EXAMS + SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION LECTURE#5 PSY280
advertisement

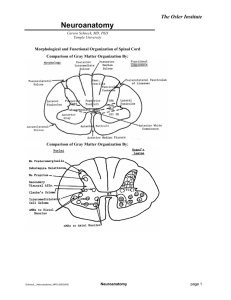
EXAMS + SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION! LECTURE#5 ! PSY280: BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY! DR. OLLIE HULME, SPRING 2011, SFU! Details! Lectures:! Mon, 12.30-2.20! Wed, 12.30-1.20! Essential! Office hours:! Wed 1.40-3.40pm! Room RCB 6242! Recommended! Prerequisites:! Psyc100! Exams:! Midterm#1 30%, ~ Wed 9th Feb! Midterm#2 30%, ~ Wed 16th March ! Final 40% ~ exam period (april 13-24)! Multiple choice + essays! Non-cumulative! Internet: ! If questions, check website first hyooom.com! If not answered, and if answerable in few lines email ollie.hulme@gmail.com! All else in person! Follow announcements on Twitter @PSY280! Materials! Biological Psychology 6th ed. Breedlove Substantial updates to 6th ed. therefore recommended over 5th ed. Companion website at biopsychology.com/6e/ Additional reading Lecture Material Alternatives to hardback Looseleaf textbook Interactive ebook CourseSmart ebook Textbook Material Course outline! Scope & outlook Approach, History, Issues 1 Biological foundations Neuroanatomy 2 Neurophysiology 3 Neurochemicals 4 Hormones 5 Evolution &development Evolution 6 Development 7 Perception Touch 8 Pain 8 Hearing 9 Taste & smell 9 Vestibular system 9 Vision 10 Action Lower Motor system 11 Upper Motor system 11 Action selection 11 Regulation Sex 12 Homeostasis 13 Sleep 14 Emotions & Disorders Emotion 15 Addiction 16 Depression 16 Schizophrenia 16 Cognitive Learning & memory 17 Attention 18 Decision making 18 Language 19 Special topics (reading beyond book) Consciousness - reading Happiness Neuroaesthetics Numbers = Textbook Chapter CV points! 2 Student Assistants: Provide feedback / input for improving course Act as representative if other students want to communicate through them ~30 mins every couple of weeks Helps me write more detailed reference Email me or see me after class Roadmap! Exam guide Synaptic transmission Midterm1! 30% of final grade! Wed 9th Feb! Review session = Mon 7th Feb! Content: Biological Foundations! Everything up to today + neurochemicals + hormones ! Lectures 1-7, Chapters 1-5! Midterm1: Format! In class – 50mins! Exam booklet – closed book! 2 part (aprox 25 mins per part):! 1. 20 x Multiple choice (20 marks) – testing broad knowledge and understanding, only based on material in slides and videos for lectures 1-7! 2. 1x Mini essay (20 marks) – more detailed knowledge and deeper understanding only based on 2 textbook chapters (+ equivalent slides + lectures) – answer = page of ~a4 ! Multiple choice sample! What ion is responsible for the rapid depolarisation phase of the action potential?! a) K+! b) Cl-! c) Ca2+! d) Na+! e) None of the above! Excitatory post-synaptic potentials (EPSPs)…! a) Always cause action potentials! b) Decrease the probability of action potentials! c) Inhibit the neuron! d) Increase the probability of action potentials! e) Cannot cause action potentials! Mini essay format! You will choose to specialise in answering either question 1, 2 or 3, which will require you to know 2 chapters from text book (+ equivalent slides & videos)! Q1: which could ask you about either…! Approaches, Issues + History (ch1) or Neuroanatomy (ch2)! Q2: which could ask you about either…! Neuroanatomy (ch2) or Neurophysiology (ch3)! ! ! ! ! ! ! Q3: which could ask you about either… ! Neurochemicals (ch4) or Hormones (ch5) ! ! ! ! 50% probability of being asked either topic – you don’t know ahead of time what you will be asked therefore you have to revise both Example1: mini-essay Qs! Q1 [Approaches (ch1) or Neuroanatomy (ch2)]! What are the different approaches taken by biological psychology and how do they differ?! Q2 [Neuroanatomy (ch2) or Neurophysiology (ch3)] ! What are the key anatomical features of the nervous system? ! Q3 [Chemicals (ch4) or Hormones (ch5)]! What are the different ways hormones effect the brain and behaviour? ! Example2: mini-essay Qs ! Q1 [Approaches (ch1) or Neuroanatomy (ch2)]! From single cells to brain regions, describe the anatomical features and terminology of the central nervous system ! Q2 [Neuroanatomy (ch2) or Neurophysiology (ch3)] ! Describe the sequence of events leading from synaptic potentials to release of neurotransmitters in a single cell?! Q3 [Chemicals (ch4) or Hormones (ch5)]! What role do the different neurotransmitters play in the brain?! Do I need to know X?! Multiple choice:! If itʼs in slides or videos (lecture 1-7) then itʼs relevant! Mini-essay:! If itʼs in 2 chapters or equivalent lecture materials then its relevant ! But donʼt have to know every single detail to answer question well! Best to focus on good understanding first, then learn some detail Lectures emphasise most important aspects of chapters. ! How to write mini-essay ! I will go through this in class on monday Roadmap! Exam guide Synaptic transmission Core question! Brain and body: Molecules, cells, systems etc. synapses, systems etc. Everything else: physical, social, economic, geographic etc. How does our biology and its interaction with the environment relate to mental and behavioural phenomena? Of the mind: experience, motivation, memory, thought, etc. Observable behaviour: actions, reactions, expressions, verbalisations Previously…! Early 1900ʼs! Synapses, I say Neuron 1 Neuron 2 Debate raged as to how the signal was transmitted between cells Was it bioelectric? Was it chemical? Otto Loewi! Professor Loewi was fixated on this problem After long day, working hard at the lab… He fell asleep in his bed Dreams! He dreamt… Aha!! Next night! The dream returns Aha!! Not wanting to trust his handwriting again, rushes down to lab in the middle of night to begin work Ottoʼs Idea! If signal is chemical, one should be able to collect it from one system + apply it to a seperate system, and see if it has the same effect ? Otto Loewi! So I tried this out on the vagus nerve Vagus nerve! Vagus nerve = part of the autonomic nervous system which connects brain to heart Vagus nerve effects on heart ! Stimulating Vagus decreases heart rate Heart to heart! Fluid linking 1st beating heart to a 2nd disconnected beating heart Heart to heart! Vagustoff! Loewi inferred that a chemical called ‘Vagustoff’ was released from the Vagus nerve to cross the synapse onto cardiac muscle, causing it to slow Later identified as Acetyl Choline Well done old chap! His discovery was of great importance for understanding synaptic transmission of information, later found to generalise to brain Synapse TV! Action potential release! Action potential arrives at axon terminal Change in membrane potential causes Ca2+ channels to open Ca2+ flows into cell … Vesicle fusion! Ca2+ causes vesicles to fuse with membrane Causes release of neurotransmitter into synapse … Receptor binding! Neurotransmitter diffuses across synapse Binds to receptors in postsynaptic membrane … Receptor TV! Two classes of receptor! Ionotropic Receptor + channel = Same structure Metabotropic Receptor + channel = Independent structures Synaptic Potential! Flow of ions into postsynaptic cell causes EPSP or IPSP Influences action potential! Synapses Axon hillock Axon Balance of EPSPs & IPSPs from synapses determines the membrane potential at the axon hillock If sufficient depolariation to cross threshold – this causes action potential to fire Stopping the signal! To stop neurotransmitters continually exciting or inhibiting the cell… Degraded (inactivated) Reuptake (transported out of synapse Many addictive drugs work by interfering with this process Next lecture! Chemical Bases of Behaviour + Essay writing guide Please read ch4 for Monday