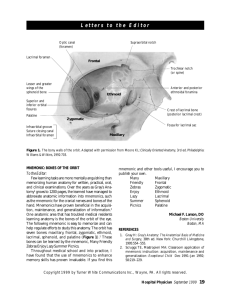
1. Which bones contain the paranasal sinuses? What function do the
advertisement

1. Which bones contain the paranasal sinuses? What function do the sinuses serve? Sphenoid, ethmoid, frontal, maxillary – function to provide mucus as well as lighten the skull and provide greater resonance for the voice 2. What two areas are separated from each other by the hard palate? Name the two bones that form the hard palate. Nasal and oral cavities and the bones that form the hard palate are the palatine and maxilla 3. Most of the nasal septum is formed by what bones (be specific)? Ethmoid – perpindicular plate and vomer 4. The main sources of oxygenated blood supplying the brain are the internal carotid and vertebral arteries. Deoxygenated blood leaves the brain by way of the internal jugular veins. What openings in the axial skeleton transmit these vital blood vessels? Jugular foramen, carotid canal and foramen magnum 5. What important nerves are transmitted throught the cribriform plate and optic foraminae? Olfactory – cranial nerve1 and optic – cranial nerve 2 What special senses would be affected if these nerves were damaged? Olfaction (smell) and vision 6. What is the function of the hyoid bone? Support the trachea, tie in with the muscles that are inferior to the mandible and offer some protection to the superior portion of the trachea 7. What delicate structures are protected by the petrous portion of the temporal bone? Auditory ossicles 8. What connection occurs within the foramen magnum? Medulla oblongata and the spinal cord 9. The occipital condyles participate in forming which joint? Atlo-occipital 10. What endocrine gland is cradled by the sella turcica? pituitary 11. The condylar process of the mandible articulates with the mandibular fossa to form which joint? Temporomandibular (tmj) 12. A fracture of the orbit (from a fist, for example) could potentially damage which bones? Frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, palatine, maxilla, zygomatic and lacrimal 13. What are fontanels? What is their function? Cartilaginous connections between small bone plates in the skull of a new born baby. The function of fontanels is to allow the head to adjust as it comes out of the birth canal. 14. Why are the lacrimal bones so named? Lacrima in Latin = tear and the lacrimal foramen is the drainage point for tears from the lacrimal gland, across the eye, through the lacrimal puncta and into the lacrimal foramen to drain into the nasal cavity 15. Which two bones form the zygomatic arch? Where can the arch be palpated externally? Zygomatic and temporal bones form the zygomatic arch and they may be palpated from the cheek to the ear 16. What are the alveoli and in which bones are they found? Alveoli are pockets that teeth fit into and they can be found in the mandible and maxilla 17. Where can the mastoid process be palpated externally? Slightly inferior and posterior to the ear