11.6 NOTES How is air pressure measured?
advertisement
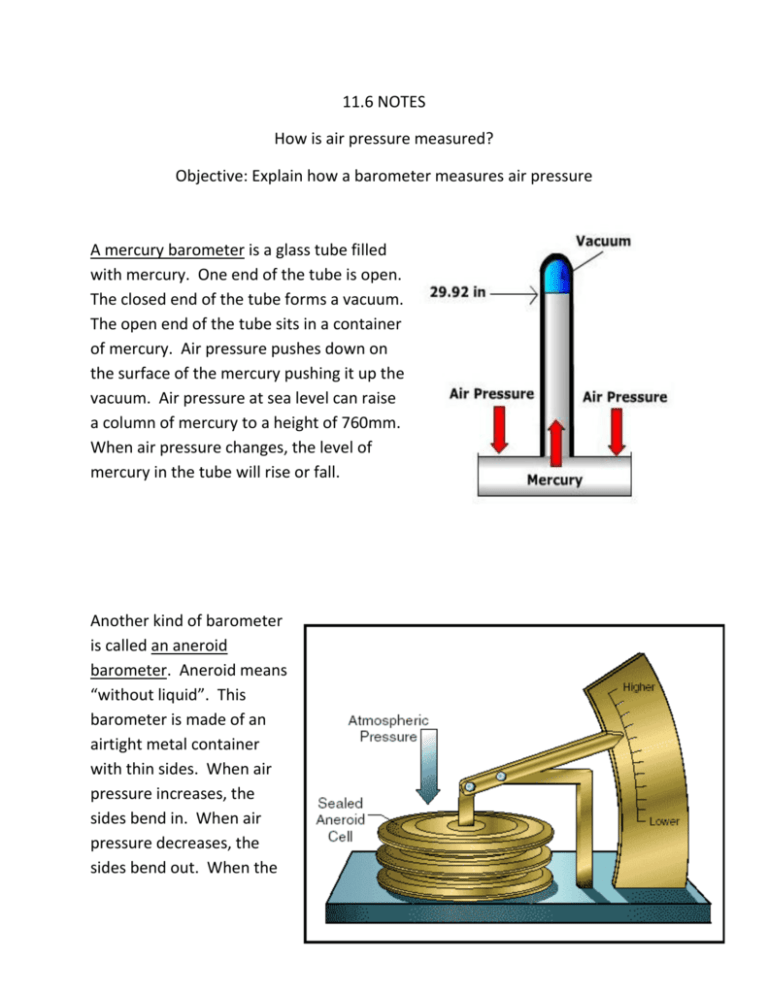
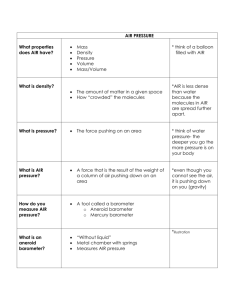
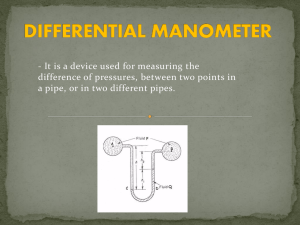
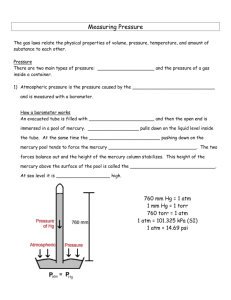
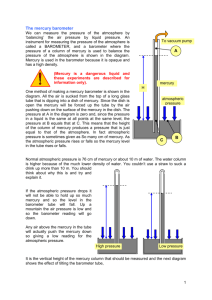
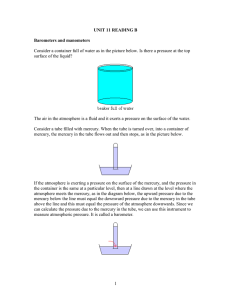
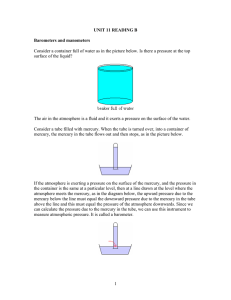
11.6 NOTES How is air pressure measured? Objective: Explain how a barometer measures air pressure A mercury barometer is a glass tube filled with mercury. One end of the tube is open. The closed end of the tube forms a vacuum. The open end of the tube sits in a container of mercury. Air pressure pushes down on the surface of the mercury pushing it up the vacuum. Air pressure at sea level can raise a column of mercury to a height of 760mm. When air pressure changes, the level of mercury in the tube will rise or fall. Another kind of barometer is called an aneroid barometer. Aneroid means “without liquid”. This barometer is made of an airtight metal container with thin sides. When air pressure increases, the sides bend in. When air pressure decreases, the sides bend out. When the sides bend, the pointer moves on a scale, measuring air pressure in millimeters of mercury. Air pressure at sea level is 760 mm, also called one atmosphere. Air pressure can also be measured in millibars (mb). Standard air pressure is equal to 1,013.20 mb. Altitude is measured with a device called an altimeter. As you go higher, air pressure decreases. Pilots, scientists, surveyors, and mountain climbers use altimeters. Mount Everest is the highest point on Earth, standing at about 8,900 meters high. The mercury column here is only about 250 mm high. Skydivers and parachuters use aneroid barometers to monitor their altitude.