unsanitary conditions that existed in the meat-packing industry. 31. Teddy Roosevelt weakened himself politically after his election in 1904 when he [A] refused to do anything in response to the “Roosevelt Panic.” [B] announced that he would not be a candidate for a third term as president. [C] got into a quarrel with his popular secretary of war, Taft. [D] began to reduce his trust-busting activity. [E] supported the Federal Reserve Act. 33. While president, Theodore Roosevelt [A] was a poor judge of public opinion. [B] held rigidly to ideological principles. [C] showed no skill and little interest in working with Congress. [D] greatly increased the power and prestige of the presidency. [E] was surprisingly unpopular with the public. 34. During his presidency, Teddy Roosevelt did all of the following except [A] use the Sherman Antitrust Act to regulate monopolies. [B] expand presidential power. [C] create the Federal Reserve and first national income tax. [D] develop an environmental conservation plan. [E] shape the progressive movement at the national level. 35. As president, William Howard Taft [A] was not a progressive-minded president. [B] held together the diverse wings of the Republican party. [C] thought the presidency was a “bully pulpit”. [D] tended to side with conservative Republicans rather than progressives . [E] effectively carried on the legacy of Theodore Roosevelt. 37. The Supreme Court used the “restraint-of-trade” clause of the Sherman Antitrust Act for the first time to break up [A] General Electric. [B]. Standard Oil [C] Armour Meat-Packing. [D] United States Steel. [E] Northern Securities. 38. TR decided to run for the presidency in 1912 because [A] Senator Robert La Follette encouraged him to do so. [B] the Democratic party was split. [C] he was drafted by the Republican party. [D] Taft decided not to run for a second term. [E] Taft had seemed to discard Roosevelt’s policies. 39. Before he was elected president in 1912, Woodrow Wilson had been a [A] Progressive Republican. [B] university president. [C] Presbyterian minister. [D] successful businessman. [E] United States Senator. 40. As governor of New Jersey, Wilson established a record as a [A] mild conservative. [B] passionate reformer. [C] man who would work with the party bosses. [D] moderate liberal. [E] reactionary. 41. In 1912, Wilson’s Democratic platform was called: [A] New Freedom. [B] New Deal. [C] Square Deal. [D] Big Stick Diplomacy. [E] New Nationalism. 56. The Sixteenth Amendment provided for [A] prohibition. [B] abolition of child labor. [C] woman suffrage. [D] a personal income tax. [E] direct election of senators. 42. When Jane Addams placed Teddy Roosevelt’s name in nomination for the presidency in 1912, it [A] demonstrated his concern for international peace. [B] showed that Roosevelt had lost touch with public opinion. [C] demonstrated that Republicans supported woman suffrage. [D] symbolized the rising political status of women. [E] ensured Roosevelt’s defeat by William Howard Taft. 58. The Federal Reserve Act gave the gov’t the authority to [A] print paper currency. [B] increase the amount of money in circulation. [C] close weak banks. [D] govern federal banks without public control. [E] raise protective tariffs. 43. Teddy Roosevelt’s New Nationalism [A] favored capitalist markets without regulation. [B] supported a broad program of social welfare. [C] pinned its economic faith on competition. [D] favored state rather than federal government activism. [E] opposed consolidation of labor unions. 44. Woodrow Wilson’s New Freedom [A] opposed fragmentation of big industrial combines. [B] opposed banking and tariff reform. [C] advocated social-welfare programs. [D] favored small enterprise and entrepreneurship. [E] supported minimum-wage laws. 45. The 1912 presidential election was notable because [A] the Democratic party had split. [B] the Socialists were a serious third party. [C] it was the first time women had the right to vote. [D] it gave the voters a choice of political and economic philosophies. [E] personalities were the only issue of the campaign. 46. According to the text, the runaway philosophical winner in the 1912 election was [A] conservatism. [B] progressivism. [C] capitalism. [D] feminism. [E] socialism. 55. When Congress passed the Underwood Tariff Bill in 1913, it intended the legislation to [A] raise tariff rates. [B] aid American farmers. [C] lower tariff rates. [D] eliminate tariffs as a source of revenue. [E] essentially maintain the existing tariff schedule. 59. The Clayton Anti-Trust Act [A] legalized strikes and ended government use of injunctions. [B] included farmers as possible monopolists. [C] hurt unions more than any other group in America. [D] regulated railroads. [E] was used against small businesses rather than monopolies. 60. Because of the benefits that it gave to workers, Samuel Gompers (of the AFL) called the __ “labor’s Magna Carta.” [A] Clayton Anti-Trust Act [B] Workmen’s Compensation Act [C] Federal Reserve Act [D] Underwood Tariff Act [E] Sixteenth Amendment 62. Woodrow Wilson showed the limits of his progressivism by [A] vetoing the Federal Farm Loan Act. [B] opposing workingmen’s compensation. [C] refusing to appoint the Jewish Louis D. Brandeis to the Federal Trade Commission. [D] accelerating the segregation of blacks in the federal bureaucracy. [E] opposing the entry of women into politics. Unit 10 Review Game—The Progressive Era—Answer Key [1] [C] [23] [B] [40] [B] [3] [B] [24] [D] [41] [A] [4] [B] [25] [E] [42] [D] [5] [B] [26] [A] [43] [B] [7] [E] [27] [B] [44] [D] [9] [E] [28] [E] [45] [D] [10] [A] [29] [A] [46] [B] [12] [E] [31] [B] [55] [C] [13] [E] [33] [D] [56] [D] [14] [B] [34] [C] [58] [B] [17] [C] [35] [D] [59] [A] [19] [A] [37] [E] [60] [A] [21] [A] [38] [E] [62] [D] [22] [E] [39] [B] Unit 10 Review—The Progressives 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 1st Place _____________________________________________ 2nd Place_____________________________________________ 3rd Place _____________________________________________ 4th Place _____________________________________________ Unit 10 Review—The Progressives 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 1st Place _____________________________________________ 2nd Place_____________________________________________ 3rd Place _____________________________________________ 4th Place _____________________________________________