School District of the Chathams Curriculum Profile
advertisement

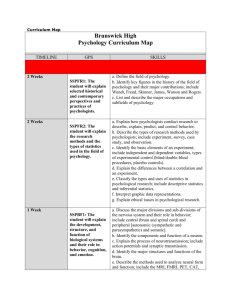
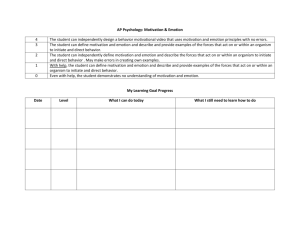
School District of the Chathams Curriculum Profile Program of Study: A.P. Psychology Course Title: A.P. Psychology Grade Level: 11, 12 I. Course Description This is a college level introductory psychology course offered to motivated high school students. The textbook is Psychology, in Modules (7th edition - 2004) by David G. Myers. Students will be working through the entire textbook during this year long course. The goal of this course is to help students learn to think like psychologists, both as researchers and as clinicians. Students who do well in this course should also perform well on the A.P. Psychology exam. II. Course Objectives and Alignment with APA National Standards for the Teaching of High School Psychology (1997) 1. Students will study fundamental concepts, vocabulary and theories of psychology. Standards from Introduction and Research Methods Domain: 1.1, 6.1, 6.3 Standards from Bio-Psychological Domain: Biological Bases of Behavior: 1.1, 1.2, 2.1, 2.2, 3.2, 8.1 Sensation and Perception: 1.1, 1.2 Motivation and Emotion: 3.1, 4.1 Stress, Coping and Health: 1.1, 2.1, 3.1 Standards from the Cognitive Domain: Learning: 2.1, 3.1, 4.1, 4.2, 5.1 Memory: 1.1, 4.1 Thinking and Language: 1.2, 2.1, 3.2 States of Consciousness: 1.1, 1.3, 3.1 Standards from the Developmental Domain: 1.1, 1.3, 3.1 Date of Last Review or Revision: Members of Review/Revision Committee: Standards from the Sociocultural Domain: Individual Differences: 1.1, 3.2, 3.3 Personality and Assessment: 1.1, 2.1, 2.2 Psychological Disorders: 1.1, 1.4, 3.1 Treatment of Psychological Disorders: 1.1, 1.2, 2.1 Social and Cultural Dimensions of Behavior: 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 4.1 2. Students will learn the skills of psychological research. Standards from Introduction and Research Methods: 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 5.1, 6.2 Standards from Bio-Psychological Domain: Biological Bases of Behavior: 4.1, 5.1 Sensation and Perception: 1.4, 3.1, 3.2 Motivation and Emotion: 6.1, 7.1 Stress, Coping and Health: 4.1, 4.2 Standards from the Cognitive Domain: Learning: 2.1, 3.1 Memory: 1.2, 5.1 Thinking and Language: 4.2, .4.3 States of Consciousness: 1.2, 2.2 Standards from the Developmental Domain: 1.1, 2.1 Standards from the Sociocultural Domain: Individual Differences: 1.2, 2.1, 4.2, 4.3 Personality and Assessment: 3.1, 3.2 Psychological Disorders: 2.1, 2.2 Date of Last Review or Revision: Members of Review/Revision Committee: Social and Cultural Dimensions of Behavior: 1.4, 4.1 3. Students will develop scientific reasoning, critical thinking skills and build their reading, writing, and discussion skills. Standards from Introduction and Research Methods: 2.1, 2.2, 5.1, 6.4 Standards from Bio-Psychological Domain: Biological Bases of Behavior: 7.1 Sensation and Perception: 1.4, 2.1 Motivation and Emotion: 1.1, 2.1, 2.3 Standards from the Cognitive Domain: Learning: 5.3 Memory: 2.1, 2.2, 3.1, 5.2 Thinking and Language: 2.2, 2.3, 4.2, 4.3 States of Consciousness: 1.2 Standards from the Developmental Domain: 1.2, 1.4, 3.2 Standards from the Sociocultural Domain: Individual Differences: 3.1, 4.1 Psychological Disorders: 1.3, 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 Treatment of Psychological Disorders: 2.2, 3.1 Social and Cultural Dimensions of Behavior: 3.1, 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 4. Students will apply psychological principles to their own lives. Standards from Introduction and Research Methods: 1.1, 1.2, 2.1, 6.4 Standards from Bio-Psychological Domain: Biological Bases of Behavior: 1.3, 7.1, 7.2 Sensation and Perception: 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 3.2 Date of Last Review or Revision: Members of Review/Revision Committee: Motivation and Emotion: 1.1, 2.3, 5.1, 7.1 Stress, Coping and Health: 1.1, 4.1, 4.2 Standards from the Cognitive Domain: Learning: 1.2, 4.1, 5.2 Memory: 3.1, 3.3, 5.2 Thinking and Language: 1.2, 2.3, 5.1 States of Consciousness: 1.2, 2.1 Standards from the Developmental Domain: 1.2, 1.4, 3.2, 3.4, 5.2 Standards from the Sociocultural Domain: Individual Differences: 2.1 Personality and Assessment: 2.1, 3.2 Psychological Disorders: 1.3, 4.3 Treatment of Psychological Disorders: 2.1 Social and Cultural Dimensions of Behavior: 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 5. Students will develop introspective skills to examine their decisions and relationships more thoroughly. Standards from Introduction and Research Methods: 1.1, 1.2, 2.1, 6.4 Standards from Bio-Psychological Domain: Biological Bases of Behavior: 1.3, 7.1, 7.2 Sensation and Perception: 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 3.2 Motivation and Emotion: 1.1, 2.3, 5.1, 7.1 Stress, Coping and Health: 1.1, 4.1, 4.2 Standards from the Cognitive Domain: Learning: 1.2, 4.1, 5.2 Date of Last Review or Revision: Members of Review/Revision Committee: Memory: 3.1, 3.3, 5.2 Thinking and Language: 1.2, 2.3, 5.1 States of Consciousness: 1.2, 2.1 Standards from the Developmental Domain: 1.2, 1.4, 3.2, 3.4, 5.2 Standards from the Sociocultural Domain: Individual Differences: 2.1 Personality and Assessment: 2.1, 3.2 Psychological Disorders: 1.3, 4.3 Treatment of Psychological Disorders: 2.1 Social and Cultural Dimensions of Behavior: 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 III. Topical Outline I. Methods and Social Psychology II. Biopsychology III. Sensation and Perception IV. States of Consciousness V. Learning and Memory VI. Thinking, Language and Intelligence VII. Developing Child; Adolescence and Adulthood VIII. Motivation and Emotion IX. Personality X. Psychological Disorders XI. Therapy XII. Stress Date of Last Review or Revision: Members of Review/Revision Committee: XIII. Social Relations XIV. Applying Psychology IV. Skills A. Students are able to describe and compare the biological, behavioral, cognitive, and socio-cultural perspectives. B. Describe the elements of an experiment and explain the importance of sampling in psychological research. C. Describe and compare quantitative and qualitative research strategies. D. Explain and describe measures of central tendency. E. Describe the concept of correlation and how it is used in psychology. F. Identify ethical issues in psychological research. G. Identify sources of attitude formation. H. Assess some methods used to change attitudes. I. Discuss how social and cultural categories affect behavior. J. Describe effects of the presence of others on individual behavior. K. Explore the nature of bias, discrimination, altruism, and aggression. L. Describe circumstances under which conformity and obedience are likely to occur. M. Describe how information is transmitted and integrated in the nervous system. N. Identify the structure and function of the major regions of the brain. O. Explain how technology can be used to analyze brain behavior and disease. P. Assess the effects of heredity and environment on behavior. Q. Explain the concepts of threshold, adaptation, and constancy. R. Describe the operation of sensory systems. S. Explain Gestalt concepts and principles. T. Explain what is meant by attention. U. Apply motivational concepts to the behavior of humans, with special attention to hunger, sex, and work. V. Describe theories of emotion. W. List and explain possible physical and psychological reactions to stress. X. Identify and explain cognitive and behavioral strategies to deal with stress. Y. Describe physical, social, and cognitive changes from the prenatal period throughout the lifespan. Z. Apply lifespan principles to personal experience. AA. Describe the role of critical periods in development. BB. Recognize how societal conceptions of gender shape the experiences of males and females. CC. Recognize learning as a vehicle to promote adaptation through experience. DD. Describe and apply the classical conditioning paradigm. EE.Describe and apply the operant conditioning paradigm. Date of Last Review or Revision: Members of Review/Revision Committee: FF. Explain how observational and cognitive learning work. GG. Describe the operation of short and long term memory. HH. Analyze the importance of retrieval cues in memory. II. Develop strategies for improving memory. JJ. Practice problem-solving as a directed and productive example of thinking. KK. Explain the characteristics of psycho-analytic, cognitivebehavioral, humanistic, and trait approaches to personality. LL.Identify important historical contributions to the understanding of personality. MM. Distinguish between objective and projective techniques of personality assessment. NN. Evaluate the efficacy of personality testing. OO. Discuss major categories of abnormal behavior. PP. Explain the challenges associated with ac QQ. Analyze the obstacles that inhibit problem-solving. RR. Evaluate the theories of language acquisition. SS. Speculate on whether animals acquire and use language. TT.Compare theories that explain why we sleep. UU. Compare theories about the use and meaning of dreams. VV. Describe several hypnotic phenomena. WW. Explain the nature of test constructs, such as intelligence, creativity and personality tests. XX. Describe theories of intelligence. YY. Explain the criteria used to determine DSM diagnosis of mental illnesses. ZZ.Discuss the stigma associated with abnormal behavior. AAA. Describe availability and efficacy of various modes of treatment for people with psychological disorders. V. Methods of Instruction and Sample Activities A. Teacher directed small group and large group discussion, including graded student-led debates B. Practice exercises – e.g. link the behavioral scenario to the appropriate level of child development C. Lectures, including use of powerpoint D. Demonstrations of experiments – classical conditioning, etc. E. Simulations – role playing therapy, etc. F. Hands on activities which reinforce vocabulary and concepts of psychology – e.g. create a model of the brain G. Individual projects and presentations – both written and oral H. Individual research – done throughout year to prepare for final project VI. Instructional Materials Date of Last Review or Revision: Members of Review/Revision Committee: Psychology, in Modules (7th edition - 2004) by David G. Myers A.P. Psychology exams from the College Board On line and printed articles from relevant journals PsychInquiry CD-Rom, Myers, 7e – student activities in critical thinking PsychSim 5: interactive CD-Rom, Ludwig Discovering Psychology video series hosted by Philip Zimbardo Excerpts from books and films, e.g. Forty Studies that Changed Psychology, The Man Who Mistook his Wife for a Hat; Opening Skinner’s Box; the Aviator, 12 Angry Men, Ordinary People, Kinsey Websites, e.g. apa.org, bcs.worthpublishers.com/myersinmodules73/, nimh.nih.gov VII. Student Outcomes and Methods of Assessment A. Improvement in ability to listen to and respond to classmates’ ideas; improvement in contributions to class discussions; ability to lead a productive class discussion B. Use of a double-entry journal for taking content and reaction notes from the textbook C. Essays and experiment write ups D. Teacher made tests and quizzes E. Mid-term and final examination, practice A.P. examinations F. General classroom preparation and participation G. Oral presentations H. Projects such as the binder of personal development, model of brain I. Clinical case study/ book review related to mental illness J. Progress towards and then completion of final project, including literature review and original research Date of Last Review or Revision: Members of Review/Revision Committee: