Chemistry 115-1C Exam 4 2 C3H6 + 9 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O Al
advertisement
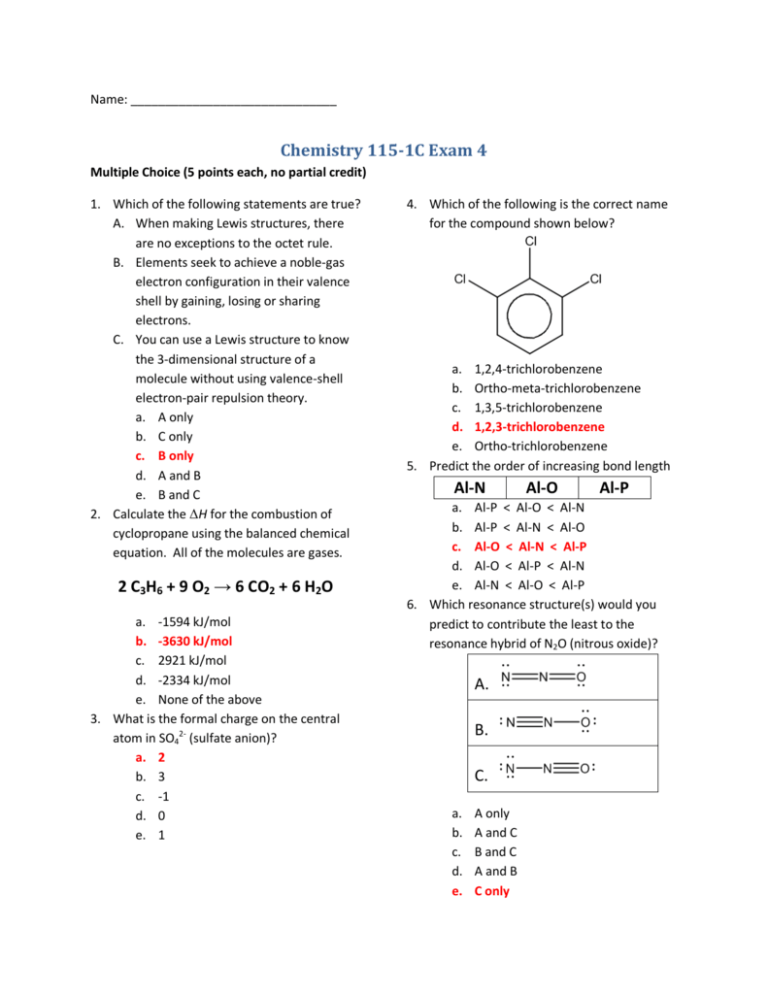
Name: ______________________________ Chemistry 115-1C Exam 4 Multiple Choice (5 points each, no partial credit) 1. Which of the following statements are true? A. When making Lewis structures, there are no exceptions to the octet rule. B. Elements seek to achieve a noble-gas electron configuration in their valence shell by gaining, losing or sharing electrons. C. You can use a Lewis structure to know the 3-dimensional structure of a molecule without using valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory. a. A only b. C only c. B only d. A and B e. B and C 2. Calculate the ΔH for the combustion of cyclopropane using the balanced chemical equation. All of the molecules are gases. 2 C3H6 + 9 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O a. -1594 kJ/mol b. -3630 kJ/mol c. 2921 kJ/mol d. -2334 kJ/mol e. None of the above 3. What is the formal charge on the central atom in SO42- (sulfate anion)? a. 2 b. 3 c. -1 d. 0 e. 1 4. Which of the following is the correct name for the compound shown below? a. 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene b. Ortho-meta-trichlorobenzene c. 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene d. 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene e. Ortho-trichlorobenzene 5. Predict the order of increasing bond length Al-N Al-O Al-P a. Al-P < Al-O < Al-N b. Al-P < Al-N < Al-O c. Al-O < Al-N < Al-P d. Al-O < Al-P < Al-N e. Al-N < Al-O < Al-P 6. Which resonance structure(s) would you predict to contribute the least to the resonance hybrid of N2O (nitrous oxide)? A. B. C. a. b. c. d. e. A only A and C B and C A and B C only 7. What is the molecular geometry for SF42-? a. Tetrahedral b. See-saw c. Square pyramidal d. Triangular bipyramidal e. Square planar 8. Predict the order of increasing bond angle for the following molecules GeH4 SeH2 AsH3 a. AsH3 < SeH2 < GeH4 b. GeH4 < AsH3 < SeH2 c. SeH2 < GeH4 < AsH3 d. GeH4 < SeH2 < AsH3 e. SeH2 < AsH3 < GeH4 9. What is the hybridization on the central atom in ICl3 (iodine trichloride)? a. sp b. sp2 c. sp3 d. sp3d e. sp3d2 10. Which of the following intermolecular forces will methanol (CH3OH) exhibit? A. London forces B. Dipole-dipole C. Hydrogen bonding a. A only b. A and B c. B only d. A and C e. C only 11. A double bond consists of a. Two single bonds b. One σ-bond and one π-bond c. Two σ-bonds d. Two π-bonds e. One σ-bond and two π-bonds 12. A gas is initially in a 3.13 L container at 1.56 atm. If the gas is transferred to a container with a volume of 8.79 L, what is the new pressure of the gas? a. 0.555 atm b. 17.6 atm c. 4.38 atm d. 8.82 atm e. 3.63 atm 13. What is the pressure of N2 gas at 325 °C if it has a density of 1.25 g/L? a. 1.00 atm b. Not enough information to answer c. 1.19 atm d. 4.38 atm e. 2.19 atm 14. What is the volume of H2 produced from the following reaction if 3.82 L of CH4(g) react with 3.82 L of H2O(g). CH4(g) + H2O(g) → CO(g) + 3 H2(g) a. 11.5 L b. 3.82 L c. Not enough information to answer d. 7.64 L e. 22.9 L 15. According to the kinetic-molecular theory of gases, which statements are false A. Gas molecules are approximately the same size as the distances between them. B. Gas molecules move randomly at various speeds in all directions C. Collisions between gas molecules are elastic (that is, they bounce off of each other) a. C only b. A and B c. B and C d. B only e. A only 16. What is the total pressure of 2.00 g of H2 and 6.00 g of N2 in an 8.00 L container at 100 °C? a. 1.24 atm b. None of the other answers c. 4.62 atm d. 30.6 atm e. 8.21 atm Fill-in-the-blank (1 point per blank, no partial credit) 17. Which bond would you predict to be the least polar? a. N-N b. C-N c. B-N d. N-H e. O-N NO2Write the Lewis structure (include all resonance structures if any) Draw the structure (using wedges & dashed-wedges) Write the electron-pair geometry (central atom) Write the molecular geometry Triangular planar List all intermolecular forces (if any) London forces & dipole-dipole Bent Average Bond Enthalpies (in kJ/mol) Single bonds H C N O F Si P S Cl Br I I 299 213 --201 --234 184 --209 180 151 Br 366 285 ------310 264 213 217 193 Cl 431 327 193 205 255 391 319 255 242 S 347 272 ----326 226 --226 P 322 264 ~200 ~340 490 --209 Si 323 301 335 368 582 226 F 566 486 272 190 158 O 467 336 201 146 N 391 285 160 Multiple bonds N=N NN C=N CN 418 946 616 866 O=O (in O2) 498 Some useful physical constants Ideal gas constant: R = 0.08206 L·atm / K·mol Ideal gas constant: R = 8.314 J / K·mol C=C CC C=O (as in CO2) C=O (as in H2C=O) CO 598 813 803 695 1073 C 416 356 H 436









