Aging and Health –SES Correlations in Asia
advertisement

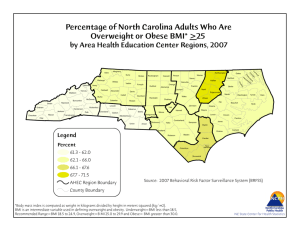
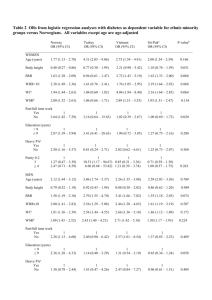
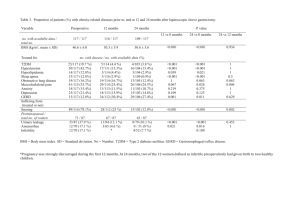
AGING AND HEALTH IN ASIA AGING AND HEALTH-SES CORRELATIONS IN ASIA: EVIDENCE FROM INDONESIA JOHN STRAUSS - USC FIRMAN WITOELAR - WORLD BANK/SURVEY METER BONDAN SIKOKI - SURVEY METER YOUNOH KIM - USC Health and Nutrition Transitions • Nutrition: from under-nutrition and malnutrition to over-nutrition • Health: from infectious to chronic diseases • Implications: – Chronic diseases affect elderly more – Unawareness of chronic illness by individuals – The public health system is designed to handle infectious diseases and not chronic diseases – Low incomes: inadequate resources to handle the expensive treatment of chronic illnesses • • • • Data: Indonesia Family Life Survey IFLS : a large-scale broad -based longitudinal survey of households and individuals that not only collects a set of socioeconomic characteristics , but also physical health biomarkers and self-reported health measures Four waves of IFLS: IFLS1 (1993), IFLS2 (1997), IFLS3 (2000), IFLS4 (2007). V ery low attrition rates: over 90% of HHs from 1993 found in 2007, 88% of individuals The paper will focus on markers and measures known to be important for elderly health for which we have data for multiple waves: • Data available at http://www.rand.org/labor/FLS/IFLS • Paper is RAND Labor and Population working paper WR-704 CDF of Body Mass Index Over Time: males and females 45+ Indonesia .8 .6 .4 .2 0 0 .2 .4 .6 .8 1 Female 45+ 1 Male 45+ 10 15 18.5 25 30 BMI 1993 2000 Source: IFLS1, IFLS2, IFLS3, IFLS4 35 10 15 18.5 25 30 BMI 1997 2007 1993 2000 1997 2007 35 Body Mass Index: Male and Female 45+ Male 1993 45-54 1997 2000 2007 12.49 9.46 22.28 16.52 12.98 9.39 % Overweight (BMI ≥ 25) 11.25 13.32 17.00 22.65 17.04 24.46 30.83 40.18 1,042 1,187 1,467 1,870 1,232 1,333 1,561 2,106 29.88 27.07 24.22 18.22 31.96 28.15 27.14 16.64 8.11 9.06 12.68 17.26 14.24 17.82 21.19 30.57 819 923 1,035 1,096 942 1,132 1,261 1,211 42.50 39.46 35.66 27.95 36.86 33.89 34.26 29.57 4.65 6.28 7.37 8.59 10.70 12.29 15.44 18.82 481 512 639 713 485 581 763 878 48.68 50.36 48.39 38.05 50.09 46.35 44.65 33.60 4.33 2.49 3.05 6.31 4.25 8.30 8.98 13.96 172 218 306 338 184 241 359 438 % Overweight (BMI ≥ 25) % Undernourished (BMI < 18.5) % Overweight (BMI ≥ 25) Observations % Undernourished (BMI < 18.5) % Overweight (BMI ≥ 25) Observations Mean BMI 45+ 1993 16.34 Observations 75+ 2007 17.02 % Undernourished (BMI < 18.5) 65-74 2000 % Undernourished (BMI < 18.5) Observations 55-64 1997 Female % Undernourished (BMI < 18.5) % Overweight (BMI ≥ 25) Observations Source: IFLS1, IFLS2, IFLS3, IFLS4. 20.30 20.69 21.06 21.75 20.86 21.43 21.88 22.90 28.25 26.60 23.50 17.54 29.77 25.78 24.51 17.40 8.49 9.83 12.68 17.31 14.20 18.84 22.78 31.14 2,514 2,840 3,447 4,017 2,843 3,287 3,944 4,633 Body Mass Index and education: males and females 45+ Indonesia 20 20 21 21 22 BMI 23 22 BMI 23 24 24 25 25 26 Female 45+ 26 Male 45+ 0 1 2 3 1993 4 5 6 7 8 Y ears of Education 1997 Source: IFLS1, IFLS2, IFLS3, IFLS4 9 10 1 1 12 2000 2007 0 1 2 3 1993 4 5 6 7 8 Y ears of Education 1997 9 10 1 1 12 2000 2007 Waist circumference and BMI: male and female 45+ Indonesia 1 10 100 W aist (cm) 80 90 70 60 50 50 60 70 W aist (cm) 80 90 100 1 10 120 Female 45+ 120 Male 45+ 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 BMI 2000 Source: IFLS1, IFLS2, IFLS3, IFLS4 2007 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 BMI 2000 2007 Hemoglobin level: males 45+ Indonesia 0 .2 .4 .6 .8 1 Male Age 45+,1997, 2000, and 2007 8 9 10 11 1997 12 13 Hb level 2000 14 15 2007 16 17 Hemoglobin level: females 45+ Indonesia 0 .2 .4 .6 .8 1 Female Age 45+, 1997, 2000, and 2007 8 9 10 11 1997 12 13 Hb level 2000 14 15 2007 16 17 Table 2. Percentage of adults 25+ with blood hemoglobin level below 13.0 g/dL (men) or 12.0 g/dL (women), 1997, 2000 and 2007 Men Women 2000 2007 Age groups 1997 2000 2007 1997 25-44 years % <12.0/13.0 22.01 15.45 9.69 36.07 38.62 26.58 Observations 3,397 4,961 6,485 4,478 5,555 6,904 45-54 years % <12.0/13.0 32.22 22.09 17.72 39.49 39.96 28.08 Observations 1,167 1,460 1,869 1,298 1,553 2,091 55-64 years % <12.0/13.0 41.57 37.32 26.01 40.16 41.96 32.82 Observations 911 1,039 1,093 1,122 1,260 1,212 65-74 years % <12.0/13.0 48.53 46.58 40.86 46.00 48.93 40.25 Observations 513 645 728 575 774 886 75+ years % <12.0/13.0 62.81 53.60 52.24 53.52 53.49 50.06 Observations 220 312 350 237 387 461 45+ years %<12.0/13.0 40.62 34.08 27.12 41.91 43.66 33.81 Observations 2,811 3,456 4,040 3,232 3,974 4,650 Source: IFLS2, IFLS3, IFLS4 Observations are weighted using individual sampling weights. The thresholds are 12.0 g/dL for women and 13.0 g/dL for men. Hemoglobin level against years of education: males 45+ in Indonesia Hb (g/DL) 14 15 Male Age 45+, 1997, 2000, and 2007 12 13 1997 2000 2007 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Years of Education 9 10 11 12 Number of difficulties with ADLs and age over time : males and females 45+ in Indonesia Female 45+ 0 0 1 Number 2of difficulties 3 1 Number of2difficulties 3 4 4 Male 45+ 45 50 60 70 80 45 50 Age 1993 1997 Source: IFLS1, IFLS2, IFLS3, IFLS4 60 70 80 Age 2000 2007 1993 1997 2000 2007 CES-D 10 Score by years of education: male and female 45+ Indonesia CES-D Score 3.5 4 4.5 Age 45+, 2007 2.5 3 Male Female 0 2 4 6 8 Years of Education, 2007 10 12 Word recall by age and education: male and female 45+ Indonesia Word recall and education 3.5 3 Words Recalled 1 2 2.5 3 2 Words Recalled 4 4 4.5 Word recall and age 40 50 Male 45+ Source: IFLS4 60 Age 70 Female 45+ 80 0 2 4 6 8 Years of Education, 2007 Male 45+ 10 Female 45+ 12 Proportion with hypertension: female 45+ Indonesia Proportion with hypertension .4 .5 .6 .7 Female Age 45+, 1997, 2000, and 2007 .3 1997 2000 2007 40 50 60 Age 70 80 Hypertension: male and female 45+ Male Female % with hypertension 1997 2000 2007 1997 2000 2007 Age 45-54 (%) 35.16 36.06 34.72 41.11 36.95 41.15 Observations 1,189 1,472 1,876 1,330 1,565 2,101 Age 55-64 (%) 47.17 46.23 48.76 54.69 50.94 53.79 Observations 926 1,044 1,098 1,140 1,272 1,216 Age 65-74 (%) 52.86 55.01 56.02 65.69 67.07 68.74 Observations 519 646 723 585 783 892 63.57 62.52 61.90 79.52 72.87 76.32 Observations 222 313 347 252 391 464 Age 45+ (%) 43.78 44.21 44.19 52.61 49.63 52.70 Mean systolic 137.47 136.96 139.76 143.55 141.2 144.52 Mean diastolic 82.19 83.39 82.62 82.95 83.51 83.22 Observations 2,856 3,475 4,044 3,307 4,011 4,673 Age 75+ (%) Source: IFLS2, IFLS3, IFLS4. Hypertension if systolic ≥ 140 or diastolic ≥ 90. o l ci ≥ 9 0 . s sty o icl ≥ 1 4 0 ro iad st IF L S 3 , I F L S 4 .H y p re et sin o n if T able 5. Underdiagnosis of hypertension, adult 45+, 2007 Adult 45 + years Men 4,044 Observations % hypertensive % diagnosed a) 44.2 Women 4,676 52.8 26.4 37.9 Underdiagnosis of hypertension by education, adult 45+ highest completed level of education no schooling primary schooling junior high senior high + all adult 45+ a) % underdiagnosed 79.0 69.4 74.4 58.1 73.2 52.1 68.0 62.3 73.6 62.1 Source: IFLS4 Observations are weighted using individual sampling weights. a) "Diagnosed" if answered "Yes" to the question "Has a doctor/nurse/paramedic ever told you that you have hypertension?". Percentages are out of individuals 45+ whose sytolic>=140 or diastolic >=90. Table 6. Hypertension and medication, adult 45+, 2000 and 2007 Men Adult 45 + years 2000 2007 Women 2000 2007 Observations 3,477 4,044 3,631 % hypertensive 44.2 44.2 49.6 % taking medication for hypertension a) 2.6 4.7 2.5 a) Percentages are out of individuals 45+ whose systolic >=140 or diastolic >=90 4,674 52.8 4.7 a) Hypertensive and not taking medication, by completed education Men Highest completed level of education no schooling primary schooling junior high senior high + all adult 45+ 2000 98.7 99.1 95.4 93.9 97.4 2007 97.6 96.7 91.2 92.5 95.3 Women 2000 2007 98.7 97.3 96.9 94.9 96.7 88.1 92.3 94.1 97.5 95.4 Source: IFLS3 and IFLS4 a) Percentages are out of individuals 45+ whose systolic >=140 or diastolic >=90. Observations are weighted using individual sampling weights. Health status-SES gradients • SES variables: education, log per capita expenditure •In this analysis is not causal! •Omitted variables: •For instance childhood health which can affect completed schooling and adult income •Reverse causality from health to income •Can show health status differentials by SES Impact of Respondent Schooling and Household Per Capita Expenditure • Have data on household PCE-better measure of longrun resources than current income • Regress health outcomes for those 45+ in each wave (1993, 1997, 2000, 2007) on health measures-pooled regression for measures collected in multiple waves • Covariates include: – dummies for level of schooling – linear spline in log PCE (around median) – dummies for respondent age – dummies for location (province/rural-urban) at survey, year and interaction of year/location dummies Multivariate results BMI* Male Hemoglobin† Female Male N= Female Hypertension† Male N= Female #ADL problems* Male N= Female Poor GHS* Male N= Female N= 12,836 14,735 10,035 11,853 10,376 11,994 12,711 14,095 12,705 14,094 --- --- --- --- ++ +++ +++ +++ ++ . Education +++ +++ ++ . . . . . . ++ Age x educ +++ + . . ++ . . . -- --- PCE +++ +++ +++ ++ +++ ++ ++ + -- . V ariables Age Source: * = IFLS1, IFLS2, IFLS3, IFLS4 † = IFLS2, IFLS3, IFLS4 Multivariate results Underdiagnosis of hypertension Cognition / Correct # Words Male Male Female N= Female # IADL Problems Male N= Female CES-D 10 Score Male N= Female Vigorous physical activity Male N= Female Moderate physical activity Male N= Female N= 1,813 2,474 3,748 4,063 3,902 4,401 3,901 4,402 3,902 4,403 3,902 4,403 Age --- . --- --- . . +++ +++ --- --- --- --- Educ . --- +++ +++ ++ . . . - - . +++ Age x Educ . . +++ +++ --- --- --- -- --- . . - PCE . --- +++ +++ -- - . . -- . --- . Variables: Source: IFLS4 Impact of Parental Health and Schooling • Have measures of mother and father schooling and health • Health measures: – Mother/father dead at 2007 (about 5% of sample parents still alive) – Mother/father in poor health at time of 2007 survey or just prior to death, if dead – Mother/father has difficulties with ADLs at time of 2007 survey or just prior to death, if dead • Regress health outcomes for those 50+ in 2007 on these measures, plus dummies for level of parental schooling, plus dummies for respondent age, plus dummies for province/rural-urban location at birth • Then regress changes 2007-1993 or 2007-1997 on same vars Static Analysis Static 07 # ADL Problems V ariables Male Female Male Female Male Female N= 3081 N= 3605 N = 2983 N = 3491 N = 3081 N= 3608 Age Educ father Educ mother Death father Death mother Poor GHS father Poor GHS mother ADL problems father ADL problems mother Static 07 V ariables Age Educ father Educ mother Death father Death mother Poor GHS father Poor GHS mother ADL problems father ADL problems mother +++ -. . . ++ . . . # IADL Problems +++ + + . . + +++ . BMI --. + . . . . . . Hemoglobin Poor GHS --+++ . . . . . . + +++ . -. . + ++ . . Hypertension +++ . . +++ +++ . . . Cognition /Correct # Words Male Female Male Female Male Female Male Female N= 3081 N = 3605 N= 2980 N= 3475 N= 2985 N = 3493 N= 2317 N= 2309 +++ --+ . . +++ ++ . . +++ . + . . ++ ++ . --. ++ . -. . . . --+++ . . . . . . . +++ . . . ++ . . . . +++ . . . ++ . . . . +++ +++ +++ . . . . . . +++ +++ + -. . . . . Dynamic Analysis Dynamic diff V ariables # ADL Problems BMI Poor GHS Hemoglobin Hypertension Male Female Male Female Male Female Male Female Male Female N=2380 N=2820 N=2200 N=2710 N=2388 N=2828 N=2309 N=2843 N=2340 N=2894 +++ +++ --- --- +++ . -- --- . --- Educ father . + . . . +++ - - . -- Educ mother . . . . - - . -- . . Death father . ++ . + . . . . + . Death mother . . . . . . . . . + Poor GHS father Poor GHS mother ADL problems father ADL problems mother . . . . . . . . . . ++ . . . . . . . . . . + . . . . . . . . . . . + . . . . . . Age CONCLUSIONS Asian countries in midst of demographic, health and nutrition transitions- Indonesia illustrative V ery rapid aging, decline in importance of infectious diseases and increase in importance of chronic diseases Health sectors are behind in keeping up with these transitions, as underdiagnosis of hypertension in Indonesia (and China) shows Are strong health-SES gradients in Indonesia, similar to higher income countries, but also to China Also strong intergenerational correlations between measures of parental health and schooling and health of their adult children when 50+