Relative Time
advertisement

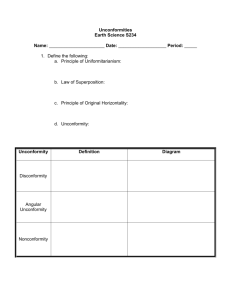
Instructions: The geologic cross-section below shows a series of rock layers and geologic events. All layers are sedimentary except for I and J. Answer the following questions below. 1. Which layer is younger M or C? What geologic principle tells you this? Layer M is younger (happened more recently) than C because the Principle of Superposition tells us that in non-overturned sedimentary sequences that layers on top are youngest. 2. Between what two events did folding occur? What geologic principle tells you this? The principle of original horizontality tells us that M,C,D,E,F,G,and H were originally deposited horizontally, and they must have been folded later. The youngest of the folded units is M, so folding must have happened after M and before the angular unconformity L. 3. Which event happened most recently, deposition of A or intrusion of J? What geologic principle tells you this? Intrusion J must be younger than A. The principle of cross-cutting relationships tells us that because J cuts I, and I cuts A that J must be younger than both I and A. 4. What type of fault is shown with letter K? What type of plate boundary would you expect to find this type of fault? Letter K shows a normal fault (hanging wall went down). This type of fault forms at divergent plate boundaries because normal faults accommodate extension. 5. What type of unconformity is letter L representing? Why? Letter L shows an angular unconformity because sedimentary rocks on bottom are tilted (folded) at different angles than the sedimentary rocks on top. This is basically the definition of an angular unconformity.