Course Outline
advertisement

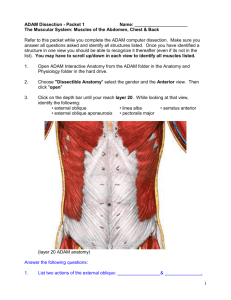
DISCLAIMER: The course outline below serves as a general informational guide for students. Course content and assessment modes may vary for different lecturers. Actual course outlines will be made known to students on edveNTUre by the individual lecturers. DO NOT purchase textbooks based on the information contained in this document. SS1001: Structural and Functional Human Anatomy Course Description: Functional anatomy deals with the various systems of the body and the part each plays in physical performance, health and fitness. Learning Objectives: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: 1. 2. 3. Identify the different structures of the human anatomical system systems. Explain the functions of each anatomical system. To relate anatomical systems to the promotion of health, fitness and physical performance. Course Outline: Introduction to Functional Anatomy Objectives and Rationale of the module Structural Organisation of Human Body Cell structure and function Common Terms in Anatomy Cardiovascular System (Plowman & Smith Chap Four) Macro and micro anatomy of the heart, contraction of the heart, cardiac cycle, blood pressure Heart rate, stroke volume, cardiac output Vascular system: Arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, blood, blood volume Respiration System Structure of pulmonary system, mechanics of breathing, respiratory circulation, minute ventilation, measurement of static and dynamic lung Regulation of pulmonary ventilation Gas exchange and transport and acid base balance Digestive System Overview of the Structure and Function of Digestive Tract Oral Cavity Pharynx and Oesophagus Stomach, pancreas and liver Small and Large intestine Nutrition and Nutrients Endocrine System General characteristics of endocrine system Hormone action Control of Hormonal secretion About various Glands and Pancreas Stress and Health Introduction of Skeletal-Muscular System Bone Tissue, function of skeletal system Bone development, growth, modelling, remodelling, skeletal adaptations to exercise, skeletal injuries Types of muscles Macroscopic and microscopic structure of skeletal muscle and muscle fibre Myofilaments and muscle fibre contraction Types of muscular contractions Skeletal- Muscular System –Upper Extremity Names of bones and selected prominent features Identification of major muscles and muscles groups, attachments and functions Articulations at shoulder, elbow and wrist Common Injuries Skeletal- Muscular System –Lower Extremity Names of bones and selected prominent features Identification of major muscles and muscles groups, attachments and functions Articulations at hip, knee and ankle Common Injuries Skeletal- Muscular System –Trunk and Spinal Column Names of bones and selected prominent features Identification of major muscles and muscles groups, attachments and functions Intervertebral articulations: Axial Skeleton, Vertebral Column, Thoracic Cage, Shoulder girdle Common injuries The Nervous System (Plowman & Smith, Chap 20, 485 – 497, and handouts) Organisation of central and peripheral nervous system Structure of motor neuron, types of receptors Neural control of muscle contraction Reflex control of movement Volitional control of movement Course Assessment: Mid-term Examination Final Examination Course Textbook: 40% 60% 1. Marieb, N Elaine (2000). 6th Edition. Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology, Benjamin/Cummings Science Publishing. 2. Thompson, CW and Floyd, RT (2001). 14th Edition. Mannual of Structural Kinesiology, McGraw Hill. References Materials: Plowman, S A & Smith, D L (2003) 2nd Edition. Exercise Physiology for Health, Fitness and Performance, Allyn and Bacon.